In the United States, where over $300 million is spent annually on intraarticular hyaluronic acid injections, yet another study shows such therapy to be no better than placebo.
BMJ has published a metanalysis of the efficacy and safety of viscosupplementation (intraarticular hyaluronic acid injection) in knee osteoarthritis patients. This is one of many such reviews, all ending with the same conclusion.
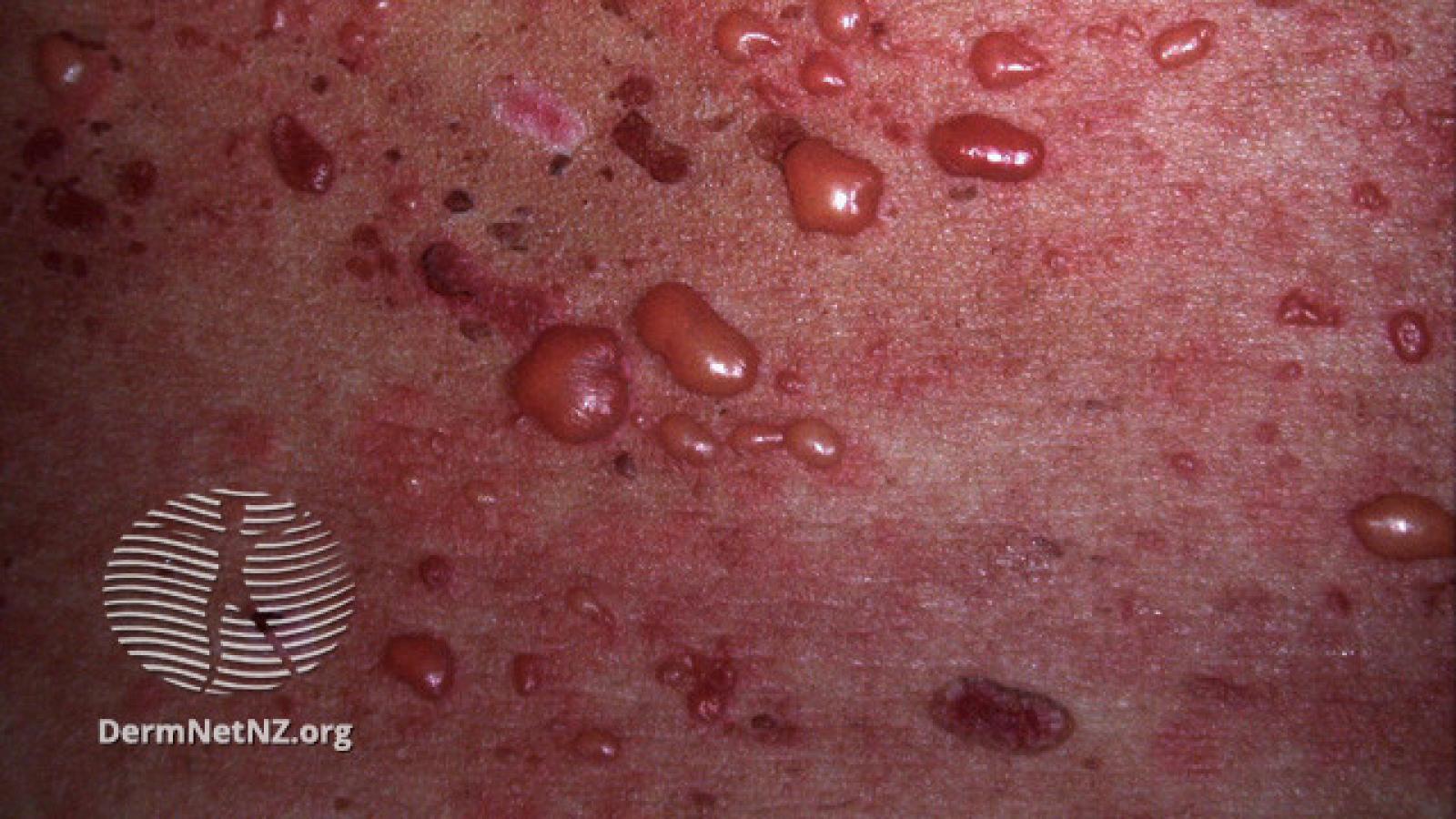
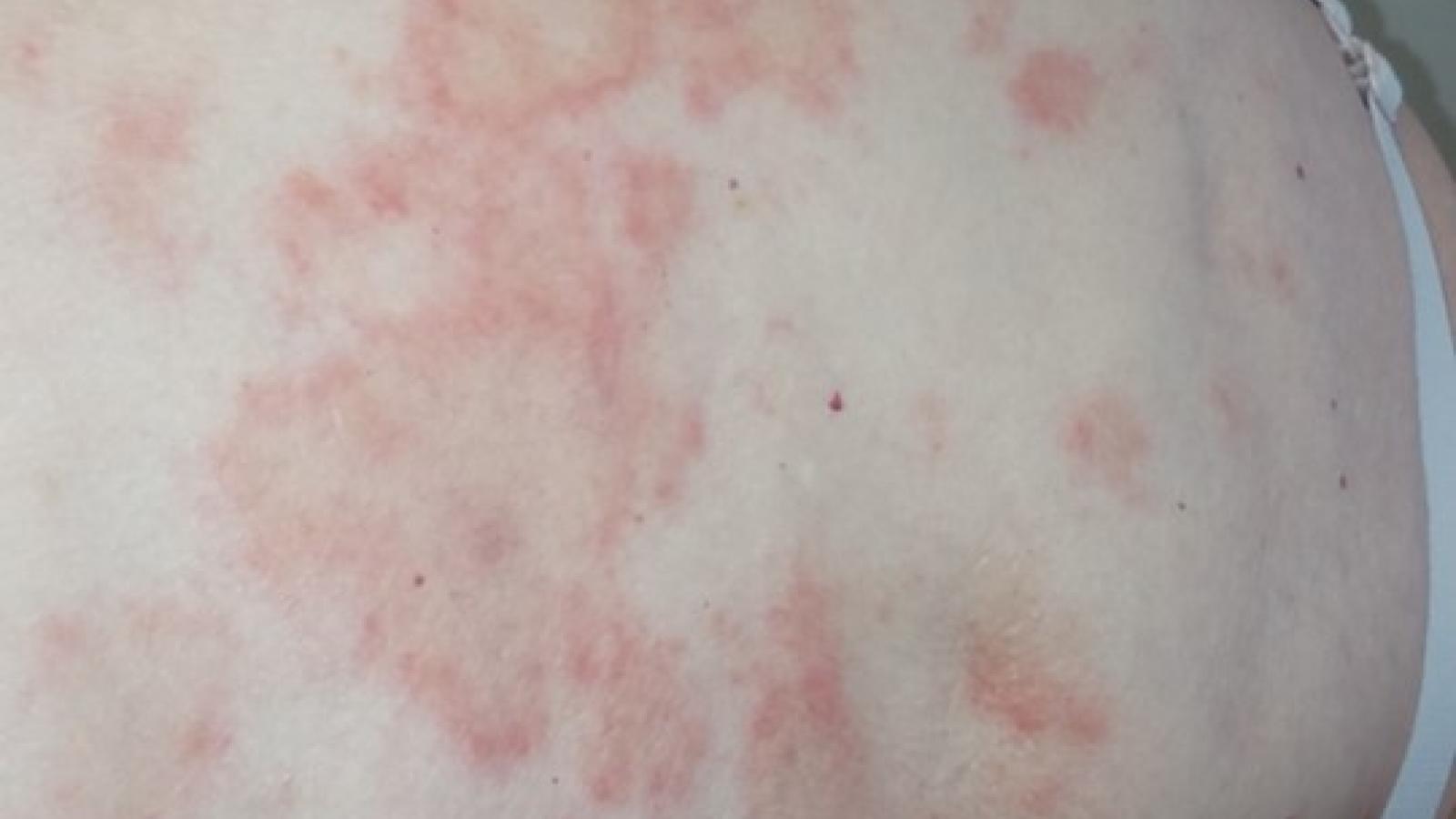
Bullous systemic lupus erythematosus (BSLE) is a rare blistering cutaneous manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
As goes SLE, bullous disease typically affects women, especially those of African descent.
The NY Times reports that a recent survey of drug use indicates that daily consumption of marijuana among young adults nearly doubled in the last decade. This is coupled with growing mainstream acceptance of cannabis and hallucinogenic compounds.
A recent meta-analysis suggests a bidirectional association between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and depression. Finding RA patients with depression yields an 80% increased mortality risk.
Anti-cytokine therapies represents a potential alternative for the treatment of depression.
Analysis of 11 cohort studies included 39,130 RA patients, 550,782 patients with depression and 7,802,230 controls.
Declines in body mass index (BMI) were linked with slower worsening of knee osteoarthritis (OA), according to data from three large longitudinal cohort studies.
A cohort analysis from Toronto suggests that axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is distinctly different from axial ankylosing spondylitis (AS) with psoriasis.
Researchers examined two PsA and AS cohorts - patients with PsA with axial disease and isolated axial patients with AS with psoriasis.
A current Medscape article on patient "no shows" in private medical practice examines the cause and approach to the problem.
The most common reason for no shows is lack of knowledge about the scheduled appointment. Here are other common causes of no-shows, and how to address the problem.
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports from this past week on RheumNow and discusses a case of refractory juvenile dermatomyositis with calcinosis.
With nearly one-third of adults, adolescents and children having sleep difficulties, many resort to using melatonin. JAMA reports substantial increases in the use of over-the-counter (OTC) melatonin, in all age groups. But is it effective, safe and warranted?
The National Health Interview Survey found a 7-fold increase in melatonin use; it 0.1% in 2007 and rose to 0.7% in 2012 amongst youths.
The DESIRES trial studied rituximab (RTX) in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) and showed clinically significant improvement in skin and lung outcomes after a subsequent 24-week open-label extension phase.
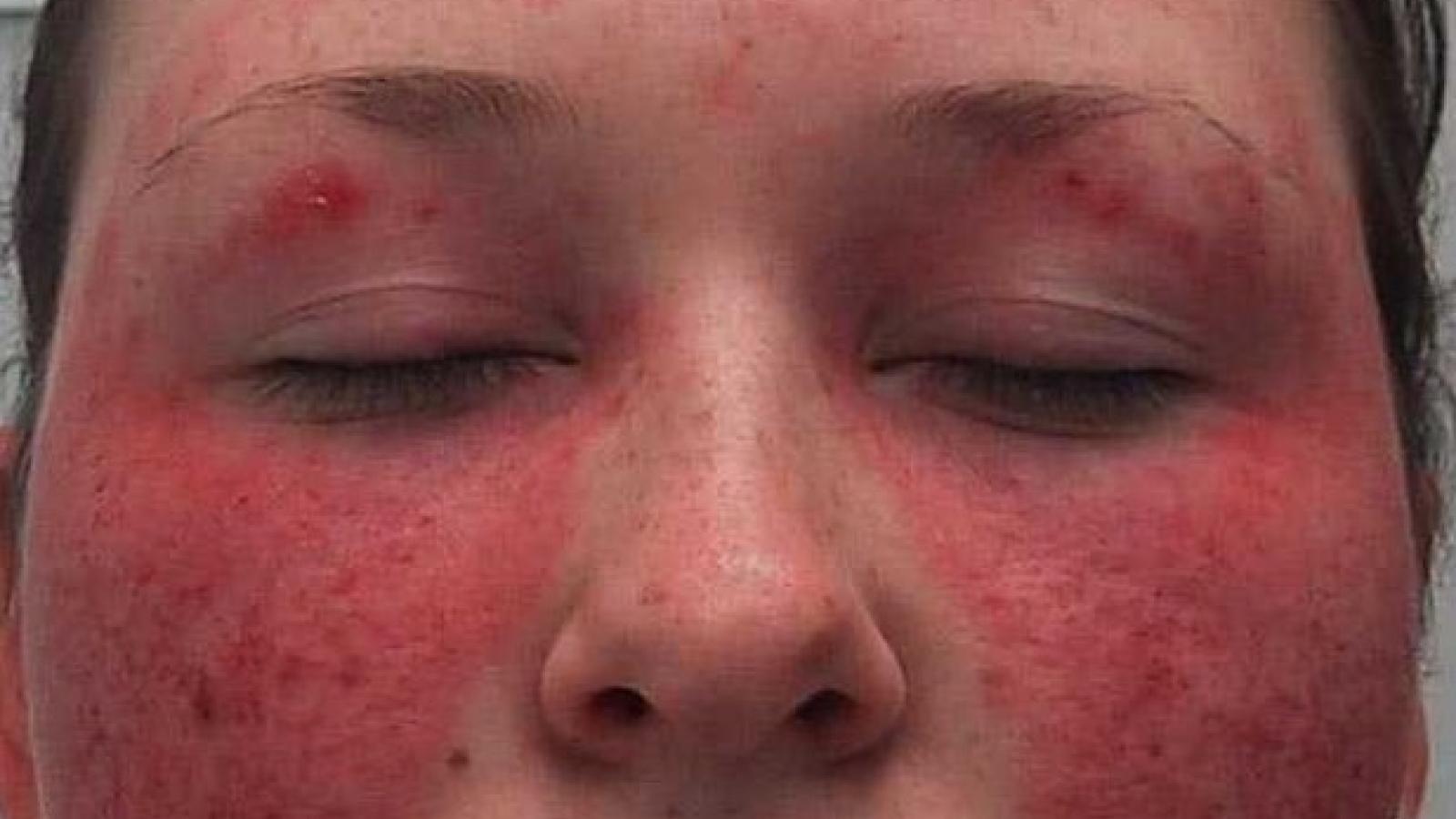
A multicentre, proof-of-concept trial of suggests that low-dose IL-2 therapy may be effective in moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This is not surprising as IL-2 is needed to bolster insufficient regulatory T cell (Treg) activity, thought to be pivotal to the pathophysiology of SLE.
A wide range of therapies have been implicated in causing drug-induced lupus erythematosus (DIL); now it appears that proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can be added to the list of causative drugs.
Pregnancy often occurs in women with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), and a recent cohort study suggests outcomes are generally better than what had been reported in the literature.
Data was collected from axSpA patients from 4 registries who were pregnant. This included a total of 332 pregnancies from 304 axSpA women (mean age 31 years; disease duration 5 years). Recorded outcomes included:
JUNIPERA study evaluated secukinumab (SEC) in children with enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA) and juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA) and was found to be safe and effective in patients with active ERA and JPsA who previous failed to respond to conventional therapy.
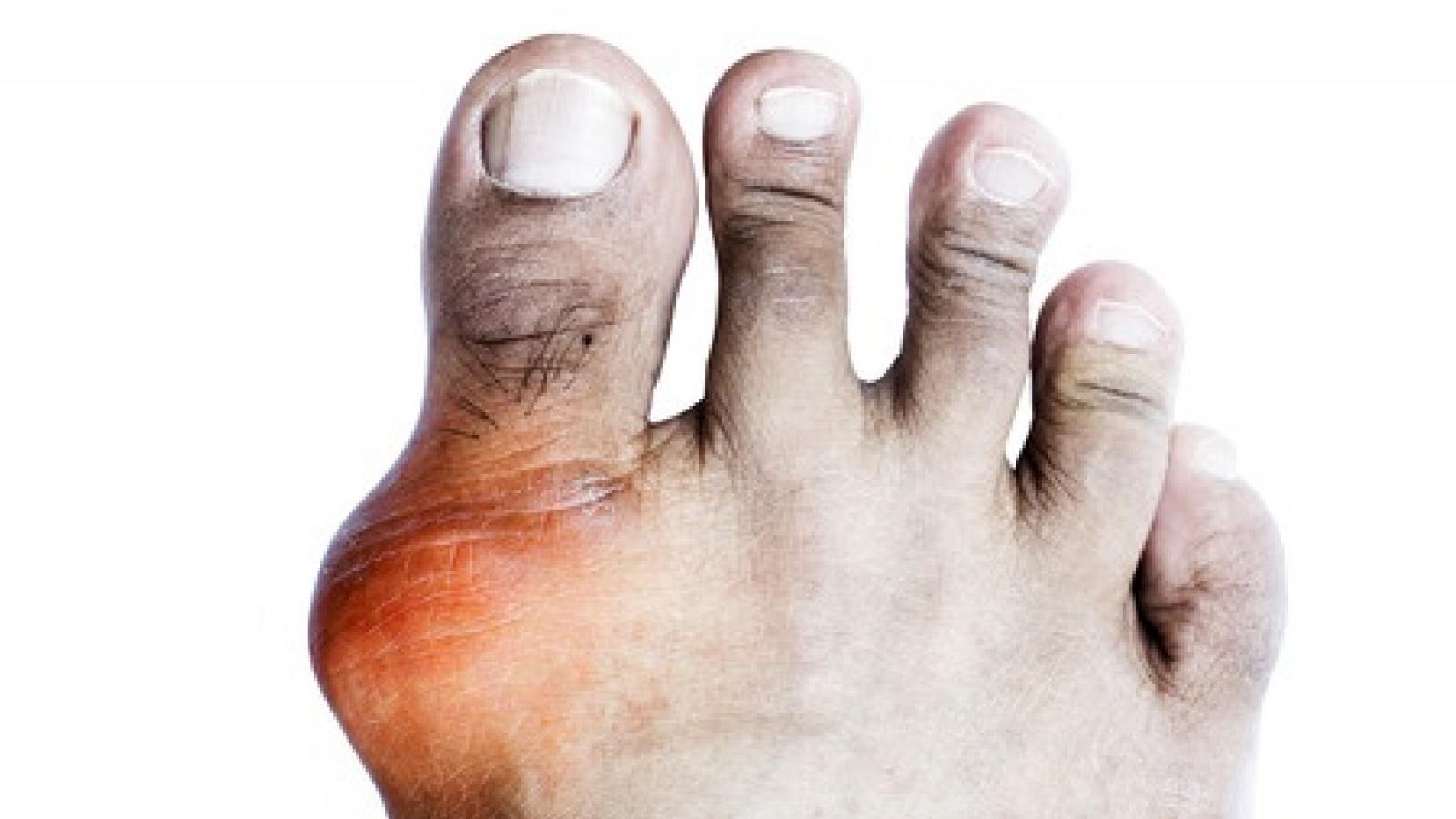
In a cross-sectional study of US adults, gout was more prevalent in black adults compared to white adults; possibly explained by sex-specific dietary differences and social determinants of health and clinical factors.

































 Poster Hall
Poster Hall