Chronic Kidney Disease Augments Gout Risks Save
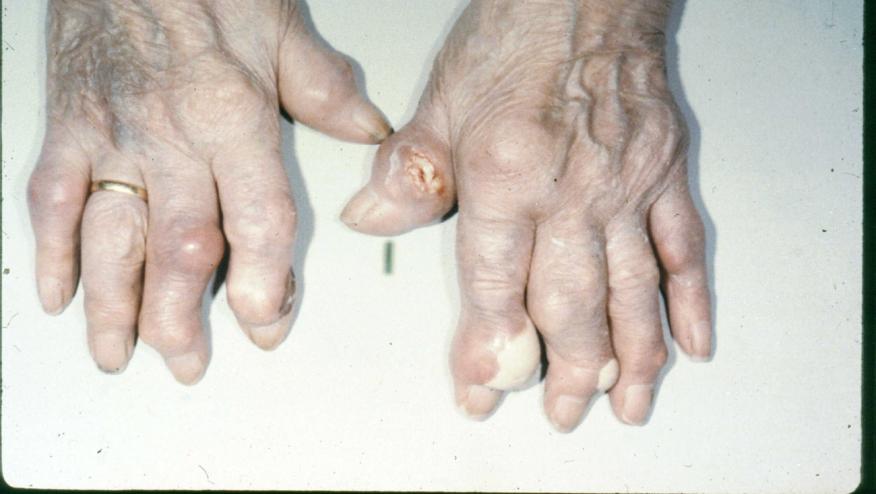
A population based cohort analysis shows that patients with incident gout and chronic kidney disease (CKD) have far worse outcomes than those without CKD.
A retrospective population-based cohort study of incident gout between 2006-2009 identified those with CKD; defined as a pre-existing diagnosis of chronic kidney disease, chronic renal failure, kidney transplantation, or dialysis at index date.
Among 12,940 incident adult gout patients, 64% with CKD and 36% without CKD, were followed for 55,206 person-years.
Overall, gout patients with CKD (vs those without CKD) had:
- Significantly more healthcare utilization; Hospital admissions were at least 3 times higher for Gout+CKD adults < 55 (mean = 0.51 vs 0.13) and approximately 1.5 times higher for adults 55+ (mean = 0.46 vs 0.29) without CKD.
- All-cause mortality was higher among those with CKD compared to those without CKD for both age groups (HR< 55 years = 1.65; 95% CI 1.01-2.71; HR55+ years = 1.50; 95% CI 1.37-1.65).
Gout plus CKD constitutes a high risk population that merits focused efforts to better control their gout and optimize comorbidity management.









If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.