All News
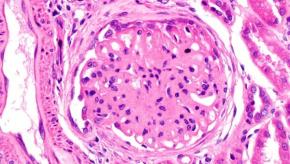
Tacrolimus Measures Up in Lupus Nephritis Trial
In a phase III trial, oral tacrolimus (Prograf) proved non-inferior to intravenous cyclophosphamide for treating lupus nephritis, researchers said.
Read ArticleFDA Authorizes 2nd Booster for Older and Immunocompromised Individuals
Today, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorized a second booster dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccines for older people and certain immunocompromised individuals.
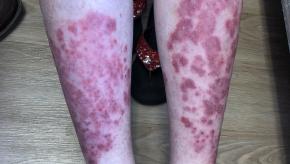
Read ArticleDifferences in Biologic Persistence in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis
Administrative claims analysis of biologic use in psoriasis (PsO) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in French health insurance databases shows that despite widespread biologic use, overall drug persistence (beyond 3 years) was low for PsO and PsA biologics.
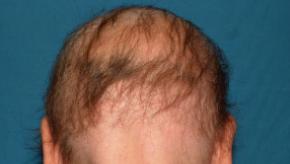
Read ArticleBaricitinib Efficacy in Alopecia Areata
The NEJM has published the results of the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials, demonstrating that baricitinib is effective at regrowing hair in alopecia areata (AA) patients, thus paving the way for future regulatory approval for this difficult to treat disorder.
Read ArticleComorbidity Drives Risk of Death in Gout Patients
A study of men with gout from the US Veteran’s Health Administration (VHA) shows that excess mortality in gout could be attributed to comorbidities.
Read ArticlePoor Outcomes in Lupus Patients Not at Target
A prospective, longitudinal systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) cohort study examined outcomes and showed that failure to control SLE was common and associated with poorer outcomes including organ damage, glucocorticoid exposure, poor quality of life, and increased mortality.
Read ArticleAdalimumab Addition vs. Methotrexate Escalation in Psoriatic Arthritis
An interesting study in Lancet Rheumatology shows that psoriatic arthritis patients not responding to methotrexate alone can respond after adding or escalating adalimumab (ADA) on top of methotrexate (MTX) to reach minimal disease activity (MDA) response.
Read ArticleConsequences of TNF inhibition (3.18.2022)
This week we're going to talk about the downside of TNF inhibitors, a few interesting observations in gout, and yes, kids do get COVID. We're also going to preview what's coming in April (hint: it's about PsA). This and more as Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow.com.
Read ArticleIberdomide in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
The NEJM reports that systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients treated with iberdomide, a cereblon modulator, was effective at yielding a significant SRI-4 clinical response after 24 weeks.
Read ArticleIndividualized Therapy in Ankylosing Spondylitis
Whether patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) would improve substantially with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy was predicted with moderate to high accuracy based only on a standard lab test and two measures of disease activity, researchers reported from a modeling study.
Read ArticleLow Dose IL-2 Efficacy in Rheumatoid Arthritis
A novel biologic intervention trial has shown that subcutaneous, intermittent therapy with low-dose interleukin-2 (Ld-IL2) is potentially effective and safe in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Read ArticleEfficacy and Safety of Mavrilimumab in Giant Cell Arteritis
A phase II trial in patients with active giant cell arteritis shows that mavrilimumab, a monoclonal antibody against granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor [GM-CSF]) is capable of inducing clinical remission.
Read ArticlePredicting Spondylitis in At-Risk Relatives
The risk of developing axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) if you’re a first-degree relative (FDRs) of an ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patient has been deflined by a 35 year follow-up study showing that if you are a FDR of axSpA you may be at higher risk of acute anterior uveitis (AAU).
Read ArticleRheumNow Live is Coming to Town (3.11.2022)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow.com.
Read ArticlePsoriatic Arthritis Responds to Tyk2 inhibition with Deucravacitinib
Deucravacitinib, a selective tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor, was studied in a phase II trial of active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients and shown to be effective and safe.
Read ArticleCould Anifrolumab Work in Lupus Nephritis?
Anifrolumab is effective and FDA approved for use in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE); and now, a trial in lupus nephritis that almost shows benefit.
Read ArticleKawasaki Disease Guideline from ACR and Vasculitis Foundation
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR), in partnership with the Vasculitis Foundation (VF), released a new guideline for the management of Kawasaki disease that addresses diagnostic issues relating to Kawasaki disease, the treatment of high-risk patients, and the management of
Read ArticleBaricitinib’s COVID-19 Efficacy in the RECOVERY Trial
Pre-print results of the RECOVERY Trial has shown that when baricitinib (BAR) is given to hospitalized severe COVID-19 patients, it results in significantly less mortality.
Read ArticleFailed Osteoarthritis Pulse Ultrasound Study
A promising therapy aimed at halting and even reversing the pathology underlying osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee failed to show any benefit in a randomized trial.
Read ArticleTocilizumab Works Best in Non-Mechanical Ventilated COVID-19 Patients
JAMA has published a meta-analysis of 15 studies of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 treated with tocilizumab and corticosteroids, showing that a clinically meaningful mortality benefit from tocilizumab (and steroids) was best seen in those not requiring invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV).
Read Article