All News

Tell me what do you focus more on in virtual learning? I will try to vary my backgrounds as a virtual home yours! @RheumNow @CRASCRRheum #ACR20
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)
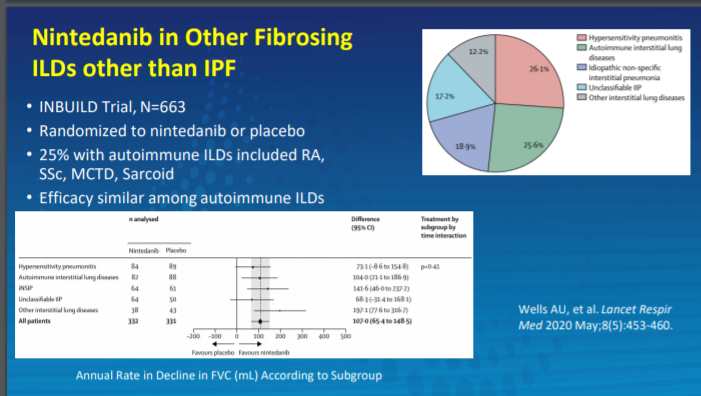
Nintedanib for RA-ILD? In the INBUILD Trial, pts on Nintedanib did better than PBO, efficacy similar among autoimmune ILDs including RA. @RheumNow #ACR20 @joanbathon https://t.co/I4AJlemIhD
sheila RHEUMarampa ( View Tweet)

Dr Hansen at 3S008 on "Bone for the Holidays": individualize the decision for drug holidays - here are the key questions: #acr20 @Rheumnow https://t.co/lMHtYW4OzE
Eric Dein ejdein1 ( View Tweet)

Which Axial SpA outcome score do you use in clinic as a target to achieve? @RheumNow #ACR20
Dr. Antoni Chan synovialjoints ( View Tweet)
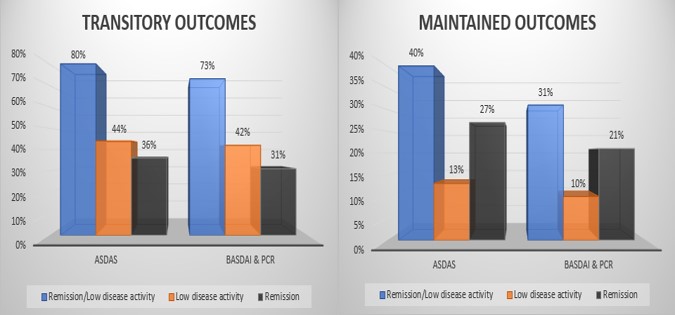
In SpA-paz cohort 80% of axSpA pts achieved R or LDA at one visit, but only 40% maintained this level of disease control. #ABS0893 #ACR20 @RheumNow https://t.co/3MKBKOoNSw https://t.co/pTMJhtfKbU
Dr. Rachel Tate uptoTate ( View Tweet)

OBRI Canadian registry showed real world retention data for Tofa and TNFi are both similar, but RA pts on TNFi w/o MTX d/c drug more compared to those who stay on MTX (does not matter with Tofa if they are on MTX)
Abstr#808 #ACR20 @rheumnow
https://t.co/TDmV0EJTp8
k dao KDAO2011 ( View Tweet)
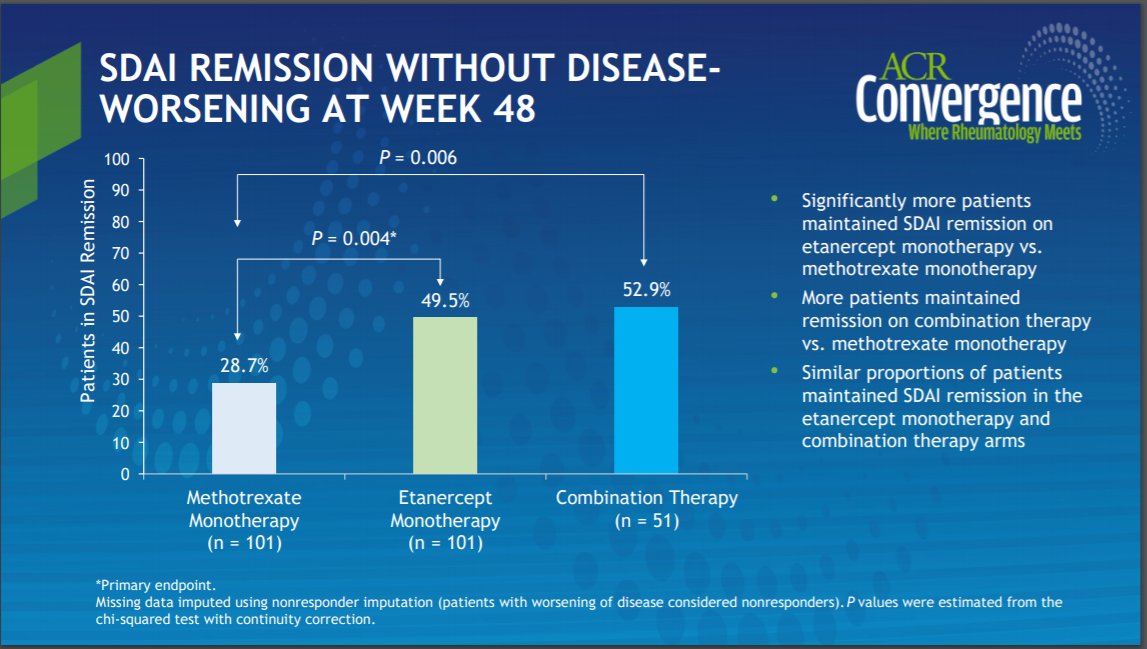
SEAM-RA: SDAI remission greater in pts on ETN alone vs. MTX alone; ⬆ pts in remission w/ combined tx vs. MTX alone. These may guide tx decisions re withdrawal in well-controlled RA @Rheumnow #ACR20 https://t.co/33GhuMuL3I
sheila RHEUMarampa ( View Tweet)
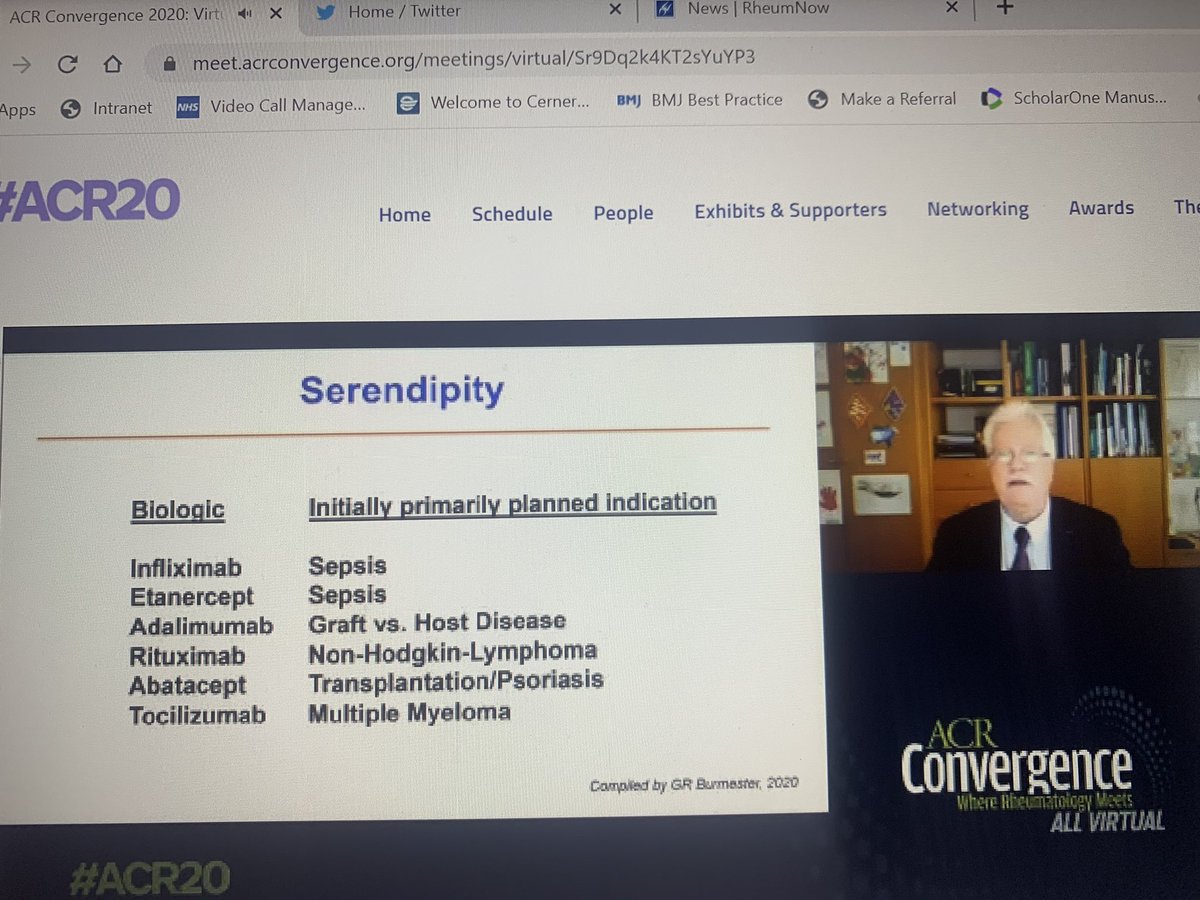
Wonderful Philip Hench Memorial Lecture from Prof Gerd Bursmester on the development of biologics in rheumatology from infections, the magic bullet, serendipity, perseverance, research to the present day @RheumNow #ACR20 #3S007 https://t.co/9H1AmZLTpJ
Dr. Antoni Chan synovialjoints ( View Tweet)
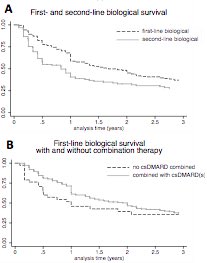
ACPA+ RA should likely NOT taper bDMARDs as less Bio survival if ACPA+ &/or monoRx. Should EULAR guidelines be changed? What about retention with JAKis? #ACR20 @RheumNow @CRASCRRheum abstr804 https://t.co/vjzIIgVJ0s
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)

For patients with #rheumatic disease, what test do you request in the work-up for Latent TB infection? @RheumNow #ACR20
sheila RHEUMarampa ( View Tweet)

Dr. Aggarwal Abs#0955 showed efficacy of IVIG in tx of Dermatomyositis.
How/when do you use IVIG for tx of DM?
@RheumNow #ACR20
Robert B Chao, MD doctorRBC ( View Tweet)

Great talk by @lovetolearn27 Prosthetic joint infection doubles the risk of venous thromboembolism after revision of knee replacement. 15 yr data New York state -25K revisions! @RheumNow #ACR20 ABS#0960 https://t.co/4PHHSEstKs
Bella Mehta bella_mehta ( View Tweet)
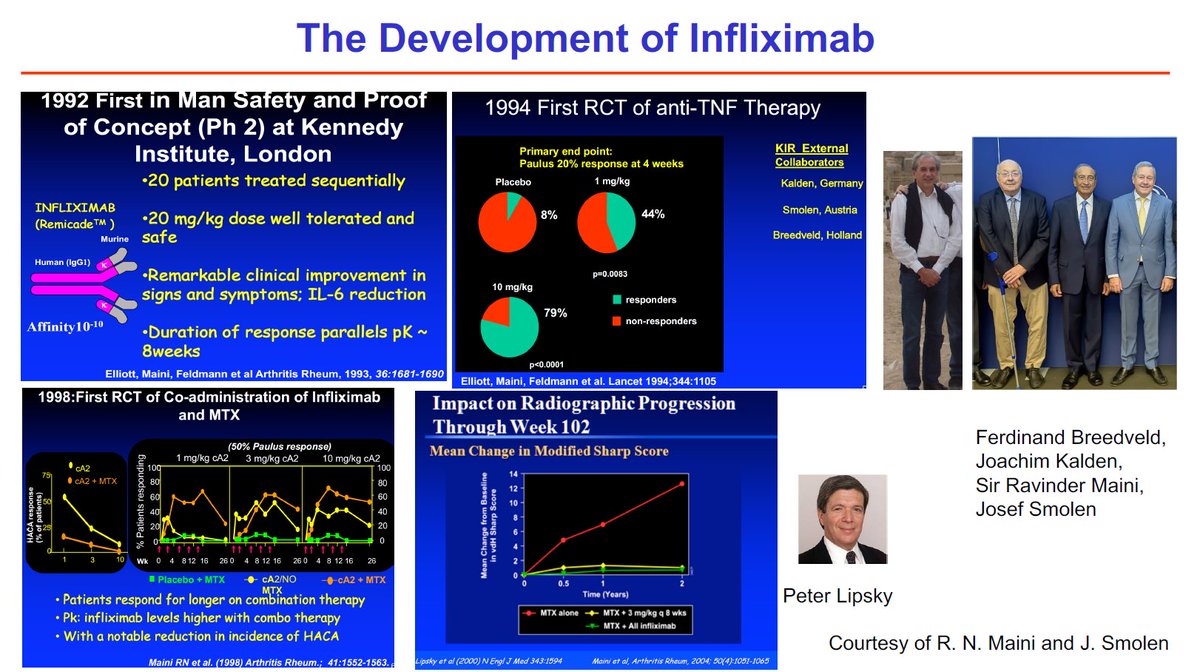
Never forget how far we have come in rheumatology therapeutics, in a very short period of time.
Some of the original slides that Tiny Maini and Marc Feldmann used. @r_burmester giving the Phillip Hench Lecture #ACR20 @RheumNow https://t.co/YI32BX2iw8
David Liew drdavidliew ( View Tweet)

How often, if ever, do you use DECT to diagnose gout?
Olga Petryna DrPetryna ( View Tweet)
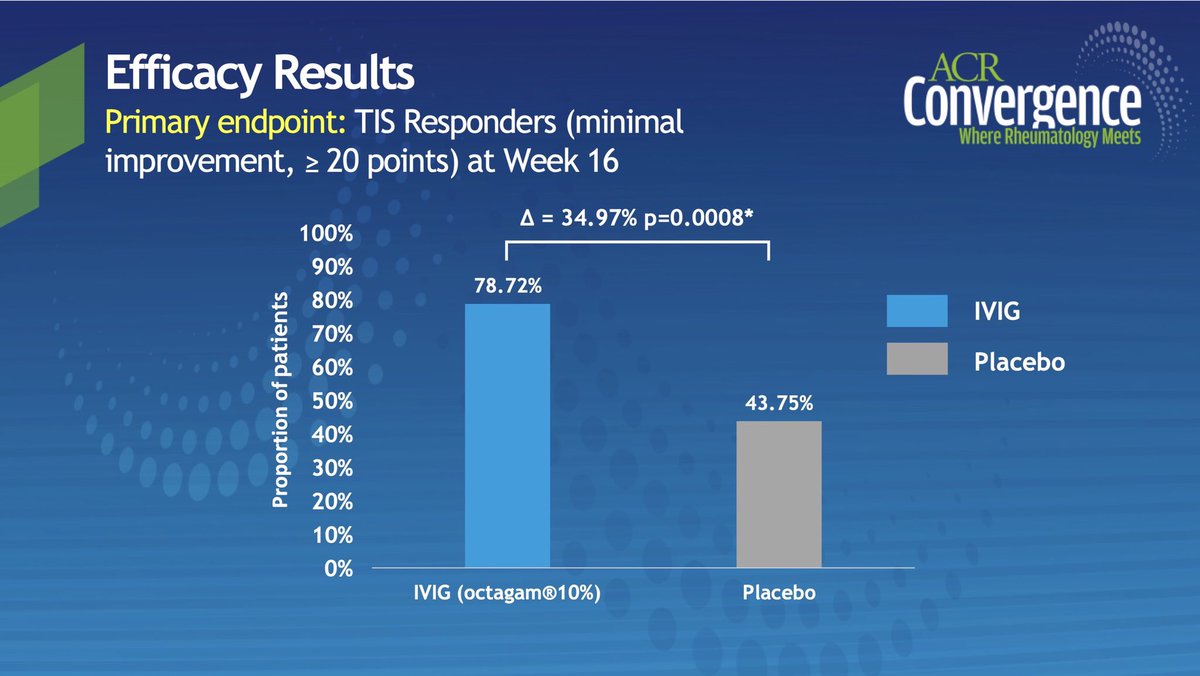
Efficacy of IVIG in Dermatomyositis Treatment
1st Placebo controlled RCT
1️⃣79% responder by total improvement score vs. 44%
2️⃣Efficacy sustained thru wk 40
3️⃣6% serious AE - thromboembolic event
@RheumNow #ACR20 Abs#0955 #ACRbest https://t.co/715h1UkZ9X
Robert B Chao, MD doctorRBC ( View Tweet)
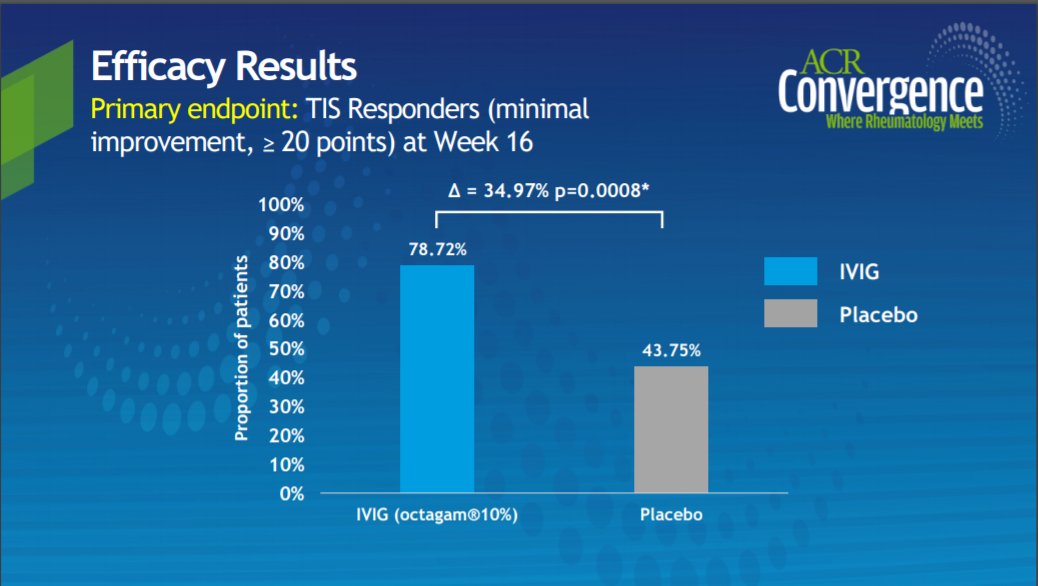
ProDERM study:10% IVIG is effective and safe in pts with DM. First large PBO-controlled, randomized ph 3 trial. @RheumNow #ACR20 abs0995 #ACRbest https://t.co/aJyASaAMlJ
sheila RHEUMarampa ( View Tweet)
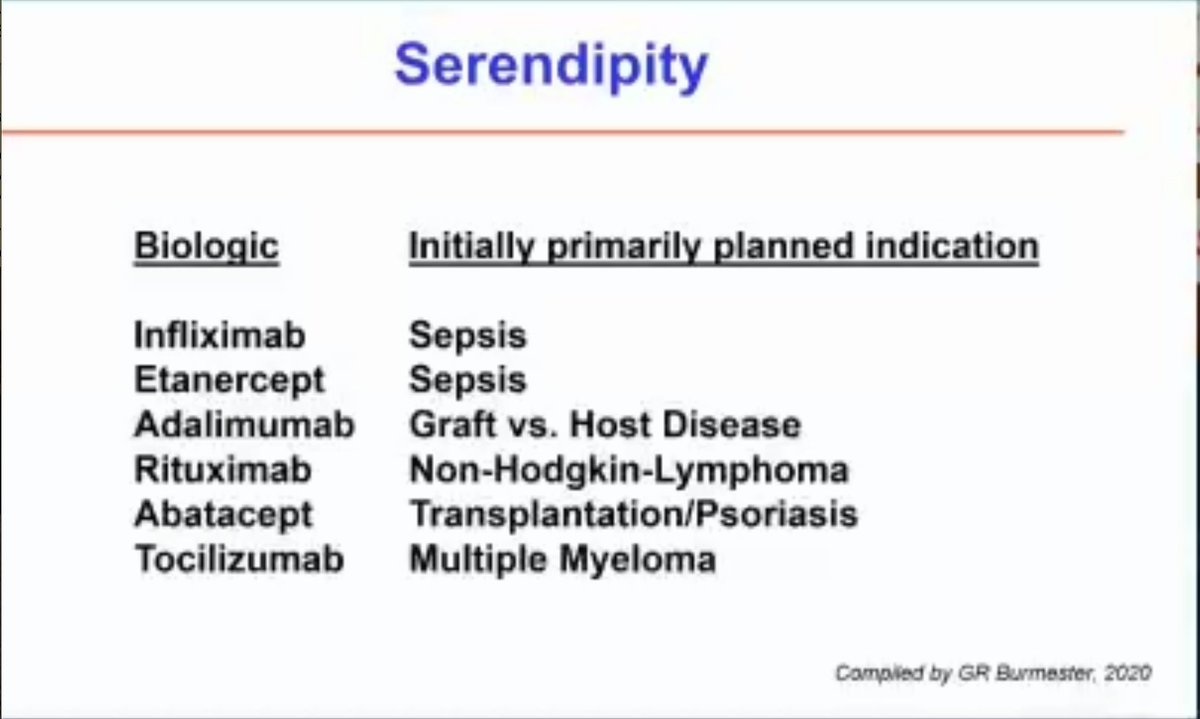
Dr. Burmester on serendipity in the development of rheumatologic meds. As we study #COVID19, we need to keep our minds open that we don't always find what we want, but we can always learn something to bring us ahead. #ACR20 @Rheumnow. https://t.co/s5WZEjrbnk
Eric Dein ejdein1 ( View Tweet)

Australian study looking at clinical outcomes following in-class switching vs switching MOA. Rapid effect of IL-17i and JAKi with PsA rated highly. This study highlights ever-growing need for precision medicine based on domain. #ABS09003 #ACR20 @RheumNow https://t.co/7qKH6aw6f0
Dr. Rachel Tate uptoTate ( View Tweet)

#HCQ assoc. w/ ↓platelet activity & ↑vascular health in #SLE:
- 132 patients, 108 on HCQ
- Ex-vivo expts show ↓platelet aggregation & downregulation of platelet functional pathways
- HCQ may improve vascular health in SLE
Abs#0870 #ACR20 @RheumNow
https://t.co/ST9n2HGyhM
Mrinalini Dey DrMiniDey ( View Tweet)
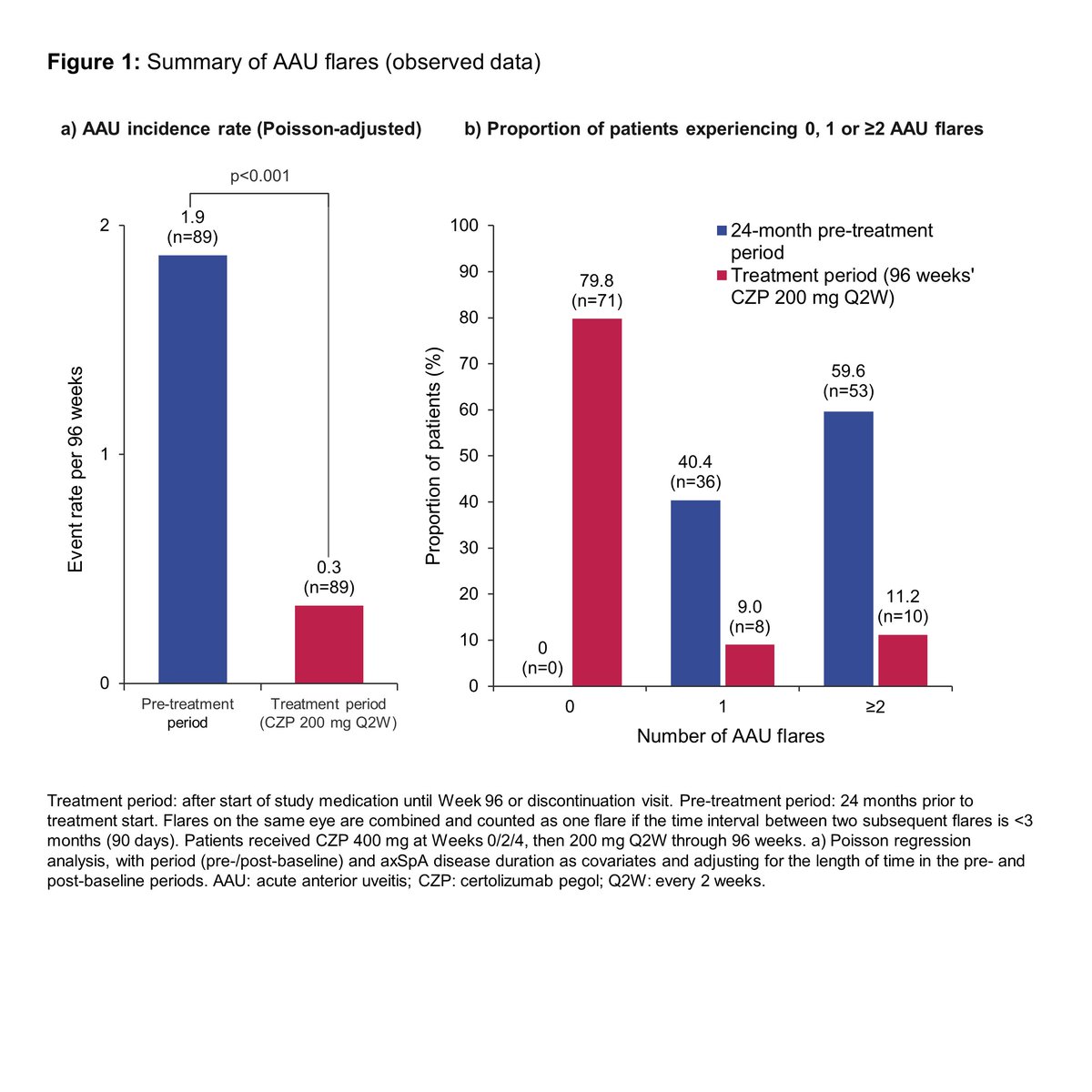
CZP tx in axSpA pts showed significant reduction of 82% in the AAU flare rate and MSK symptoms over 96 week C-VIEW trial. #ABS0881 #ACR20 @RheumNow https://t.co/bNFHXbKEuF https://t.co/3Z232vKGPC
Dr. Rachel Tate uptoTate ( View Tweet)



