RWCS 2016 - Updates in AS, PsA and Lupus Save
Update on Ankylosing Spondylitis and Spondyloarthritis
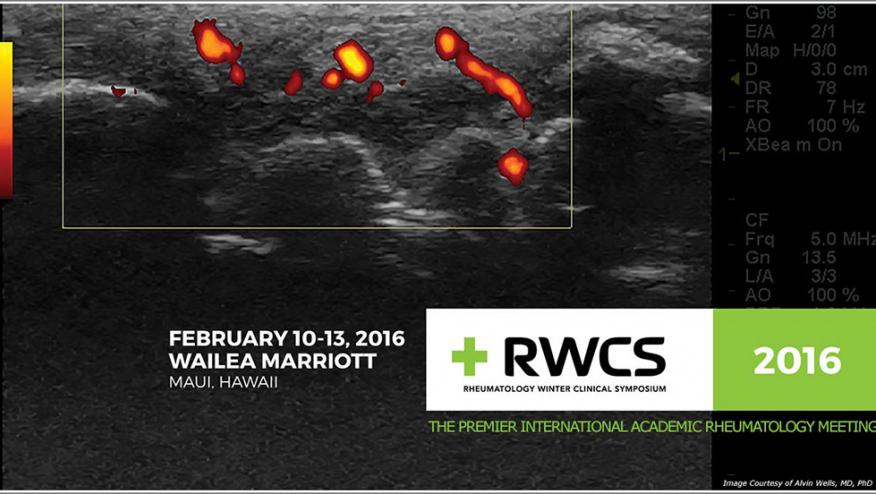
Dr. Eric Ruderman reviewed the clinical trial data that lead to the recent approval of secukinumab (SEC) for both ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). The MEASURE 1 and 2 trials examined the dose effects showing that SEC 150 mg dose was somewhat better than 75 mg, with ASAS20 responses of 60% at week 16. Not surprisingly, better responses were seen in those who were naïve to TNF inhibitors. MRI responses to SEC showed marked reduction in sacroiliac (SI) inflammation at week 16 and was maintained over 52 weeks.
MEASURE 1 assessed X-ray data progression over 2 years (371 patients) with mSASSS scores trending towards no change (the mean mSASSS change was 0.30) and 80% of patients showed no X-ray progression over 2 years. Changes were more likely in men, and those with high CRP or baseline syndesmophytes.
A study from Sieper, et al from 2015 showed that continuous NSAID (diclofenac) showed structural benefits with no/less radiographic progression for AS patients who took continuous (daily) diclofenac compared to on-demand diclofenac. These findings replicate that previously reported for continuous use of celecoxib.
Tofacitinib was studied in AS at a dose of 10 mg bid, meeting its primary endpoint with an ASAS20 of 56% (vs. 41% placebo) at 12 weeks. But it appears unlikely that manufacturers will develop tofacitinib for use in AS in the future.
Non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-AxSpA) was studied by the Mayo clinic. In their study of 83 patients with nr-AxSpA, only 19% went on to develop AS, suggesting nr-AxSpA is not necessarily an early form of AS but rather a distinct subset.
An interesting study presented at ACR 2015 examined 61 SpA patients with both ileocolonoscopy and videocapsule endoscopy (VCE), and showed that VCE was more sensitive than colonoscopy (41% vs. 13%) in identifying active colitis (in patients not taking NSAIDs).
SLE: Evolving Concepts
Dr. Dafna Gladman reviewed lupus criteria that have undergone changes in 1970, 1982, 1997 and new SLICC criteria. With the 1997 ACR lupus criteria, you could have lupus diagnosis based on four skin features alone. With the new SLICC classification criteria (AR 2012; 64; 2677), the diagnosis requires the patient to have four criteria, with at least one clinical and one immunologic; or biopsy proven lupus nephritis in the presence of ANA or dsDNA. There will be new ACR/EULAR classification criteria for SLE. These are currently being developed using multi-decision analysis methods.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) in SLE has a bimodal mortality. Dr. Sue Manzi estimated women have a 5-50 fold higher risk of CAD. In addition to atherosclerotic disease, other common comorbidities in lupus include bone disease (osteoporosis and osteonecrosis) and neurocognitive dysfunction. In Toronto, her SLE clinic was studied and they found an abnormal BMD in 31.5% of patients with 12% SLE women having OP, 43% having osteopenia and 7% developed fragility fractures. Risk factors for an abnormal BMD were increasing age and steroid dose. Discussion revealed that antiphospholipid antibodies are generally not a risk factor for CAD and CV events.
Osteonecrosis occurs in 14% of SLE patents, with half having bilateral bony involvement. Predictors include steroid dose and bisphosphonate therapy.
Update on Psoriatic Arthritis
Dr. Artie Kavanaugh reviewed some of the newer screening tools to detect psoriatic arthritis. Many of these were intended for use by primary care and dermatologists. These tools (PEST, PASE, EARP) have a lower than expected efficiency. Dr. Kavanaugh suggests that non-rheumatologists instead just ask the question, “Do you have pain or other symptoms in and around your joints that you want to do something about”?
Major advances in the last few years have led to new therapies for PsA, including secukinumab and apremilast – a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor. SEC has been shown to be superior to TNF inhibitors and ustekinumab in treating plaque psoriasis. In the FUTURE 1 and 2 trials in PsA, high level sustained responses (ACR 20 64-79%) were seen with SEC over 52 weeks. In the PALACE 1 trial, APR showed 53-59% ACR20 responses at 52 weeks.







If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.