Romosuzumab Followed by Alendronate is Best in Fracture Prevention Save
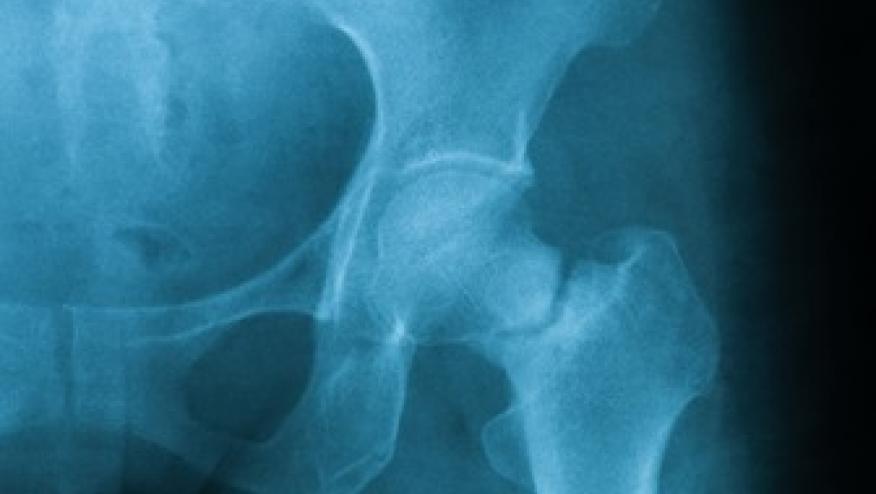
The NEJM reports that in high risk post-menopausal women, romosozumab for 12 months followed by alendronate resulted in a significantly lower fracture than alendronate alone.
A randomized 24-month trial enrolled 4093 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis and a fragility fracture and treated them with either monthly subcutaneous romosozumab (210 mg) or weekly oral alendronate (70 mg) for 12 months, followed by open-label alendronate. The primary endpoints were cumulative fracture incidence at 2 years.
In the end, the romosozumab-to-alendronate group had a 48% lower risk of new vertebral fractures (6.2%) than the alendronate-only group (11.9%).
Clinical fractures were also 27% lower risk with romosozumab (P0.001).
The risk of nonvertebral fractures was lower by 19% in the romosozumab-to-alendronate group.
Hip fracture was lower by 38% in the romosozumab-to-alendronate group.
While adverse events were balanced between groups. there were slightly more adjudicated cardiovascular adverse events with romosozumab than with alendronate (2.5% vs.1.9%).






If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.