All News
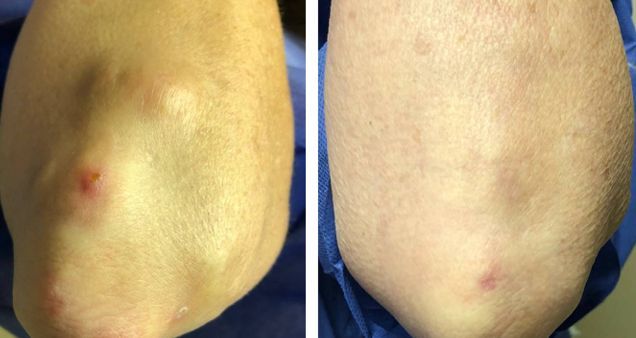
Risk Factors for Knee Osteoarthritis
New research from the University of Sydney reveals that obesity, having a knee injury and occupational risks such as shift work and lifting heavy loads are primary causes of knee osteoarthritis.
Read ArticleEmulation trials in SLE: Real or Fake?
Recently a landmark paper was published in A&R studying the results of an emulation trial on SGLT2i (sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors) showing benefit in SLE patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), for both renal protection and reducing cardiovascular events, using data from an American large insurance claim database. My colleagues and I were able to write an editorial on this paper and describe emulation trials.
Read ArticleMore Women with Autoimmune Diseases Die from Cardiovascular Disease
Women with the autoimmune diseases rheumatoid arthritis, lupus or systemic sclerosis may have a higher rate of death related to cardiovascular disease than men with the autoimmune diseases, according to new research published in the American Heart Association’s journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Read ArticleD-Lay Trial: High-Dose Vitamin D Retards Multiple Sclerosis
A randomized clinical trial with oral high-dose cholecalciferol ( vitamin D3) was shown to prevent or delay the onset of clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), typical for multiple sclerosis (MS).
Read Article

Links: