Bimekizumab demonstrates comparable one-year efficacy in male and female patients with axial spondyloarthritis: Results from two phase 3 studies
Video Poster Save
Martin Rudwaleit,1 Sofia Ramiro,2,3 Denis Poddubnyy,4,5 Marina Magrey,6 Irene E. van der Horst-Bruinsma,7 Atul Deodhar,8 Vanessa Taieb,9 Diana Voiniciuc,10 Natasha de Peyrecave,11 Lianne S. Gensler12
1Bielefeld University, Medical School and University Medical Center OWL, Klinikum Bielefeld, Department of Rheumatology, Bielefeld, Germany; 2Department of Rheumatology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands;
3Zuyderland Medical Center, Heerlen, The Netherlands;
4Division of Rheumatology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada;
5Department of Gastroenterology, Infectious Diseases and Rheumatology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany;
6Case Western Reserve University, University Hospitals, Cleveland, USA;
7Department of Rheumatology, Radboud University Medical Centre, Nijmegen, The Netherlands;
8Division of Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, USA;
9UCB, Colombes, France;
10UCB, Slough, United Kingdom;
11UCB, Brussels, Belgium;
12University of California, San Francisco, Department of Medicine/Rheumatology, San Francisco, USA
Disclosures:
MR: Speakers bureau from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB; consultant of AbbVie, Eli Lilly and Company, Novartis, and UCB.
SR: Consultant for AbbVie, Alfasigma, Eli Lilly and Company, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB; grants from AbbVie, Alfasigma, Eli Lilly and Company, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
DP: Speaker for AbbVie, BMS, Eli Lilly and Company, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB; consultant for AbbVie, Biocad, Eli Lilly and Company, Gilead, GSK, Moonlake, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, and UCB; grant/research support from AbbVie, Eli Lilly and Company , MSD, Novartis, and Pfizer.
MM: Consultancy fees from AbbVie, BMS, Eli Lilly and Company, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB; research grants from AbbVie, BMS, and UCB.
IEvdH: Consultant for AbbVie, Eli Lilly and Company, MSD, Novartis, and UCB; unrestricted grants received for investigator-initiated studies from AbbVie, MSD, Pfizer, and UCB; fees received for Lectures from AbbVie, BMS, MSD, and Pfizer.
AD: Speaker for Eli Lilly and Company, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB; consultant for BMS, Eli Lilly and Company, J&J, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB; grant/research support from BMS, Eli Lilly and Company, J&J, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
VT: Employee and shareholder of UCB.
DV: Former contractor for UCB and employee of Veramed.
NdP: Employee of UCB.
LSG: Grants from UCB paid to institution; consulting fees from Acelyrin, Eli Lilly and Company, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
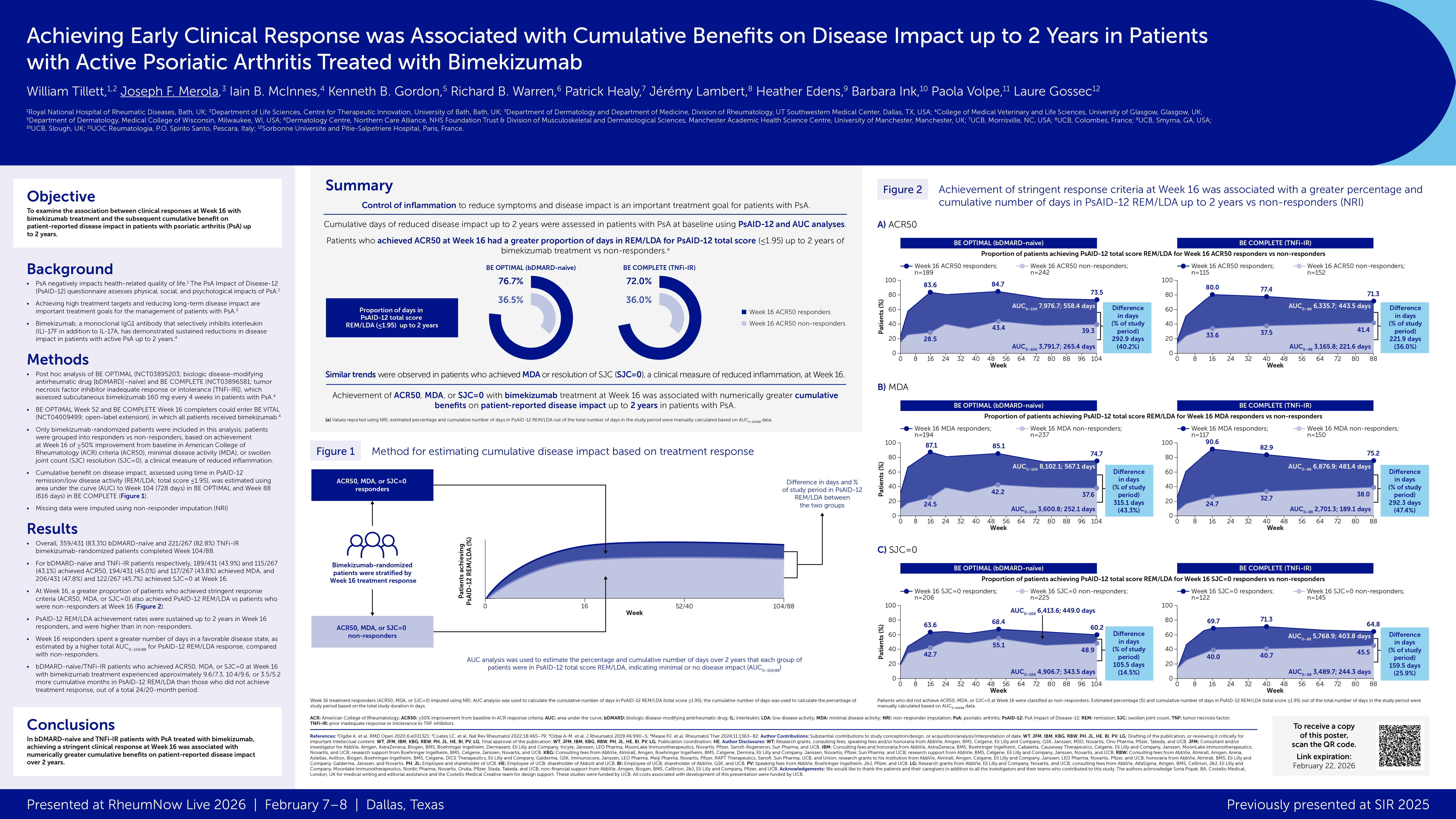
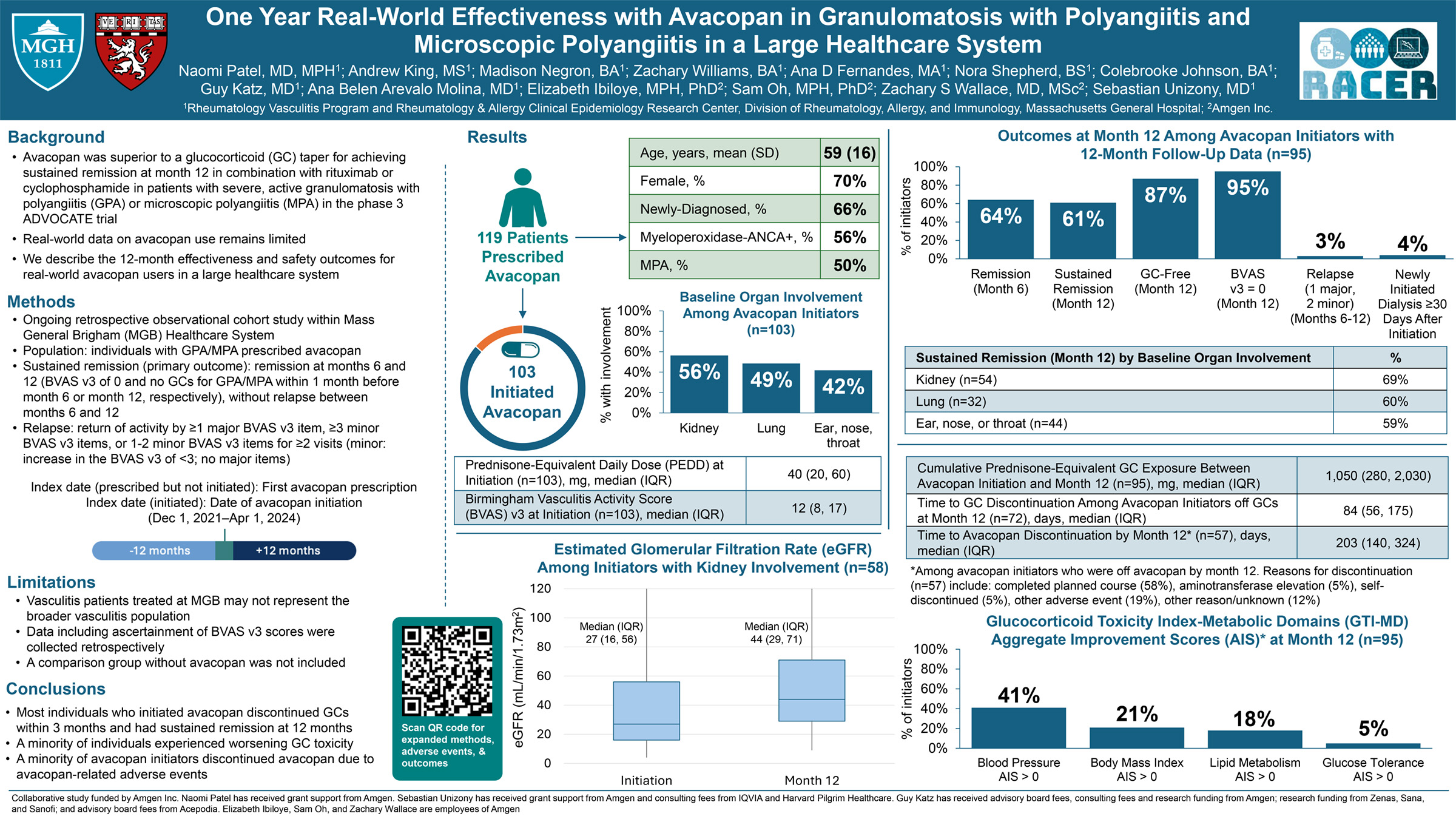
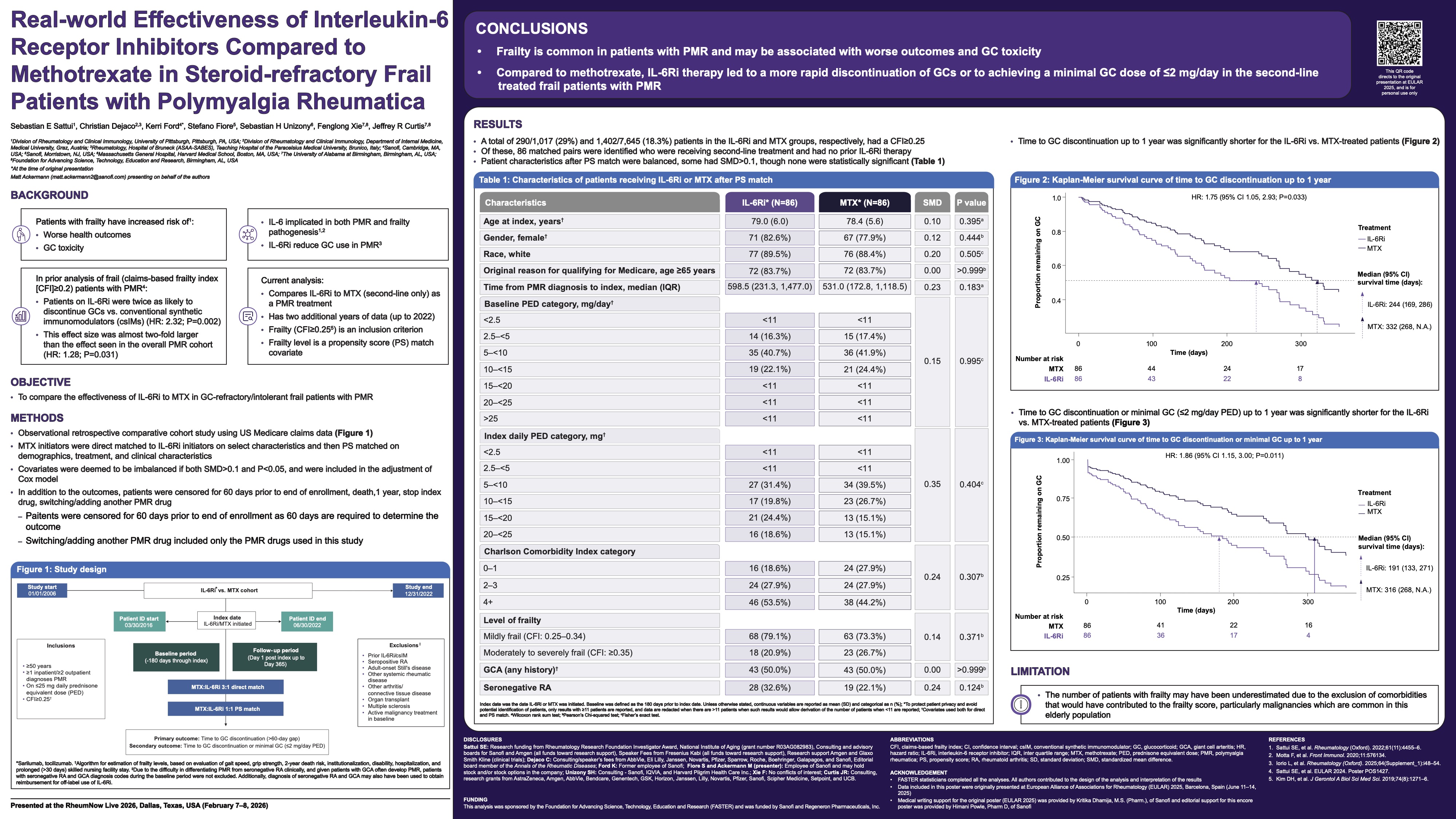
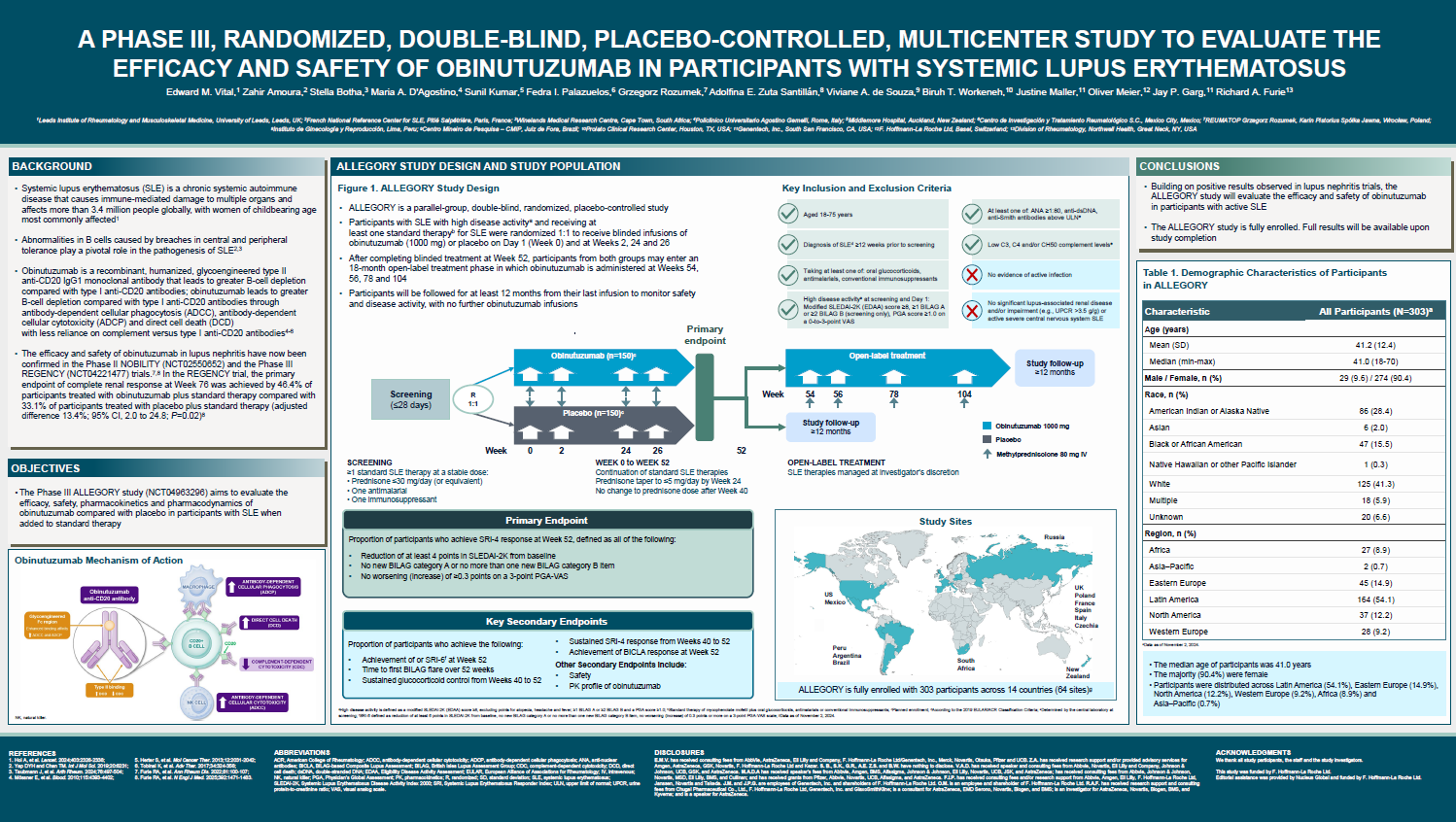
Abstract or description:Efficacy of bimekizumab treatment was assessed to Week (Wk)52 in patients with non-radiographic (nr-) and radiographic (r-)axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), focusing on potential sex-based differences in treatment response.
BE MOBILE 1 (nr-axSpA, NCT03928704) and BE MOBILE 2 (r-axSpA, NCT03928743) comprised a 16Wk double-blind period where patients were randomized to receive subcutaneous bimekizumab 160mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) or placebo, followed by a 36Wk maintenance period where all patients received bimekizumab 160mg Q4W. 254 and 332 patients were randomized in BE MOBILE 1 and 2, respectively.
Across ASAS40, ASDAS<2.1 and BASDAI, there was a pattern of higher bimekizumab versus placebo treatment effect in males versus females at Wk16. At Wk52, males/females patients achieved ASAS40 at 64.4%/56.4% for nr-axSpA, 59.4%/55.7% for r-axSpA, and ASDAS<2.1 at 72.0%/47.4% for nr-axSpA, 57.7%/55.8% for r-axSpA. Bimekizumab-randomized males and females showed good overall response in mean BASDAI improvements at Wk52 (nr-axSpA: −4.0 versus −3.6; r-axSpA: −3.6 versus −3.4).
For ASQoL, males and females demonstrated substantial improvements with bimekizumab at Wk16 (nr-axSpA: −5.5 versus −4.8; r-axSpA: −4.8 versus −5.5) compared with placebo (nr-axSpA: −2.1 versus −2.9; r-axSpA: −3.1 versus −3.7), with improvements continuing to Wk52 with bimekizumab treatment.
For change from baseline in objective signs of inflammation (OSI) outcomes, bimekizumab versus placebo treatment demonstrated greater effect in males versus females at Wk16, while absolute OSI values were comparable at Wk16 by sex and generally maintained or improved to Wk52.
Wk16 treatment effect of bimekizumab tended to be higher among male versus female axSpA patients. However, at Wk52 females showed improvement in longer-term treatment response to bimekizumab, with efficacy comparable to those seen in males at this timepoint. Overall, the efficacy of bimekizumab in clinical, patient-reported, and OSI outcomes was demonstrated in both male and female patients across the full disease spectrum of axSpA.
Acknowledgements: Funded by UCB. Medical writing support provided by Costello Medical and funded by UCB.