All News
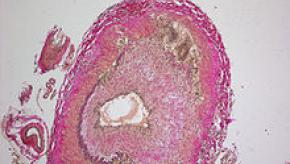
Ustekinumab: A Novel Intervention in Giant Cell Arteritis
Treatment of refractory giant cell arteritis (GCA) with ustekinumab (Stelara) showed therapeutic promise as a steroid-sparing agent in a small, open-label study, Irish researchers reported.
Read ArticleMeasures of Opioid Misuse Predict Future Opioid Overdose and Death
The current issue of Annals of Internal Medicine examines patterns of potential opioid misuse that are associated with subsequent adverse outcomes nationally.
Read ArticleFDA Approves Denosumab for Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Amgen announced that the U.S.
Read ArticleAutoinflammatory Syndromes Show Dramatic Response to Canakinumab
The New England Journal of Medicine reports that the anti-interleukin (IL)-1β monoclonal antibody canakinumab (Ilaris) was effective in the treatment of three distinct autoinflammatory recurrent fever syndromes (FMF, TRAPS, HIDS) with responses that were far superior to what was see
Read ArticleThe RheumNow Week in Review – Modifiable Behavior (5.18.18)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow.com. He discusses opioids, new approval for polyarticular JIA, running and osteoarthritis, and modifiable behaviors that influence outcomes.
Read ArticleTrends in Psoriatic Arthritis Treatment 2004-2015
Lee and colleagues from Brigham and Women's Hospital have analyzed the last decade of disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) use in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and found nearly 40% were treated with a bDMARD, along with a decreasing trend in complete DMARD discontinuations.
Read ArticleOpioid Marketing & Meals Tied to Opioid Prescribing
A current study in JAMA Internal Medicine showed that while US physicians who received no opioid-related marketing payments had fewer opioid prescriptions in 2015 compared with 2014, those receiving such payments wrote for more opioid in 2015.
Read ArticleEpigenetic Link in Rheumatoid Arthritis to Huntington's Disease
Researchers at University of California San Diego School and the Icahn School of Medicine have found a high-resolution epigenomic landscape of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) that overlaps with that seen in Huntington's disease, suggesting potentially new unanticipated pathways that could be devel
Read ArticleMortality Predictors in Rheumatoid Arthritis
A population based study from southern Denmark finds excess mortality RF-positive males with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and that employment status and comorbidity were independent predictors of mortality.
Read ArticleTrump Blasts Drug Makers on the Price of Drugs
Reuter's reports Friday that President Donald Trump blasted drugmakers and healthcare “middlemen” for making prescription drugs unaffordable for Americans.
Read ArticleThe RheumNow Week in Review - Nonadherence and Astronomic Costs (5.11.18)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews highlights, news and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow.com.
Read ArticleNew EULAR Pain Guidelines
The European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) convened a multidisciplinary task force including health professionals and patient representatives to develop evidence-based recommendations for pain management in patients with inflammatory arthritis (IA) and osteoarthritis (OA).
Read ArticleTocilizumab Beats Anti-TNFs for Treatment Retention
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who had previously had an inadequate response to one biologic agent remained on tocilizumab (Actemra) longer than on a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor, whether or not conventional disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) were given concomitantl
Read ArticlePatients May Not Fill Your Prescription
A new study linking administrative claims and electronic health records (EHRs) shows that nearly 40% of patients fill and take newly prescribed methotrexate (MTX), tofacitinib or biologics.
Kan et al set out to estimate the extent and predictors of primary nonadherence in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients who received new prescriptions for methotrexate, biologics or tofacitinib.
Read Article60 Minutes Drills Acthar - A Financially Crippling Drug
Acthar is in the news again. Previously a New York Times article lambasted the drug as the "single most expensive drug per patient", based on it costing Medicare $16,2371 per patient for nearly 3100 patients. Overall, costing Medicare a half-billion US dollars per year.
Read ArticleRising Need for Weight Loss Counseling in Arthritic Patients
The CDC's May 4th MMWR reports that from 2002 to 2014, the prevalence of health care provider counseling for weight loss among adults with arthritis and overweight or obesity increased by 10% (from 35% to 45%).
Among the 54.4 million adults with doctor-diagnosed arthritis in the United States, 32.7% are overweight and 38.1% are obese. Moreover obesity is more prevalent among persons with arthritis than among those who do not have arthritis.
Read ArticleBisphosphonate Drug Holidays May Result in Fractures
A report in Endocrine Practice shows that drug holidays from bisphosphonates results in a 15% risk of fractures. (Citation source:
Read ArticleTargeting IL-17A: A Winner in PsA
Psoriatic arthritis patients with inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors had improvements in their arthritis and psoriasis when treated with the interleukin (IL)-17A blocker ixekizumab (Taltz), according to a phase III study presented here at the
Read ArticleTick, Mosquite-Borne Diseases Triple Since 2004
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has a new report showing that from 2004 to 2016, the number of Americans infected by mosquitoes, ticks or fleas tripled from 27,388 in 2004, to 96,075 in 2016.
From 2015 to 2016, these infections rose by 73 percent. This included new Zika and chikungunya virus infections, (41,680 in 2016), followed by Lyme disease (36,429 cases). This may be an underestimation as as many infections are not reported.
Read ArticleComorbidities Undermine Clinical Outcomes in Psoriatic Arthritis
Analysis of data from the DANBIO registry of psoriatic arthritis patients treated with tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapy shows that comorbidities were associated with higher baseline disease activity, shorter TNFi persistence, and reduced clinical response rates to TNFi.
Read Article