Psoriatic arthritis

Antoni Chan MD (Prof) synovialjoints
8 months 3 weeks ago
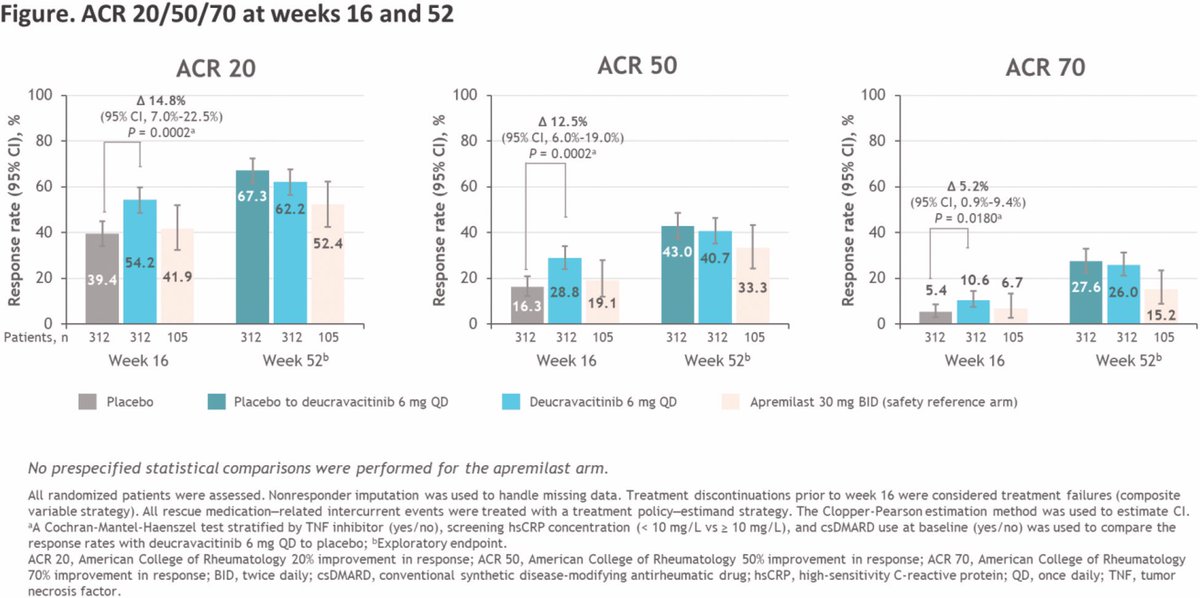
Efficacy and safety of deucravacitinib up to week 52 in the POETYK PsA-2 study
•ACR20 at W16: 54.2% (deucravacitinib) vs 39.4% (placebo), p=0.0002
•PASI75: 40.9% vs 15.4%, p<0.0001
•MDA: 25.6% vs 14.7%, p=0.0007
•FACIT-F: +2.5 vs +1.8
•SAE: 1.9% (low)
TYK2 inhibition shows https://t.co/JXTZRk2itA

Nelly ZIADE 🍀 Nellziade
8 months 3 weeks ago
❓️Is early intensive therapy with combination csDMARDs or TNFi superior to standard step care for the treatment of moderate to severe #psoriatic_arthritis?
🅰️ Yes
🔅Check out the SPEED RCT presented by @DrLauraCoates at #EULAR2025
OP0089
@RheumNow
#Strategy https://t.co/24e7wUV2FB


Aurelie Najm AurelieRheumo
8 months 3 weeks ago
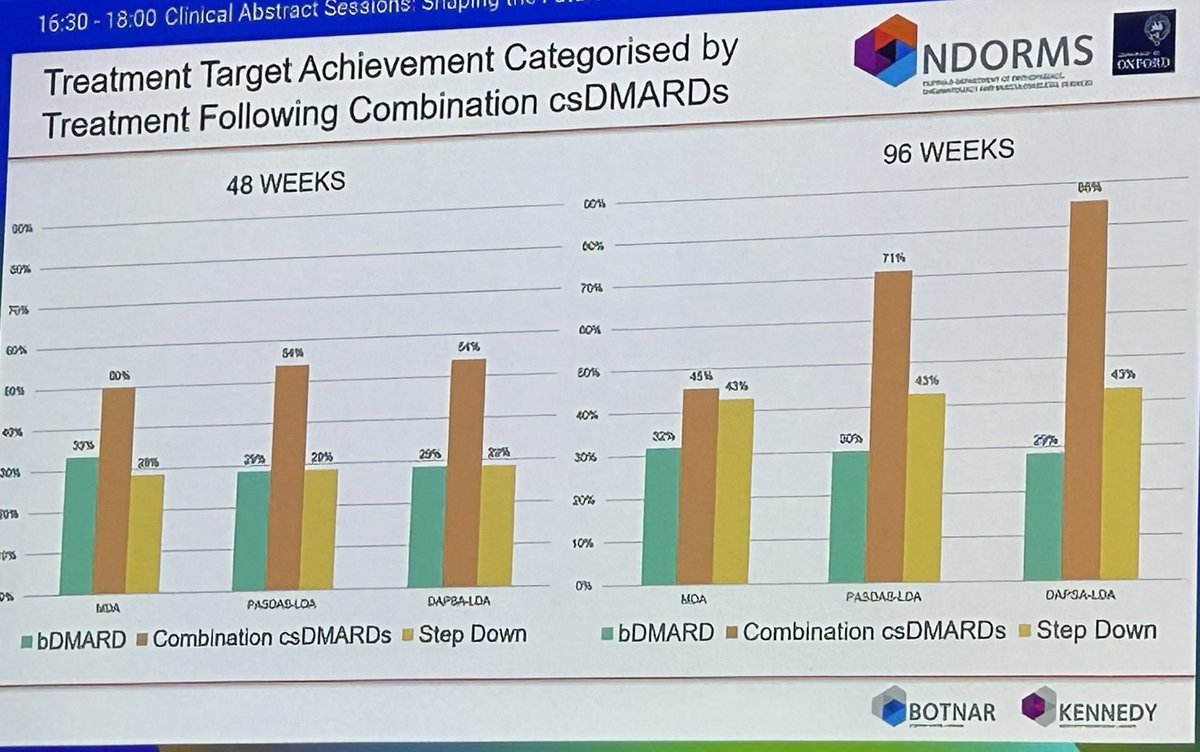
MONITOR PsA 200+ pts secondary care "real-life" cohort
65 treated w/ combi csDMARDs
48weeks outcome and 96 weeks
49% bioDMARDs, 29% retention and 23% deescalation to 1 csDMARD
‼️reasons for discontinuation was AEs in 60% cases not inefficacy
Caveat: analysis not adjusted for https://t.co/L8EczgZTpP


Jiha Lee JihaRheum
8 months 3 weeks ago
📊 POS0574 @rheumnow #EULAR2025 Real-world data from SERENA shows sustained 5-year effectiveness of secukinumab in PsA. ✔️ 57% had no tender/swollen joints at Year 5 ✔️ PASI90 in ~48% ✔️ Stable low TJC, SJC & PtGA Durability confirmed even in prior biologic users. https://t.co/eNpboTRRu3


Antoni Chan MD (Prof) synovialjoints
8 months 3 weeks ago
MONITOR-PsA (n=218):
•36.5% had >1 csDMARD
•Of those, 49.2% tried combination (combo) csDMARDs
•63.6% of combo csDMARD users in MDA at 48wks
•61.1% stopped due to side effects—not inefficacy
Real-world support for csDMARD combos where biologics delayed. Abstract#OP0093 https://t.co/3Anme39VXk

Jiha Lee JihaRheum
8 months 3 weeks ago
Early PsA? Treat fast, treat hard.
The STAMP RCT showed that early secukinumab + MTX led to faster ACR50 and PASI90 responses vs standard care in a T2T strategy. By 12 months, outcomes were similar, but early SEC needed fewer escalations.
Abstract#OP0092
@RheumNow #EULAR2025 https://t.co/cAZTc9eN16


Adela Castro AdelaCastro222
8 months 3 weeks ago
Combination therapies in PsA not so far away:
-Case series of 22 patients from large PsA cohort.
-Combination therapy in PsA used when difficult to treat skin and msk involvement.
-Deucravacitinib was the agent mostly used in combination with bDMARDs.
-No major serious adverse https://t.co/YUyvuaJcsE

Aurelie Najm AurelieRheumo
8 months 3 weeks ago
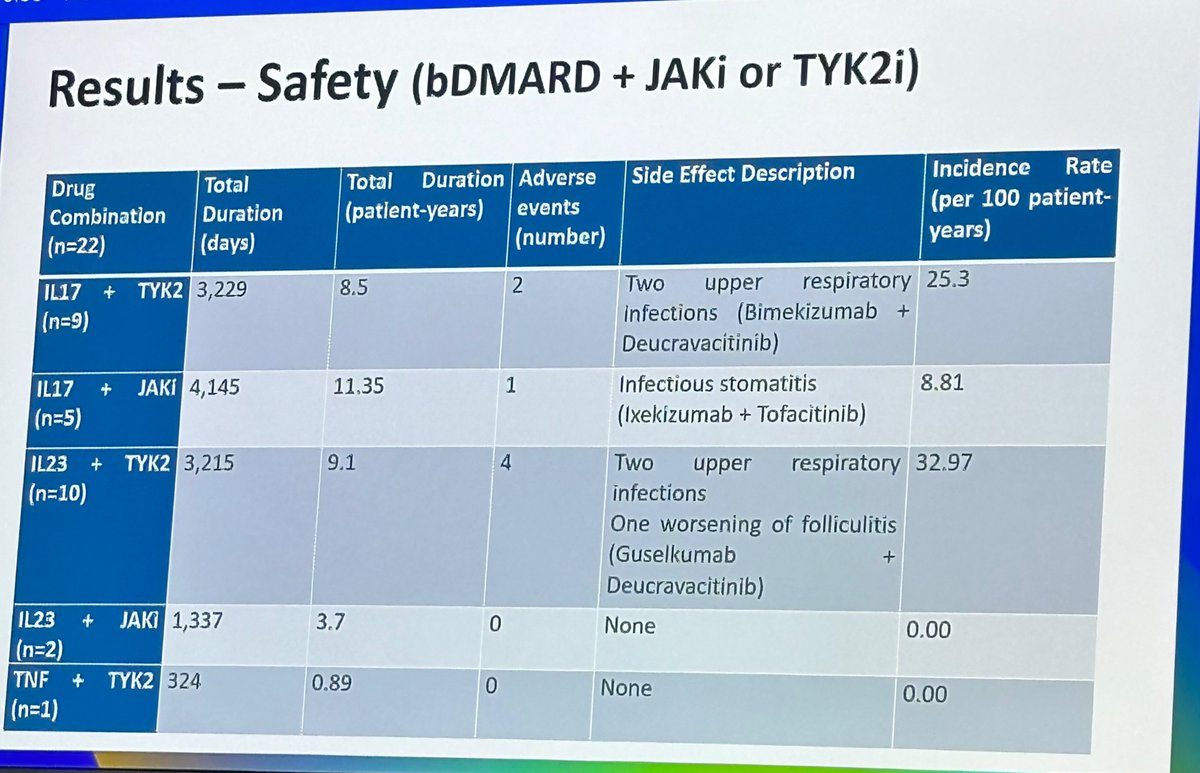
Case series of 22 PsA pts treats w/ combination bioDMARDs & JAKi,TYK2i or APR
IL17i + JAKi 10.5 PY = 1 mild infectious stomatitis
IL23i + JAKi 3.7 PY = no AE
IL-17i + TYK2i 8.5 PY = 2 mild upper respiratory infections
IL-23i + TYK2i 8.3 PY = 2 mild URIs, 1 folliculitis
TNFi + https://t.co/Qg9HIwuslJ


Adela Castro AdelaCastro222
8 months 3 weeks ago
Can IL-17F signalling be modulated by treatment with TNFi?
In PsA pts non responders to previous TNFi, there was increased expression of IL17F-related gene signature. Suggesting a potential mechanism for the consistent level of clinical response observed with BKZ.
Abstract https://t.co/D6fvp18UTz


Mrinalini Dey DrMiniDey
8 months 3 weeks ago
In #InflammatoryArthritis, baseline depression was linked to ↑ presenteeism & ↓ QoL at baseline + 3mo, but not absenteeism. Data from 9-country study provide further evidence that mental health is key to supporting work outcomes in RA, PsA & axSpA.
@RheumNow #EULAR2025 #OP0028

Antoni Chan MD (Prof) synovialjoints
8 months 3 weeks ago
Early intensive therapy in PsA.
STAMP RCT in early PsA:
•ACR50 at 3mo: 43% (early secukinumab) vs 22% (SoC)
•MDA at 3mo: 48% vs 25%
•PASI90 at 3mo: 60% vs 22%
By 12months: outcomes similar, but early secukinumab led to faster control and fewer therapy escalations. https://t.co/TKa5z24NQX


Jiha Lee JihaRheum
8 months 3 weeks ago
Should we start strong in PsA?
In the SPEED RCT (Coates et al), both early TNFi and combo csDMARDs outperformed step-up care in moderate-severe PsA. TNFi showed the most sustained benefit through 48w.
Abstract#OP0089
@RheumNow #EULAR2025
We’re seeing more patients develop rheumatic diseases for the first time in their 60s, 70s, or beyond. But are these truly the same diseases we see in younger adults, or do they behave differently, shaped by age-related biology, comorbidity, and the biases that influence medical decision-making? Several abstracts presented at EULAR 2025 challenge us to reconsider how we diagnose and treat rheumatic disease in older adults.








 Poster Hall
Poster Hall