Anti-Rheumatic Rx
Dr. Jack Cush discusses declining survival rates in the USA, FDA approvals of new COVID subvariant boosters and other odd and possibly true new research reports from the past week on RheumNow.com.
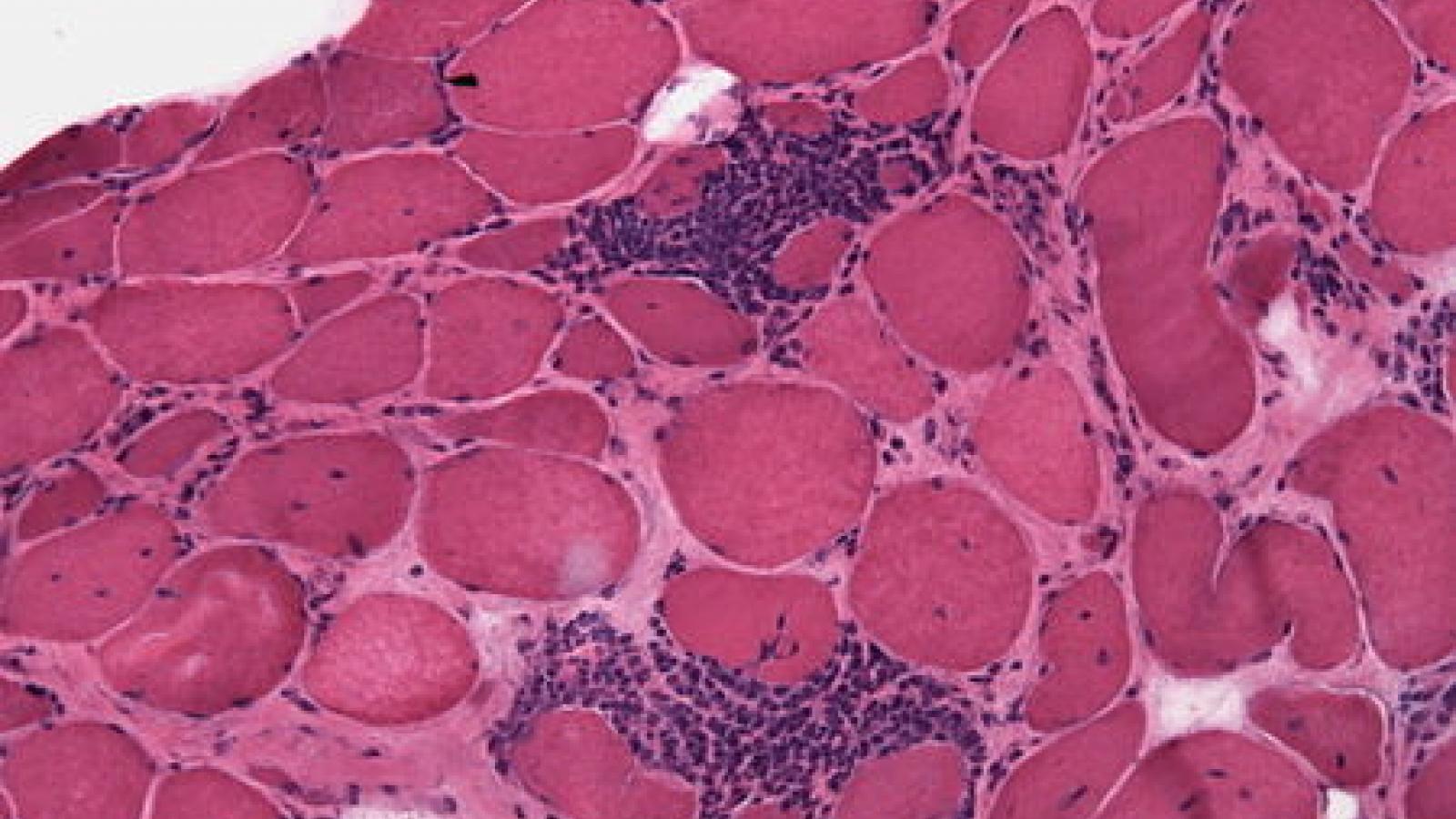
The diagnosis of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) can be informed by the 2017 EULAR/ACR classification criteria, but their utility in patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis (CADM) and anti–melanoma differentiation–associated protein 5 (anti–MDA-5)–positive IIM is less certain.
Today the FDA authorized the updated Omicron subvariant (BA.4 and BA.5) COVID-19 booster shots manufactured by Pfizer and Moderna; with an anticipated ship/start date of early September 2022. The BA.5 subvariant accounts for more than 88% of U.S. infections.
NICE (UK) has systematically reviewed current medical evidence and delivered a set of recommendations with consideration of cost effectiveness.
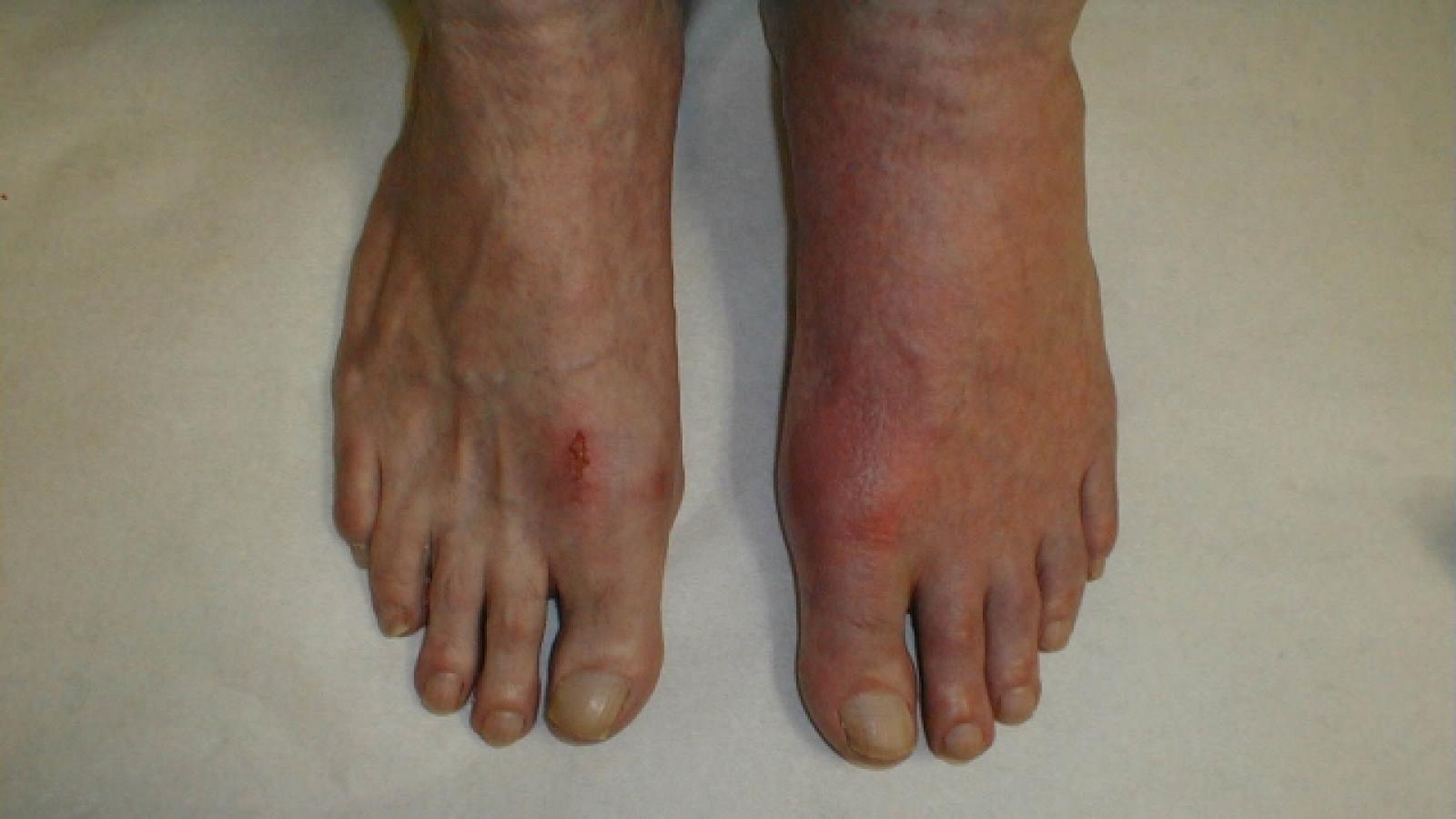
Still's disease in adults (AOSD) or children (sJIA) can have dramatic symptom severity, making it easy to gauge disease activity and response to therapy, especially at the outset. However, a validated measure of disease activity has not been agreed (for clinical trial and treatment assessments). A new study compares two such activity measuresin a large cohort of Still's patients.
Research presented in the Journal of Experimental Medicine shows that ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) may be propagated by pathogenic mechanisms triggering cGAS/STING/IRF3-dependent IFN-I release.
A large UK database study suggests that young adults with autoimmune diseases have an associated increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
Dr. Jack Cush delivers this weeks rheumatology "weather report" with the best and least of news and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow.com
“Climate is what we expect, weather is what we get.” – Mark Twain
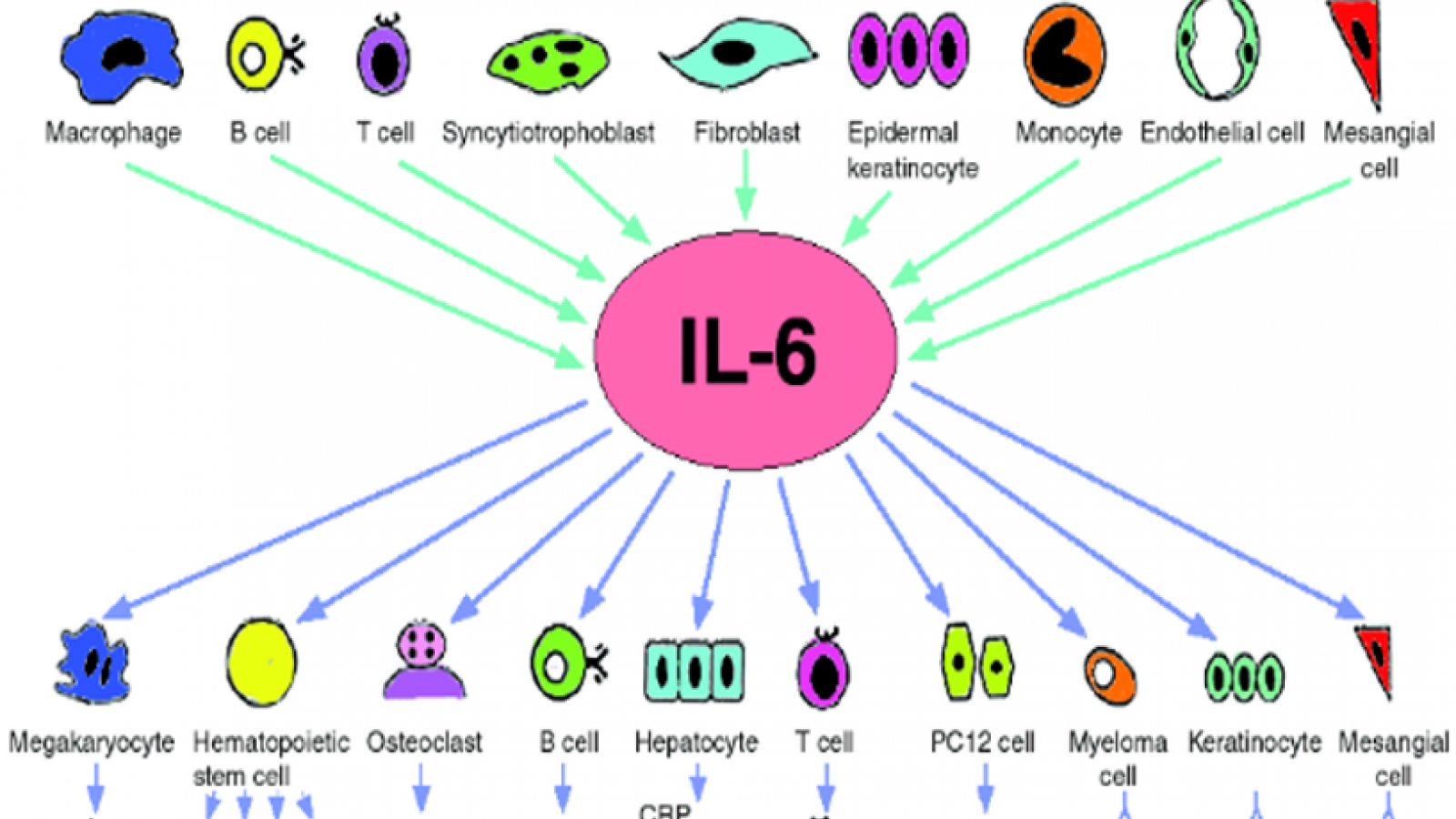
This week's NEJM has published the efficacy results of a large phase 3 trial of olokizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that directly targets IL-6 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
This is in contrast to two other marketed IL-6 inhibitors (sarilumab, tocilizumab) that bind to the IL-6 receptor.
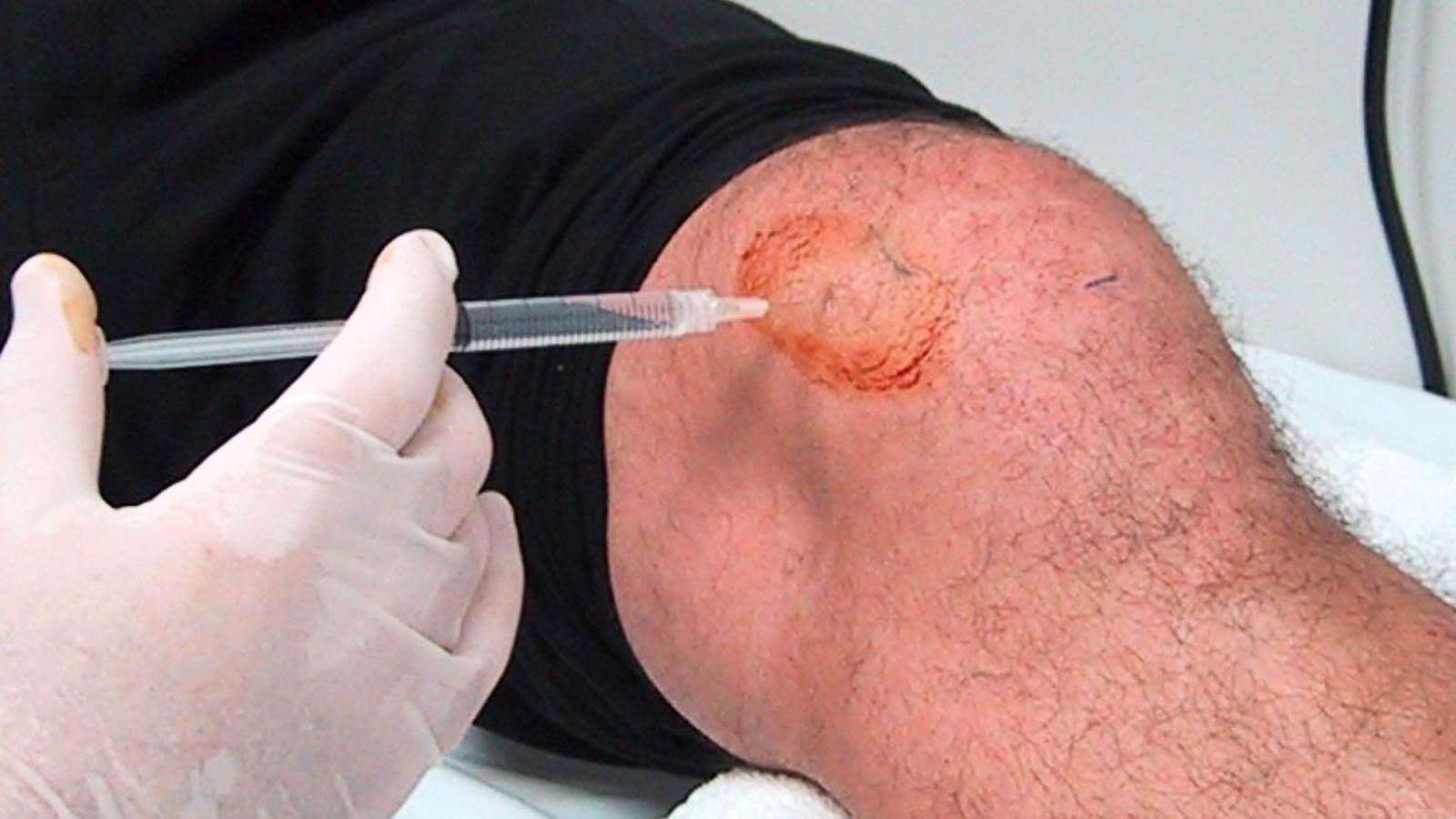
In the United States, where over $300 million is spent annually on intraarticular hyaluronic acid injections, yet another study shows such therapy to be no better than placebo.
BMJ has published a metanalysis of the efficacy and safety of viscosupplementation (intraarticular hyaluronic acid injection) in knee osteoarthritis patients. This is one of many such reviews, all ending with the same conclusion.
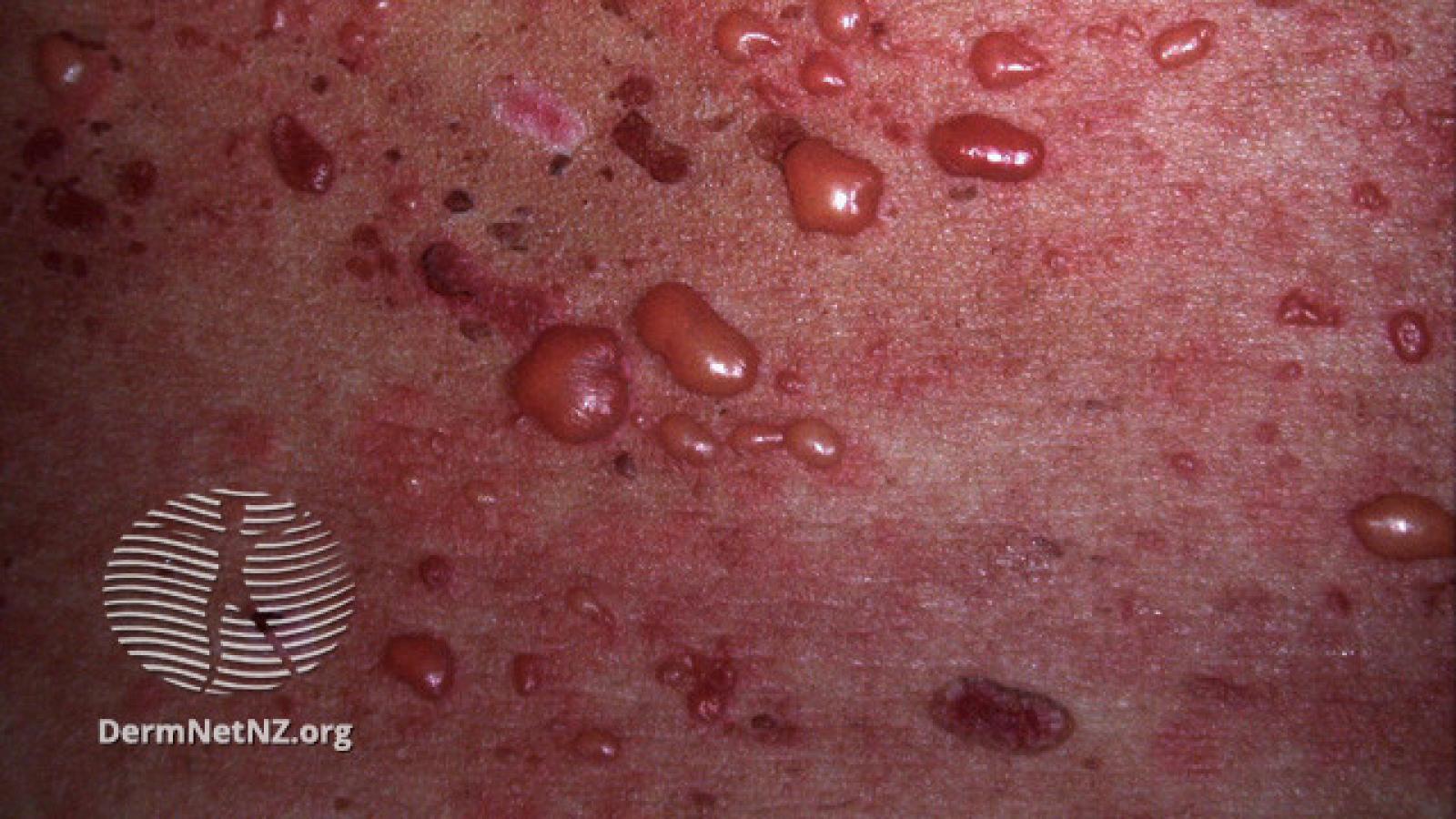
Bullous systemic lupus erythematosus (BSLE) is a rare blistering cutaneous manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
As goes SLE, bullous disease typically affects women, especially those of African descent.
Declines in body mass index (BMI) were linked with slower worsening of knee osteoarthritis (OA), according to data from three large longitudinal cohort studies.
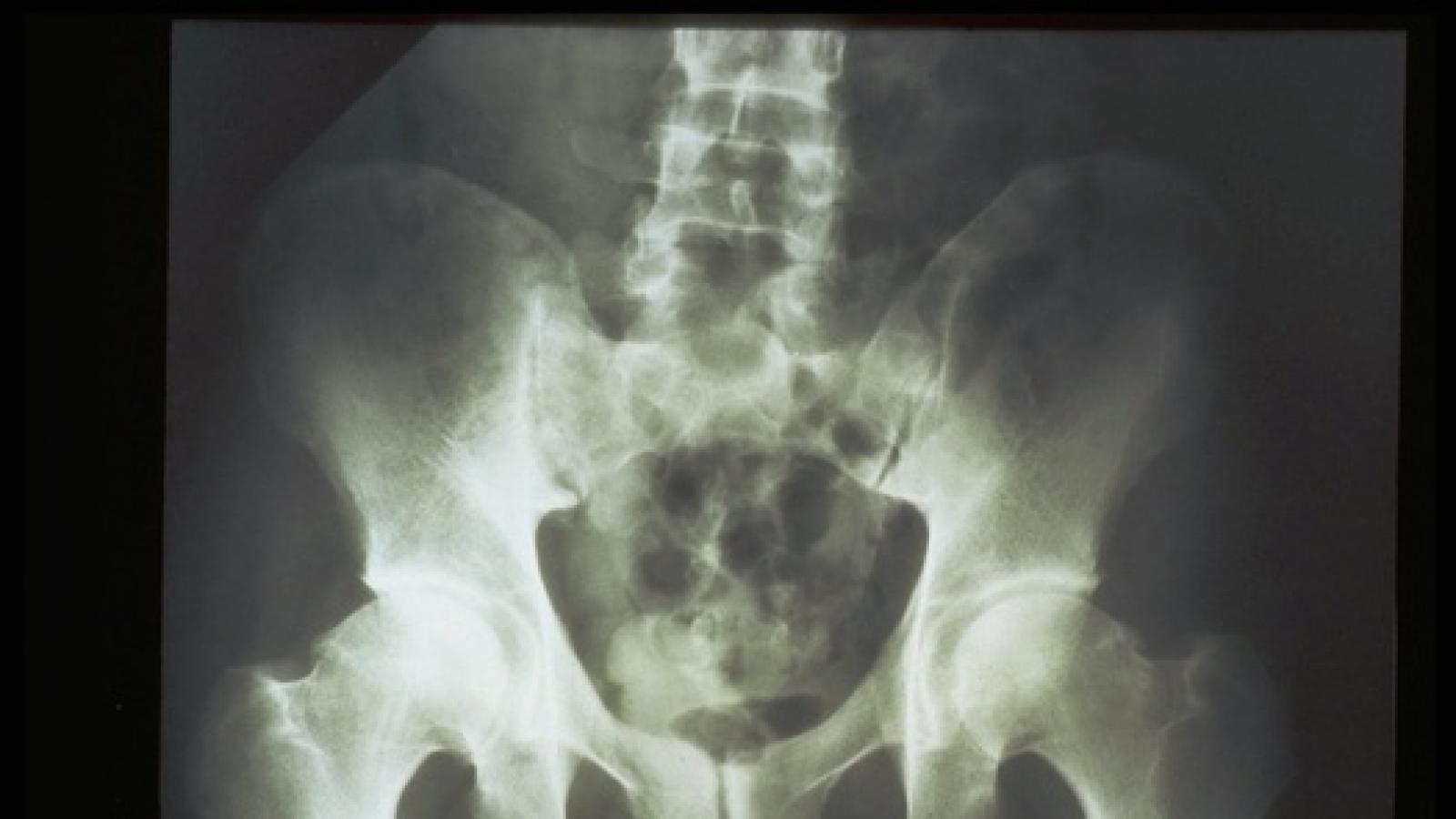
A cohort analysis from Toronto suggests that axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is distinctly different from axial ankylosing spondylitis (AS) with psoriasis.
Researchers examined two PsA and AS cohorts - patients with PsA with axial disease and isolated axial patients with AS with psoriasis.
A current Medscape article on patient "no shows" in private medical practice examines the cause and approach to the problem.
The most common reason for no shows is lack of knowledge about the scheduled appointment. Here are other common causes of no-shows, and how to address the problem.
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports from this past week on RheumNow and discusses a case of refractory juvenile dermatomyositis with calcinosis.














 Poster Hall
Poster Hall