New Sleep Medicine Guidelines for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Save
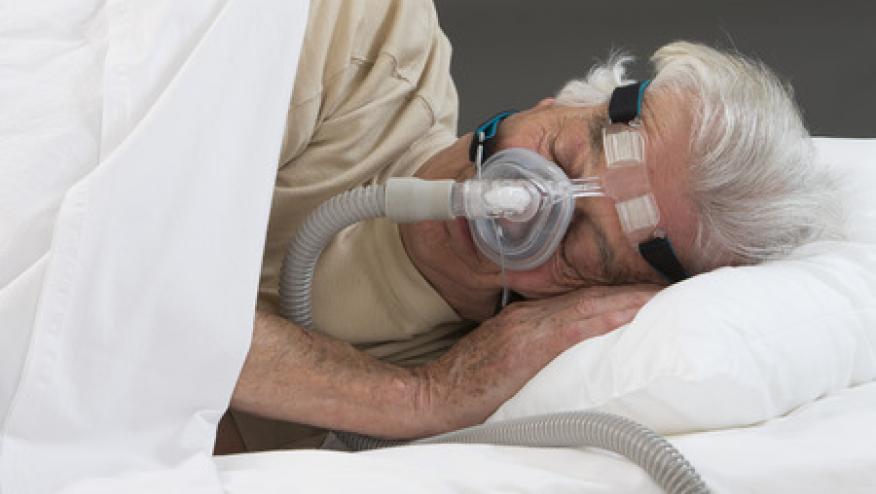
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) has established new guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of sleep-disordered breathing in adults, specifically guiding the use of positive airway pressure (PAP) in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in adults.
An AASM commissioned task force of sleep medicine experts undertook a systematic literature review, and developed consensus guidelines using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) process.
Good Practice Statements
- Treatment of OSA with PAP therapy should be based on a diagnosis of OSA established using objective sleep apnea testing
- Adequate follow-up, including troubleshooting and monitoring of objective efficacy and usage data to ensure adequate treatment and adherence, should occur following PAP therapy initiation and during treatment of OSA
Specific Recommendations
- We recommend that clinicians use PAP, compared to no therapy, to treat OSA in adults with excessive sleepiness. (STRONG)
- We suggest that clinicians use PAP, compared to no therapy, to treat OSA in adults with impaired sleep-related quality of life. (CONDITIONAL)
- We suggest that clinicians use PAP, compared to no therapy, to treat OSA in adults with comorbid hypertension. (CONDITIONAL)
- We recommend that PAP therapy be initiated using either APAP at home or in-laboratory PAP titration in adults with OSA and no significant comorbidities. (STRONG)
- We recommend that clinicians use either CPAP or APAP for ongoing treatment of OSA in adults. (STRONG)
- We suggest that clinicians use CPAP or APAP over BPAP in the routine treatment of OSA in adults. (CONDITIONAL)
- We recommend that educational interventions be given with initiation of PAP therapy in adults with OSA. (STRONG)
- We suggest that behavioral and/or troubleshooting interventions be given during the initial period of PAP therapy in adults with OSA. (CONDITIONAL)
- We suggest that clinicians use telemonitoring-guided interventions during the initial period of PAP therapy in adults with OSA. (CONDITIONAL)








If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.