All News
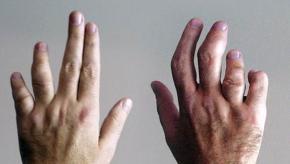
Not All RA Drug Classes Are Created Equal
Clear differences were apparent among the three major types of targeted medications for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a large European registry study.
Read ArticleFlares Not Increased Following Recombinant Zoster Vaccine Injections
Insurance claims analysis has shown that the use of the (CDC recommended) recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) for prevention of herpes zoster was highly used in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases and was safe, as higher rates of arthritis flares were not evident.
Read ArticleSpondyloarthritis and COVID-19
There are still questions surrounding COVID-19, and some common questions I receive from patients revolve around what to do with their current DMARDs or should they even start treatment during this pandemic. Two studies focused on this question.
Read ArticleImproved Pregnancy Outcomes in SLE (2010–2020)
A retrospective cohort study has shown that outcomes in pregnant systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients has significantly improved in the last decade, but there still is a high risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes (APO).
Read ArticleWhat do our lupus patients think about treat-to-target?
In SLE, two targets that are increasingly used are the DORIS 2021 Remission and the Lupus Low Disease Activity (LLDAS). T2T is more likely to be successful if the treating clinicians and the patients set the treatment goals together. What do our patients think about T2T and do they have any say/concern?
Read ArticleCan we stop RA before it happens?
Rheumatologists have long hoped and wondered whether the right type of early intervention could prevent rheumatoid arthritis occurring in at-risk individuals.
Read ArticleGout Undertreatment Persists
Despite updated gout management guidelines from European (EULAR) and British (BSR) societies, treatment of gout is suboptimal with regard to the use of urate-lowering therapy (ULT) and normalizing serum uric acid (< 6.0 mg/dl) levels.
Read ArticleIs Pain Control by Cannabis an Option?
An Annals of Internal Medicine review has shown that clinical trials and cohort studies of cannabinoids use for chronic pain may be associated with short-term improvements in chronic pain but come with an increased risk for dizziness and sedation.
Read ArticleTime to consider gender stratification in AxSpA diagnosis and management
Differences across genders in many aspects related to rheumatic diseases diagnosis, phenotyping, trajectories definition and prediction of response to treatment have been overlooked.
Read ArticleBSR Guideline for Psoriatic Arthritis - 2022 Update
The British Society of Rheumatology has published their updated 2022 recommendations for the use of biologics and targeted synthetic treatments in patients with psoriatic arthritis. These guidelines follow initial treatment with a single conventional systemic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug, typically methotrexate typically. They noted that up to 50% of people with PsA require biologic or targeted synthetic (b/ts)DMARD therapy.
Read ArticleUpdate on Axial SpA at EULAR 2022
This year at EULAR 2022, there were important and interesting topics in Axial Spondyloarthritis (AxSpA). These are my picks of abstracts from the conference.
Read ArticleTopical therapies take centre stage
Topical treatments have so often been the low level “sure you can try this” option. However there are exciting data that these approaches may become part of our main armamentarium.
Read ArticleEULAR 2022 – Day 3 Report
By now, those of us attending the meeting know how to find a free coffee or sprite, have found comfortable meeting nooks and know our way around! PAnd congrats to you virtual Rheums for mastering the multi-screen, multitask simultaneous consumption posters, tweets and oral abstract presentations.
Read ArticleEULAR 2022 – Day 2 Report
A full day at EULAR with oral and poster presentations of abstracts in the morning and a plethora of scientific (review) sessions in the afternoon. The latter covering topics like sarcoidosis, Still’s disease, fibromyalgia, back pain, sarcopenia, APS, IgG4 and imaging in vasculitis.
Read ArticleA Big Leap in Modulating Rheumatoid Disease
Intervention in individuals predisposed to develop rheumatoid arthritis (RA), with a holy grail of prevention of RA, has long been a hot topic. It is well known that seropositivity for rheumatoid factor and antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides (ACPA) can precede RA disease by many years. Many, but by no means all, patients also seem to go through a pre-RA arthalgia phase of varying duration characterised by the presence of increasing joint pain without frank arthritis.
Read ArticleUpdates in Psoriatic Arthritis at EULAR 2022
At EULAR 2022, I look forward to key topics and presentations in psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Here's a preview of nine studies I'm particularly interested in at this meeting.
Read Article
Links:

Robert B Chao, MD doctorRBC ( View Tweet)

Eric Dein ericdeinmd ( View Tweet)