HMGB1 as a Biomarker for Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis Save

High mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 (HMGB1) is a DNA-binding protein that functions as a structural co-factor. HMGB1 is actively secreted by macrophage/monocytes via inflammatory stimuli and is elaborated during apoptosis.
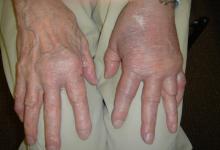
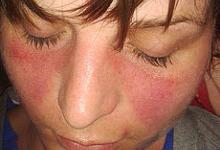
HMGB1 has been linked to a variety of chronic systemic autoimmune diseases, including polymyositis and dermatomyositis (PM/DM), lupus erythematosus and Sjogren's syndrome. HMGB1 is often expressed at sites of high cellularity along with the proinflammatory cytokines TNF alpha and IL-1beta.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) stimulated by endogenous antigens such as aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase enzymes may trigger activation of signaling pathways and propagation of disorders like PM/DM. HMGB1 is thought might interact with the same receptors to advance skeletal muscle inflammation. (citation source http://buff.ly/2byzJJ2)
Chinese investigators examined HMGB1 levels from the sera of 34 PM/DM patients and from 34 healthy controls to assess the clinical significance of HMGB1 levels in PM/DM and interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Significantly higher HMGB1 levels were seen in PM [mean: 12.75 ng/ml] and DM [20.75 ng/ml] when compared to healthy controls [5.64 ng/ml].
PM/DM patients with ILD had significantly higher HMGB1 levels compared to those without ILD [25.84 ng/ml vs. 12.68 ng/ml] (p < 0.05).
The diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of this serum HMGB1 cutoff level was 84.6% and 89%, respectively.
Patients with higher levels of HMGB1 expression had lower overall survival rates and disease-free survival rates, whereas patients with lower levels of HMGB1 expression had higher survival rates.
These analyses suggest that HMGB1 expression is a prognostic indicator for PM/DM, disease progression and patient survival.




If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.