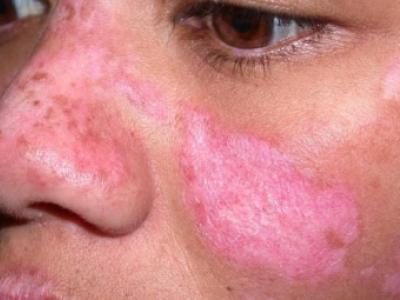
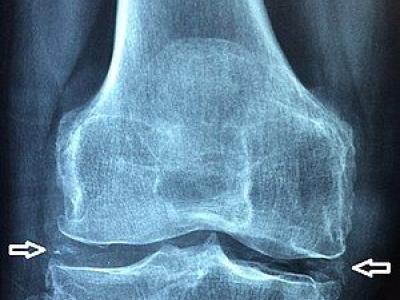
Investigators from the Netherlands have published their findings that smoking is a risk factor in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), led by the induction of local autoimmune responses at mucosal sites (in the lungs) and exemplified by RA-specific autoantibodies.
RA is characterized by the presence of autoantibodies against modified proteins, known as anti-modified protein autoantibodies (AMPAs), including ACPA (CCP) and others, particularly of the IgA isotype.