NEJM has published study results showing that vitamin D3 supplementation does not significantly lower fracture risk (vs. placebo) when used in generally healthy adults.
Krill oil supplements in knee osteoarthritis (OA) was shown to be superior to placebo in reducing knee pain, stiffness and function while increasing the omega-3 index. Krill oil, rich in anti-inflammatory long-chain (LC) omega-3 ( ω–3) PUFAs and astaxanthin, is thought to be safe and now shown to be effective nutritional treatment for mild to moderate knee OA.
Litifilimab, a humanized monoclonal antibody against BDCA2, targets the BDCA2 receptor on plasmacytoid dendritic cells. When administered to patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) was shown reducing disease activity in CLE patients.
The janus kinase inhibitor, upadacitinib, has been shown to significantly improve the signs and symptoms of non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-AxSpA), extending the efficacy of UPA beyond classic ankylosing spondylitis.
Your patient doesn't meet criteria for Still’s disease (AOSD or sJIA), now what should you do or consider?
What you do or consider next can be addressed according to the stage of current disease: A) Hospitalized Febrile Disease, or B) Outpatient “Still’s” Disease.
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news, journal reports and rheumatologist cases from the past week on RheumNow.com. This podcast is brought to you by StillsNow.com - be sure to sign up for our monthly StillsNow email and Monthly StillsNow Podcast.
Mehta et al have published a full read review of managing interstitial lung disease (ILD) in patients with inflammatory myopathies, a heterogeneous group of syndromes connected by ILD and and increased morbidity and mortality risk.
They divide myositis-ILD into three main prognostic groups with different treatment approaches:
Fever of unknown origin (FUO) represents a diagnostic challenge to many physicians and while cancer and infectious causes need to be excluded, rheumatic disorders are amongst the most common causes of FUO.
A recent metanalysisi of the medical literature from 2002 to 2021, included studies with ≥50 patients reporting on causes of FUO/IUO (inflammation of unknown origin). This series included 16884 patients.
There is no “test” (blood or other) that is solely diagnostic of Still’s disease, but labs can help make a diagnosis or manage disease, and affirm the safety of drugs in use.
The Johns Hopkins Hospital has repeated its top rank among US Rheumatology centers - ranking #1 for the 18th year in a row, according to U.S. News & World Report’s 2022–23 Best Hospitals list released yesterday.
Management of arthralgias before a certified rheumatoid arthritis (RA) diagnosis is challenging - should one use DMARD therapy before clinically evident synovitis in a preemptive effort to avoid or forestall the diagnosis or damage of RA?
Patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) related to systemic sclerosis continued to see less progression when treated with nintedanib (Ofev) in the pivotal 100-week SENSCIS trial, researchers said.
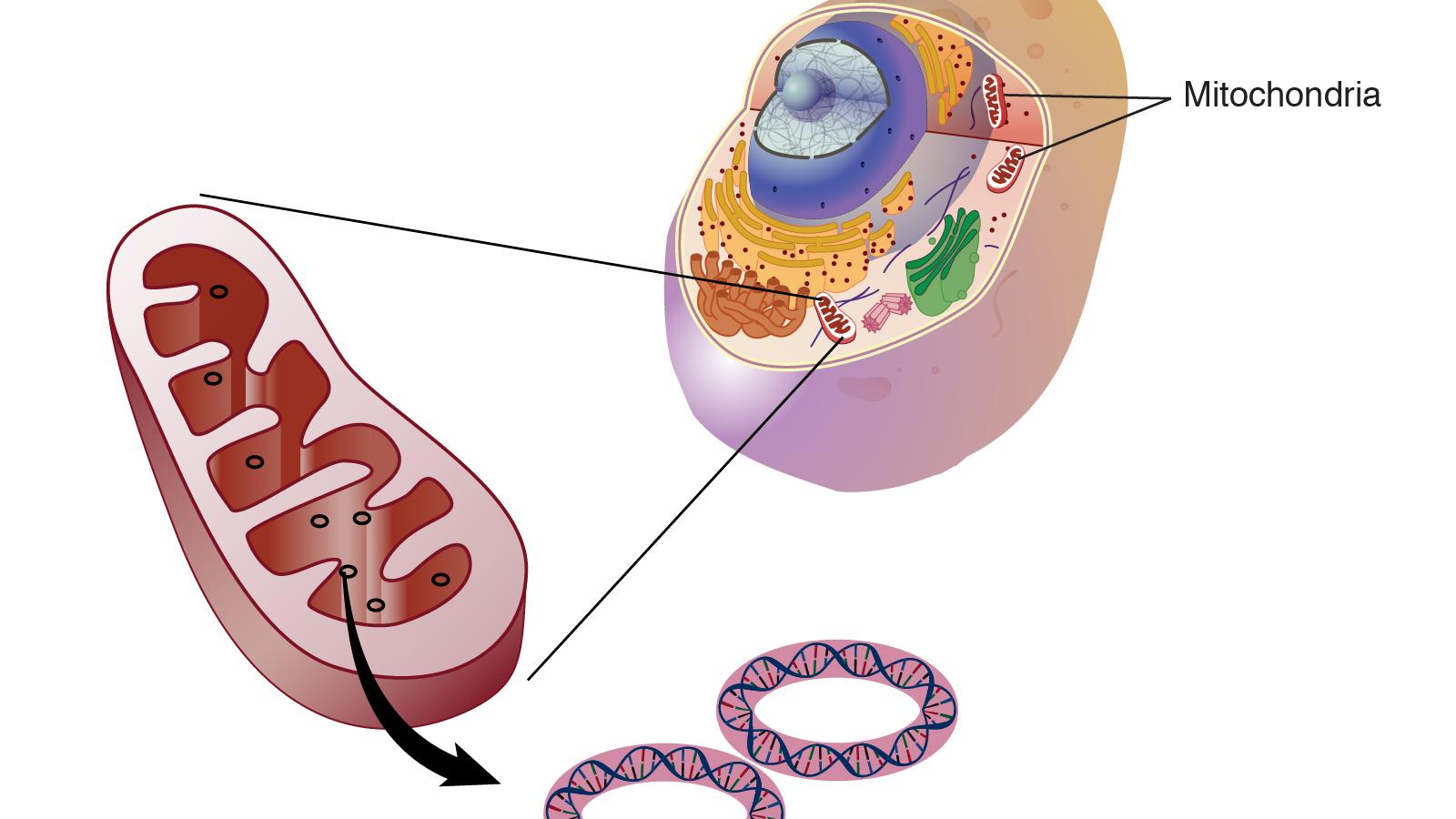
Mitochondrial constituents and metabolic products may give rise to immune activation; this is especially true for mitochondrial DNA, which can function as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) leading to inflammasome activation.
DAMPs and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are primary drivers of inflammasome activity.
Still’s disease is a rare inflammatory disorder, affecting less than 1 person per 2000 people. This disease may occur in both children and adults, namely as systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) and adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD).
The paediatric form was described by George Still in 1896, whereas the adult variant later by Eric Bywaters in 1971. However only the adult disease is identified by the name of Still.
Are you treating “systemic” or “articular” (arthritis) Still’s disease? Most Still’s patients have a dominance of one or the other. With certainty, the right therapy for the right symptoms can be chosen. What about patients who have an incomplete or no response, or who become unresponsive to a drug that once worked well?
































 Poster Hall
Poster Hall