All News
Earlier RA Diagnosis Leads to Lower Costs of Care
A study from the Leiden Early Arthritis Clinic shows that is rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is diagnosed within 12 weeks after symptom onset, treatment costs were lower in both autoantibody-negative and autoantibody-positive RA.
Updated EULAR Recommendations on the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis
Medscape has published an overview to the 2024 updated recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis (SSc) presented in Vienna at EULAR 2024 by Professor Francesco Del Galdo, MD, PhD on behalf of a 27 member task force.
Read ArticlePollution and Autoimmunity (7.12.2024)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow.com.
Read ArticlePNAS & Nature Insights into Lupus Pathogenesis
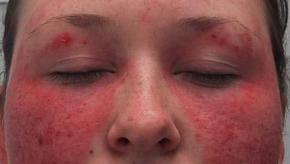
Two prominent medical journals this week published new insights into the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), with both inidicating promient roles for T cells in what is a classically viewed as a humoral (B cell) disorder.
Read ArticleProgress in SLE with new mRNA CAR-T cell Trial
Cartesian Therapeutics, has announced their first-in-class mRNA-engineered chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (mRNA CAR-T) therapy has been given to the first systematic lupus erythematosus (SLE). patient in a Phase 2 open-label clinical trial.
Read ArticleICYMI: Can Mycophenolate be Stopped in Stable SLE?
In patients with clinically stable systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis, the withdrawal of mycophenolate mofetil was not significantly inferior to mycophenolate maintenance, but MMF withdrawal had numerically more reactivations, while MMF maintenance had more infections.
Read ArticleICYMI: 2023 EULAR Psoriatic Arthritis Recommendations
EULAR has updated its treatment recommendations from the prior 2019 guidelines, since there have been several newly developed agents. The updated guidance includes 7 overarching principles and 11 recommendations regarding treatment strategy and pharmacological therapies.
Read ArticleICYMI: 9 Facts about Leflunomide
Medscape has published an informative review of leflunomide, drawn from Dr. Eric Ruderman’s recent lecture on the subject at the February RWCS meeting in Maui. Here are some highpoints from this Medscape article and lecture.
Read ArticleICYMI: Enthesitis, Synovitis, and Tenosynovitis in Psoriatic Arthritis
An ultrasound study suggests that enthesitis is associated with both synovitis and tenosynovitis in patients with Psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Read ArticleICYMI: 2023 EULAR Non-pharmacological Management of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: 2023 update
EULAR has published the 2023 updated recommendations for the optimal non-pharmacological management of hip and knee osteoarthritis (OA).
Read ArticleICYMI: JAMA: SLE Review
Drs. Caroline Siegel and Lisa Sammaritano (from HSS in NYC) have published an impressive overview of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in JAMA. This timely, well-written review covers the many complexities of this multi-organ disorder that affects nearly 3.4 million people worldwide.
Read ArticleFuture Big BiTEs (6.28.2024)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news, journal articles and regulatory announcements from the past week on RheumNow.com.
Read ArticleFactors Affecting Hydroxychloroquine Adherence
A study from the University of British Columbia has evaluated the trajectories of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) use in patients with incident RA and SLE between1997 and 2021, and identified factors associated with high adherence.
Read ArticleDifficult-to-Treat Psoriasis
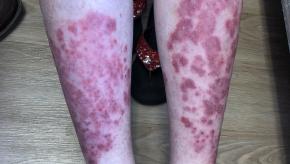
This meta-analysis of psoriasis treatments shows that biologic therapies may be less effective in certain psoriasis (PSO) patients, particularly those who are older, smokers, with higher BMI an prior exposure to biologics.
Read ArticleProtective Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors and Lupus Nephritis
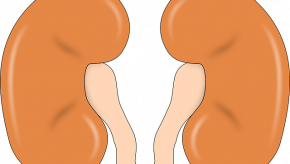
A multicenter cohort study of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with type 2 diabetes has shown the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors associated with a significantly reduced risk of lupus nephritis, dialysis, kidney transplant, heart failure, and all-cause mortality compared with no SGLT2i use.
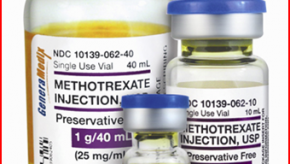
Read ArticleNo Risk of Interstitial Lung Disease with Methotrexate Use
JAMA reports a cohort study that investigated the association between methotrexate (MTX) use and Interstitial lung disease (ILD) in patients with dermatomyositis (DM).
Read ArticleEULAR 2024 Rheumatology Roundup (6.21.2024)
Drs. Artie Kavanaugh and Jack Cush discuss highlights from the EULAR 2024 meeting in Vienna
Read ArticleEULAR 2024 – Day 4 Report
The final day of EULAR 2024 was rich in posters, Late-breaking oral presentations and EULAR updates and recommendations. Below is a synopsis of the half-day's action.
Read ArticleAchieving drug-free remission in axSpA
A clinical trial in early axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) demonstrated sustained inactive disease status in over 60% of patients.
Read Article