Rheumatoid Arthritis

Richard Conway RichardPAConway
3 months ago
Bremer et al. Earlier initiation of biosimilar adalimumab (vs csDMARDs) may result in cost-savings. Reduced cost of tests, consultations, and hospitalisations. @RheumNow #ACR25 Abstr#2271 https://t.co/lHaSiX3WLd


Jiha Lee JihaRheum
3 months ago
Semaglutide isn’t just for weight loss?
In RA, users had 20–40% lower risk of synovitis, stiffness & swelling up to 1 year vs matched controls.
GLP-1 agonists may offer anti-inflammatory benefit beyond metabolism.
@RheumNow #ACR25 Abstract#2286

Richard Conway RichardPAConway
3 months ago
Mateo Faxas et al. TriNetX study, propensity score matched. 3000 patients. Arrythmia risk is higher with IL-6i vs TNFi in diabetic RA patients. V Tachy (HR 1.4), PPM need (HR 1.4) significantly higher. AF, SVT, VF all numerically increased. @RheumNow #ACR25 Abstr#2283 https://t.co/U2Tk38Mobg


Aurelie Najm AurelieRheumo
3 months ago
Effect of air pollution in RA
Prospective cohort 1000+pts w/ 12000+ visits
Higher levels of pollution
& specific size of particles PM25
asso w/
-10% higher odd of flare
-Higher DAS CRP and CDAI
Now the interesting pattern:
PM25 exposure increases 3 weeks before flares https://t.co/MOskJzk05g


Richard Conway RichardPAConway
3 months ago
Higashida-Konishi et al. RA. Insomnia and fatigue in >80%, depression in 13%. RA disease activity is associated with depression, fatigue, and insomnia. @RheumNow #ACR25 Abstr#2254 https://t.co/7SibPW6BBw


Jiha Lee JihaRheum
3 months ago
Can AI predict who stops their RA meds?
In older adults on b/tsDMARDs, interpretable ML found frailty, comorbidity & age top the list for nonadherence risk.
@RheumNow #ACR25 Abstract#2287

Richard Conway RichardPAConway
3 months ago
Girolami et al. VA study. Safety of DMARDs in RA following melanoma. 644 patients. 3 year all cause mortality. No significant difference, but graph sure looks like b/tsDMARDs are better. No melanoma specific mortality/recurrence data however. @RheumNow #ACR25 Abstr#2237 #ACRBest https://t.co/IN4LDkioT7


Aurelie Najm AurelieRheumo
3 months ago
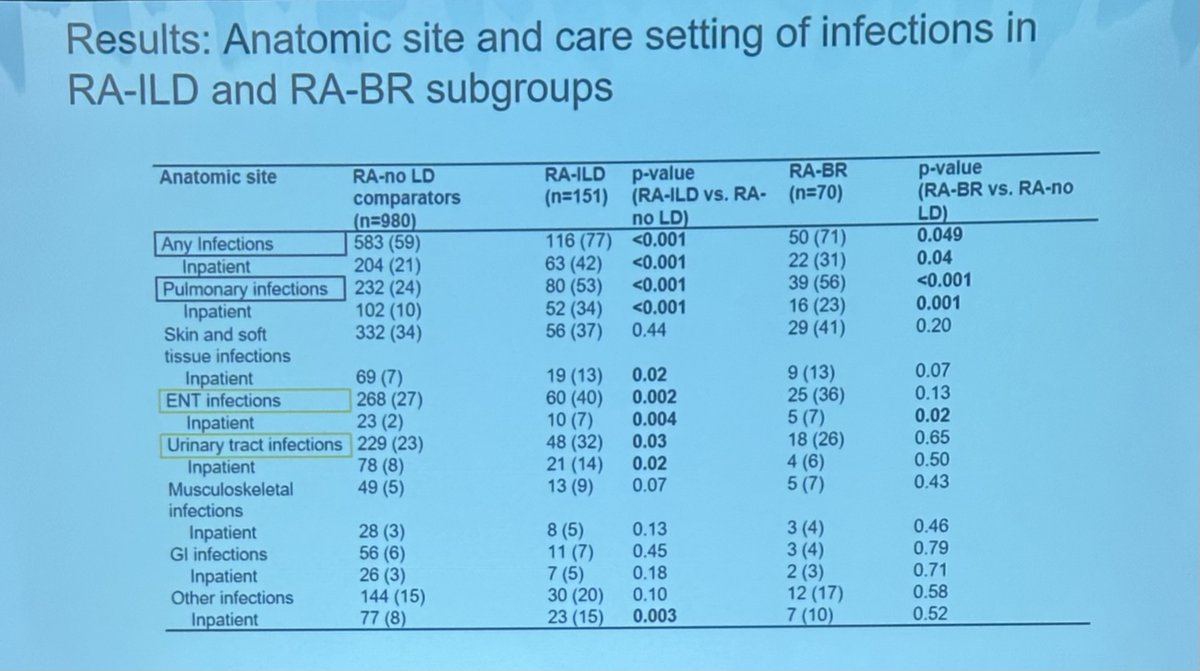
Is RA-ILD associated with/ higher risk of infection?
Retrospective US cohort study
151 RA-ILD
980 matched controls
79% higher risk of any and pulmonary infections in RA-ILD
Pathogen type: bacterial, viral and fungi
Some of these infections are preventable!
Take Home: https://t.co/fPmRjLL7Po

Aurelie Najm AurelieRheumo
3 months ago
A prediction model for RA-ILD in RA pts: is it possible?
Not quite yet!
Veterans Affairs RA registry 2700+ pts
5% of prevalent ILD
Associated w/
-GDF-15
-Pentraxin 3
No prediction for Incident disease
Needs more work to understand implications for practice
@RheumNow #ACR25 https://t.co/CmW72nybcQ


Mrinalini Dey DrMiniDey
3 months ago
#1724 MAIT cells central in RA pathogenesis. These innate-like T cells accumulate in synovial fluid, driving fibroblast activation, cytokine release & joint damage. Blocking MAIT activation or deleting MR1 reduces arthritis in mice- a potential new target in RA. @RheumNow #ACR25
Two new studies presented this year tackle a key question: can our initial treatment choices influence who ends up in the difficult-to-treat category?













 Poster Hall
Poster Hall