All News
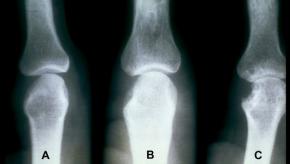
JAK Inhibitors Stimulate Osteoblasts
Science Translational Medicine has a report on how the use of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors may boost osteoblasts to battle bone erosions in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
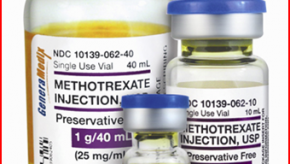
Read ArticleAdverse Effects of Low-Dose Methotrexate from the CIRT Trial
Low-dose methotrexate (LD-MTX) was studied in high risk cardiac patients in the cardiac intervention trial (CIRT), but was prematurely ended for not showing a change in cardiovascular event rates. Nonetheless this trial studied the safety and adverse event rates of LD-MTX and those results are reported in the current issue of Annals of Internal Medicine.
BSR Guidelines for Giant Cell Arteritis
NICE has commissioned an update to the 2010 British Society for Rheumatology guideline for the management of giant cell arteritis, and proposed a total of 19 recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of GCA.
Read ArticlePrimary Care Visits Decline 2008-2016
A national claims-based analysis has shown a consistent decline, by commercially insured adults (18-64 yrs), in primary care physician visits from 2008 to 2016; with nearly one half having no PCP visits in a given year by 2016.
Read Article
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)


Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)