Drugs that May Induce Raynaud's Save
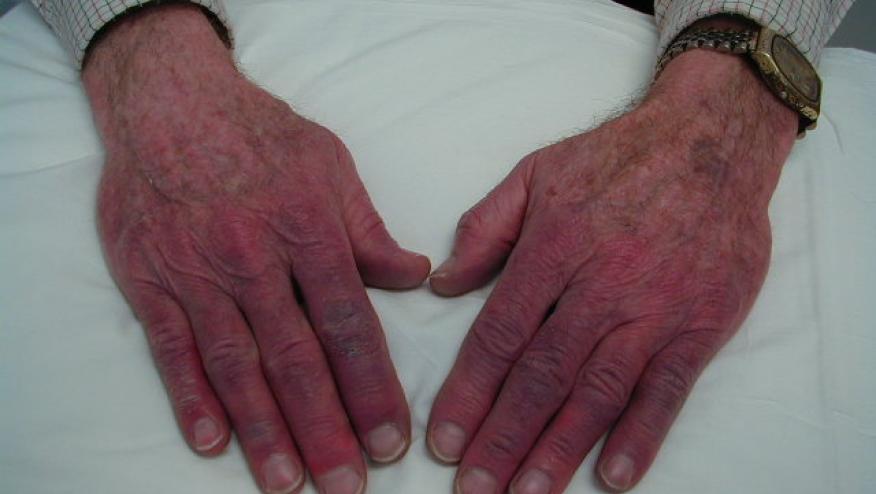
A systematic review by Khouri examined the extent drugs are capable of inducing Raynaud's phenomenon (RP).
The authors found 12 different classes of drugs responsible for RP, with cisplatin and bleomycin having with the greatest risk, followed by beta-blockers. The Framingham heart study found beta-blocker use was the most common cause of secondary RP (34.2% of secondary RP). A 2012 meta-analysis found a prevalence of 14.7% of RP in patients receiving beta-blockers.
Other less frequently cited causes include clonidine, ergot alkaloids, bromocriptine, ADHD drugs (methylphenidate and dextroamphetamine), phentermine (for weight loss), cocaine, vinyl chlorid exposure, and interferon therapy. Potential mechanisms include a variety of underlying mechanisms such as increased sympathetic activation, endothelial dysfunction, neurotoxicity or decreased red blood cell deformability. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors have also been reported to cause RP, although the mechanism is unknown.
Drug-induced RP is probably underestimated. Although most reports are benign, there are few rare, serious complications such as digital ischemia and ulceration reported.








If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.