All News

#myositis & the ❤: lab tests
⬆ Trop = myocardial stress & injury, absence doesn't r/o myocarditis
BNP - utility unclear
There are no biomarkers specific for myocardial involvement
@RheumNow #ACR20 https://t.co/eyihKPoXSc
sheila RHEUMarampa ( View Tweet)

Does your pt have myocardial inflamm? Trop specific but not sensitive, BNP neither sens or specific. Consider EKG - sensitive (85%), but non-specific- But TTE is essential and cMRI is best! #ACR20 @RheumNow Great lecture from cardiologist, @HopkinsBayview APD https://t.co/6THm37KbQ3
Eric Dein ejdein1 ( View Tweet)
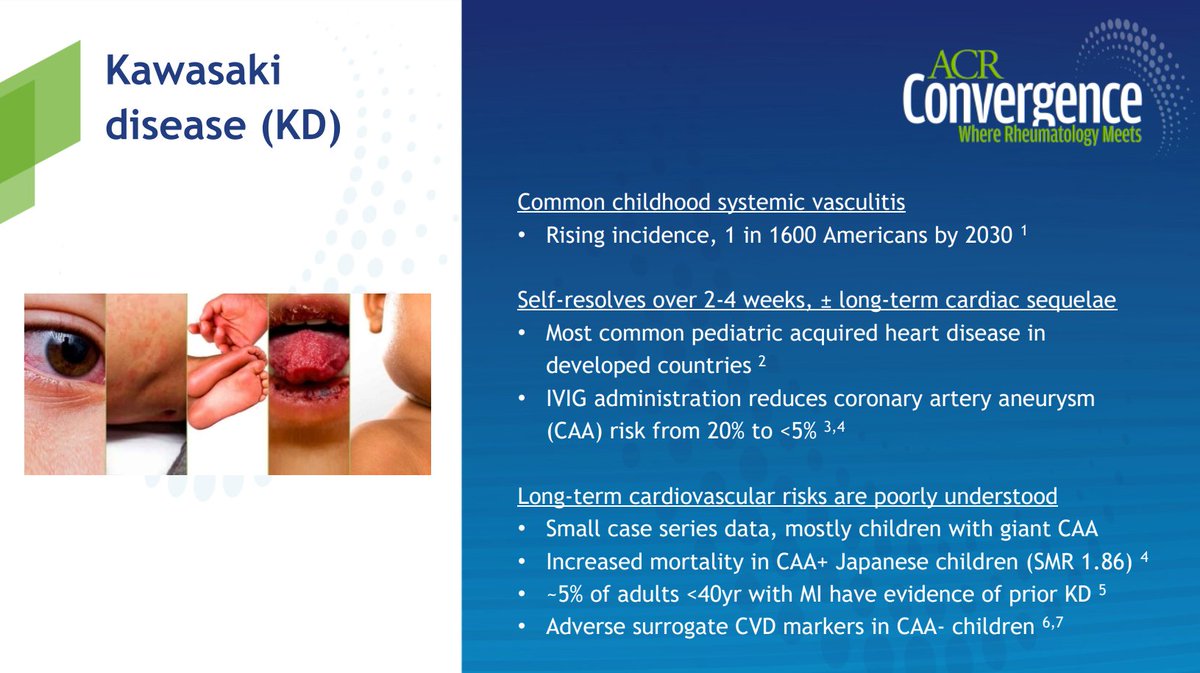
What happens long-term in Kawasaki disease now? Has IVIG availability fixed this?
Pop-based cohort, long follow-up.
Turns out cardiac event risk, whilst greatest early, continues >10y after - even in those w/o coronary aneurysms
@SickKidsNews @McMasterU #ACR20 ABST0937 @RheumNow https://t.co/1T6JmwhXNb
David Liew drdavidliew ( View Tweet)

Listen to part I of our #ACR20 Day 1 recap. Listen through the link below or find us on Apple podcasts.
https://t.co/W6EMQiF9Rf https://t.co/R1ieCFnIxz
Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)
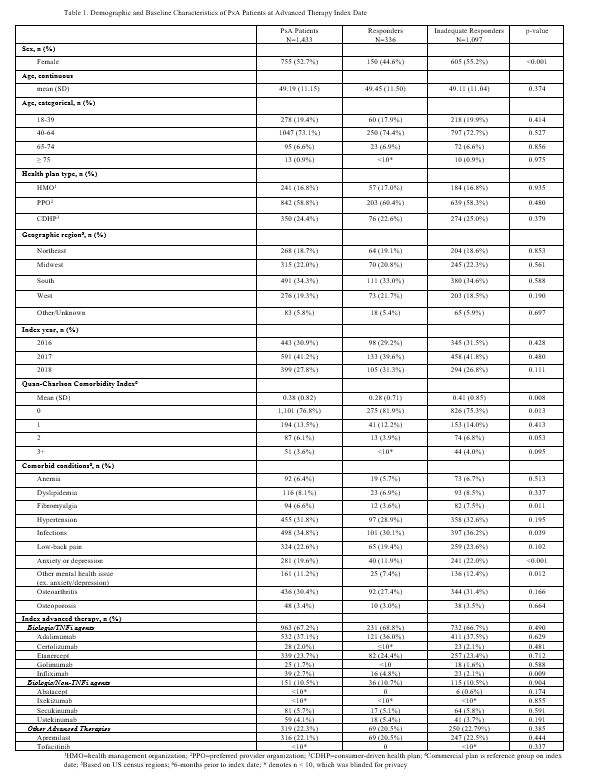
Health plan claims data appears useful to classify inadequate responders in PsA and should be studied further. #ABS0898 #ACR20 @RheumNow https://t.co/jXBr54Fc6Z https://t.co/fAESyo5Uad
Dr. Rachel Tate uptoTate ( View Tweet)
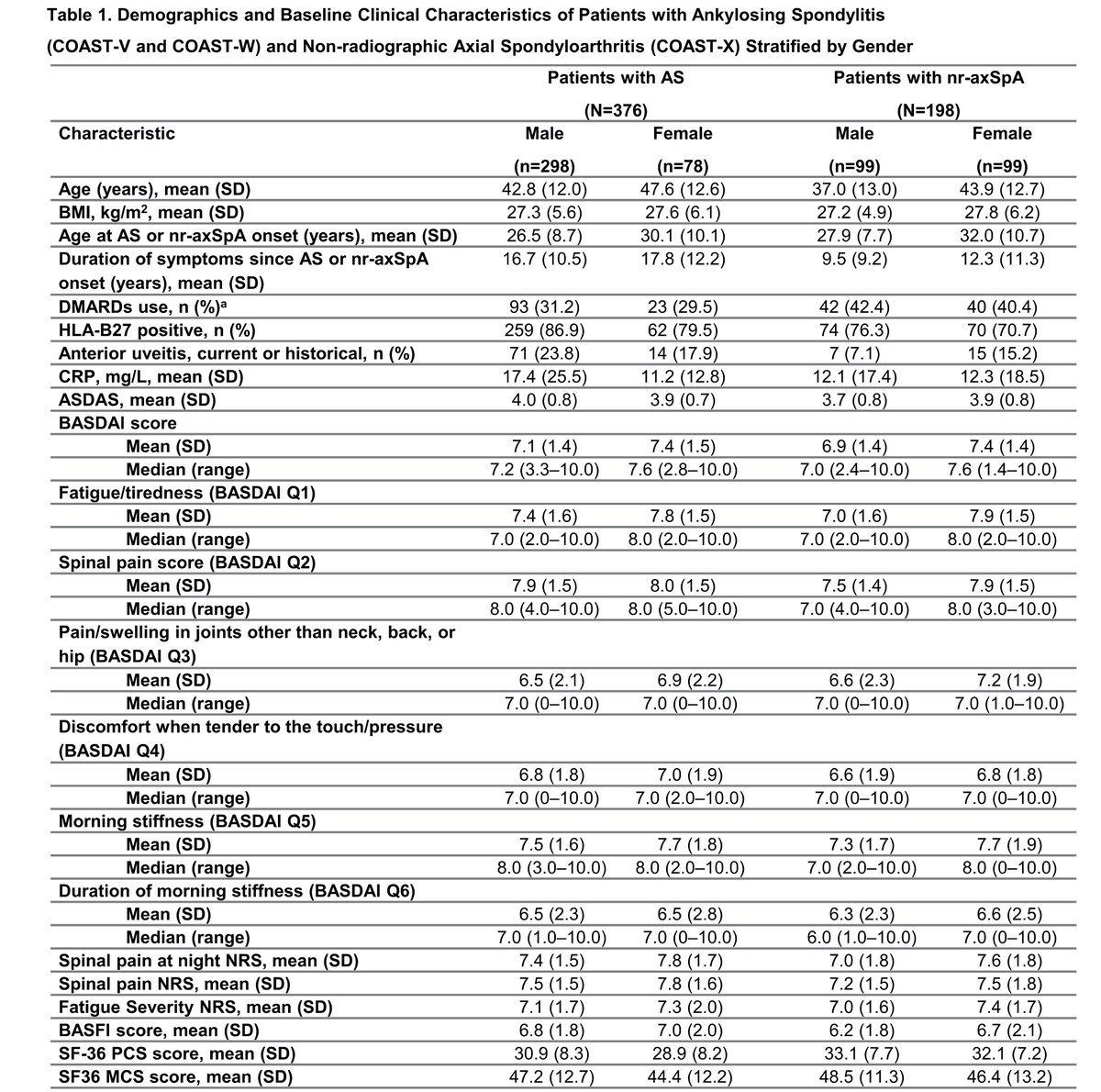
Gender differences in Axial Spondyloarthritis patients Pooled data from 3 Ixekizumab studies Women: 1⃣older at disease onset (30 vs. 26) 2⃣Longer symptom duration (17.8 yrs vs. 16.7 yrs) 3⃣More peripheral joint pain and lower HLA-B27 @RheumNow #ACR20 Abs#0876 https://t.co/qGHXApi0Ko
Robert B Chao, MD doctorRBC ( View Tweet)

@andreafava representing @jhrheumatology @HopkinsBayview at plenary session! Urine proteomic biomarkers can revolutionize the way we see LN, and decrease need for renal Bx #Acr20 @RheumNow Abst#0936 https://t.co/zGoqmBPddT
Eric Dein ejdein1 ( View Tweet)

Can we use urine testing ( and all the cells, proteins, complements, DNA, rna) to predict LN response? Plenary II @SalemAlmaani @BradRovin @RheumNow #ACR20 @OSUWexMed
alexa meara lexmeara ( View Tweet)

Great talk #ACR20 Integrating bulk and single-cell RNA-sequencing @Kahlenberglab identifies clinically actionable 5-gene signatures that can effectively differentiate DM from cutaneous lupus lesions. @RheumNow @UMIntMed Also out in @JCI_insight https://t.co/uYS6OJH0Hf https://t.co/KR0wwDb5BK
Yu (Ray) Zuo RayZuoMD ( View Tweet)

Dr. J. Berquist @BolekBerqui shares her advice on an ideal online support network for patients (and, IMO, rheumatologists, too!) @RheumNow #ACR20 https://t.co/AFUiH7ihds
Dr. Rachel Tate uptoTate ( View Tweet)
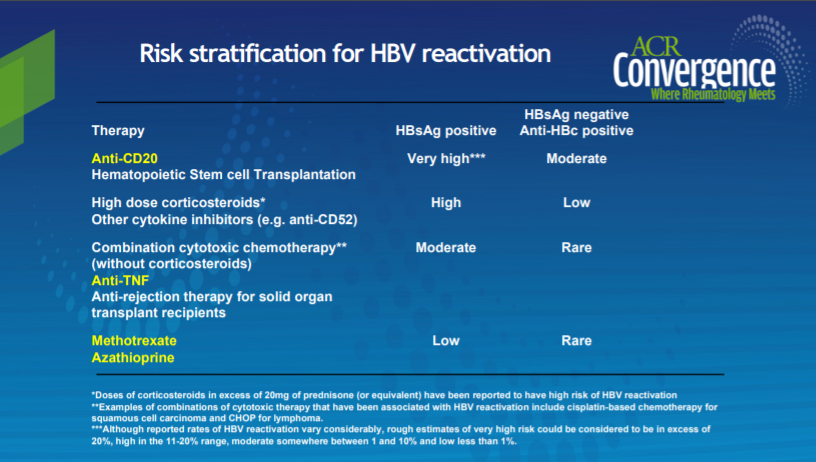
Important things to take note of re: HBV reactivation (risk stratification and RR) when we consider therapies for our RA pts. 👇 @RheumNow #ACR20 #MedTwitter https://t.co/ZJfnZHpmfw
sheila RHEUMarampa ( View Tweet)
Another biosimilar Adalimumab. SB5 switch in RA, PsA & SpA N=354 No diff in effectiveness Some minor flares. Some changed dose unsure why. #ACR2020 @RheumNow @CRASCRRheum abstr#805 https://t.co/2Zb4H2jBXQ
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)

Liver damage is NOT an extra-articular manifestation of RA BUT the ff'g factors are associated with liver disease in RA & can complicate management👇@RheumNow #ACR20 https://t.co/RqL69iVJpC
sheila RHEUMarampa ( View Tweet)
It's only now we have choices to warfarin that we can realise the effect of vit K blockade on OA.
Nested case-control (AF pts, UK primary care):
warfarin has risk vs DOAC for end-stage OA (via joint replacement) aOR 1.25
esp knee aOR 1.48
@Tuhina_Neogi #ACR20 ABST0934 @RheumNow https://t.co/XVLG8kIL0W
David Liew drdavidliew ( View Tweet)
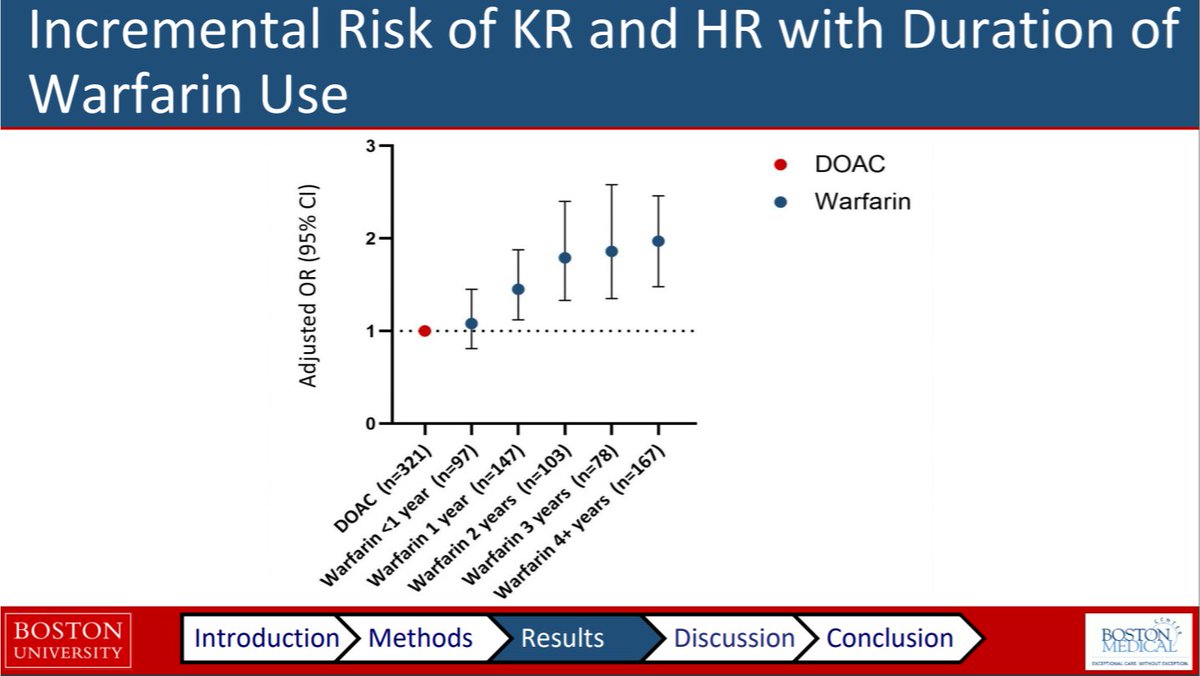
Plenary session: Dr Ballal presents data showing #warfarin use incr. risk of knee/hip replacements, compared to #DOACs
- Nest case-control study in UK THIN database
- Risk increases w/ duration of use
- Indicates need for well-powered RCT of vit K in OA
Abs#0934 #ACR20 @RheumNow https://t.co/YyxDjNQEjx
Mrinalini Dey DrMiniDey ( View Tweet)
Amazing to see a plenary by a 1st year fellow @BU_BMC_Rheum - Vit K is important in preventing #OA progression - obs study #Warfarin has higher knee and hip replacement risk compared to #DOACs #ACR20 @RheumNow ABS#0934 https://t.co/0IUS8QvzI4
Bella Mehta bella_mehta ( View Tweet)
Neihulizumab, novel immune checkpoint agonistic ab that binds to human CD162 (PSGL-1), thereby preferentially inducing apoptosis in late stage activated T cells. Phase II trial shows efficacy in PsA, further trials to come. #ABS0894 #ACR20 @RheumNow https://t.co/gzf7epPyNd https://t.co/ArLlCyzLxR
Dr. Rachel Tate uptoTate ( View Tweet)
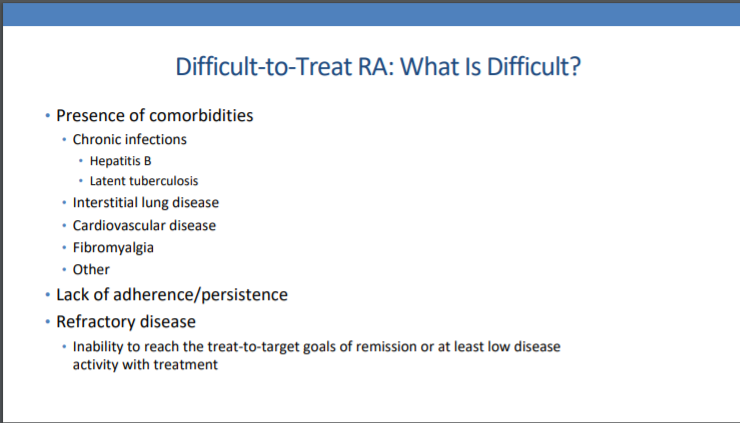
What is refractory RA? Inability to reach #T2T goals of remission or at least LDA despite various changes of tx. "We should aim at best care for the tx of refractory RA"-Prof.Josef Smolen @RheumNow #ACR20 https://t.co/7Wxjd5t3Oi
sheila RHEUMarampa ( View Tweet)
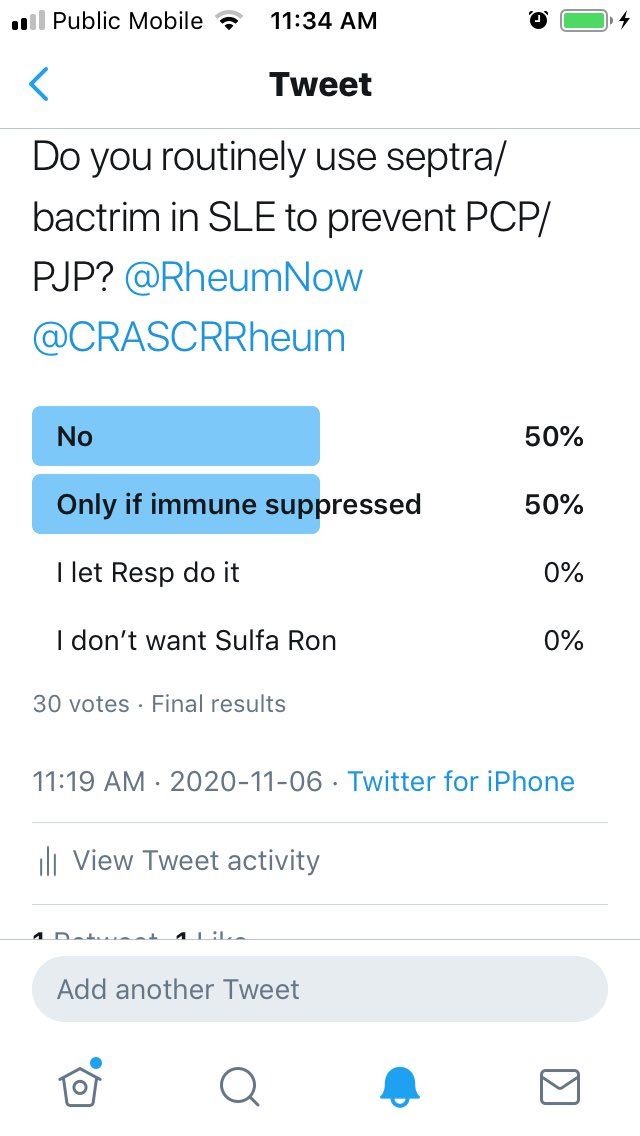
50% use septra/bactrim in SLE if immunesuppressed. I don’t use it unless if frequent serious infections or bad lungs as I am not convinced about the risk of PCP/PJP v risk of septra with adverse rxns in SLE. I await an admin database to give me the data @RheumNow #ACR20 https://t.co/3s2S9fIUVe
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)
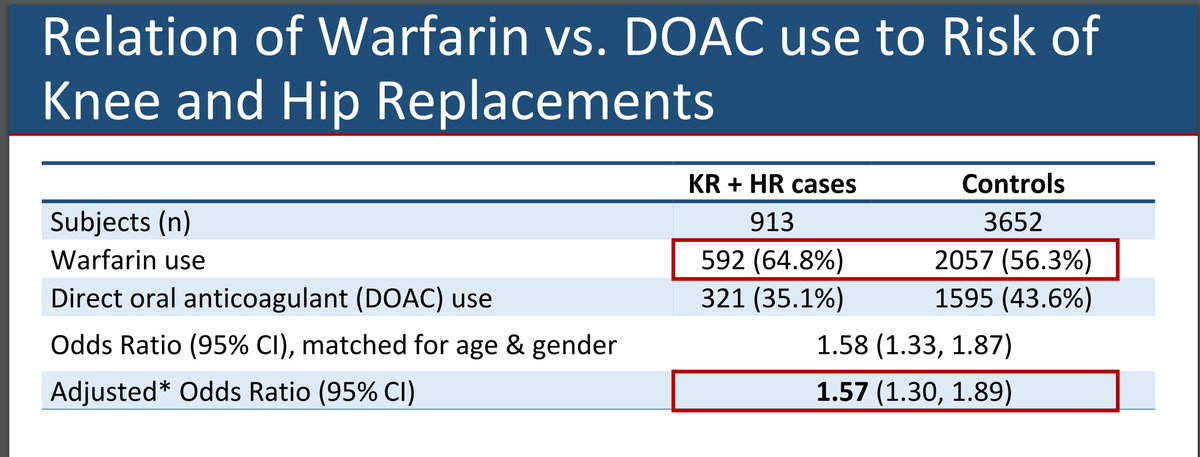
Abst#0934 by Dr. Ballal at BU looks at the role of vitamin K deficiency in OA development. Warfarin use with 57% increased risk of TKA/THA compared to NOAC, though diminished when accounting for signif practice variation in these patients @Rheumnow #ACR20 https://t.co/PsESoeurKF
Eric Dein ejdein1 ( View Tweet)



