Mitochondria as Master Regulators of Inflammation Save
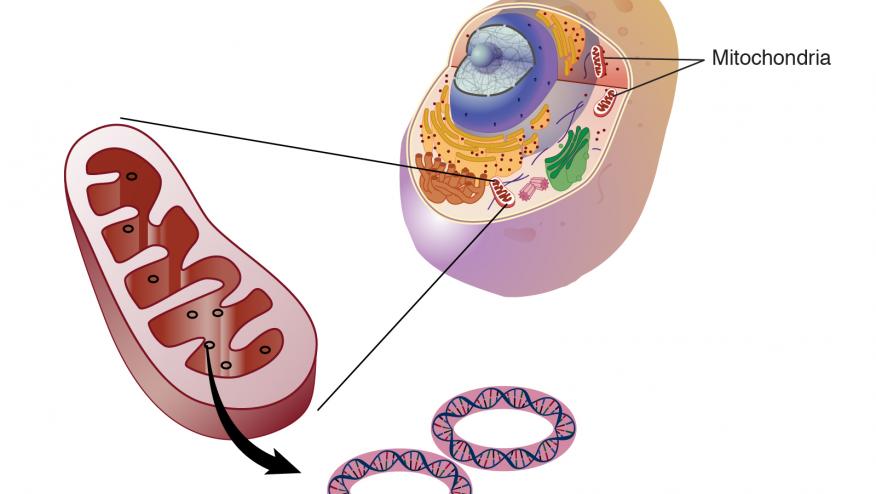
Mitochondrial constituents and metabolic products may give rise to immune activation; this is especially true for mitochondrial DNA, which can function as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) leading to inflammasome activation.
DAMPs and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are primary drivers of inflammasome activity.
When mitochondrial DNA and constituents are released into the cytosol or extracellular milieu their effect is typically minimized by autophagy of permeabilized mitochondria. But if these are defective or ineffective, mitochondrial products can lead to inflammation and autoimmunity.
Mitochondrial DNA has been implicated in the pathogenesis of SLE, as mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) are taken up by neutrophils, leading to netosis, activation of STING and the generation of type-I interferon (IFN). More specifically, cytosolic mitochondrial DNA is a potent activator of cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS), resulting in stimulator of interferon response cGAMP interactor 1 (STING1) signalling and consequent synthesis of cytokines such as interferon-β1 (IFNβ1), IL-6 and tumour necrosis factor (TNF).
Autoinflammation is also be provoded by oxidized mtDNA that provokes cGAS-STING, and binding to cytosolic NLRP3, triggering caspase and inflammasome activity.
Numerous examples of mtDAMP mediated signalling of cGAS-STING and the inflammasomes are discussed by Marchi et al in Nature Reviews Immunology.
Mitochondrial DAMPs and mt-DNA signaling have been implicated in advancing infectious and neoplastic disorders and other disorders, including Crohn's disease, SLE, interstitial lung disease, autoinflammatory disease and neurodegenerative disorders, to name but a few.
Future efforts are underway to develop mitochondria-targeted drugs to control inflammation.









If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.