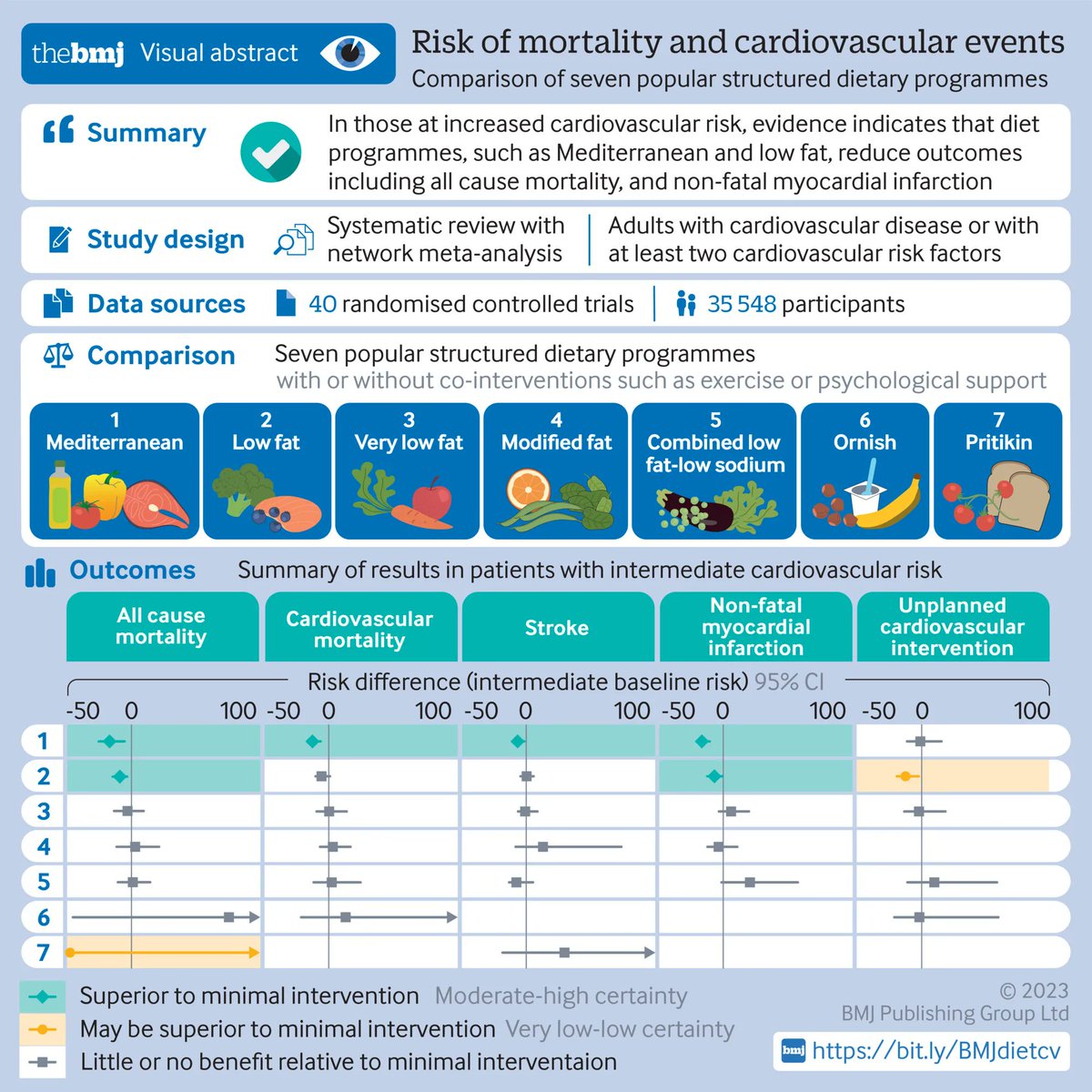
All News
Clinical Profile of RA-associated Interstitial Lung Disease
A prospective, cross-sectional analysis of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) shows those with interstitial lung disease (ILD) tend to be older, obese and have a smoking history.
Read ArticleAntiphospholipid Antibodies With Incident Cardiovascular Events
Are antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular (ASCVD) event risk? A cohort study has shown that aPL Abs are found in a substantial proportion of adults with ASCVD events and finding both positive aCL IgA and aβ2GPI IgA Abs independently predicted futur
Read ArticleEMA Final Update on JAK Inhibitors and MACE, Malignancy & VTE Risks
The EMA has updated recommendations regarding the use of JAK inhibitors by issuing a direct healthcare professional communication summarizing the data and warnings regarding an increased risk of malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), serious infections, VTE, and mortality in some patients receiving JAKi for the treatment of chronic inflammatory disorders.
Read ArticleTofacitinib May Reduce Interstitial Lung Disease Risk in RA
Tofacitinib (Xeljanz) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) stood out among several other biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (sDMARDs) when it came to the incidence of interstitial lung disease (ILD), a retrospective cohort study showed.
Read ArticleHigher Rehospitalization Rates in Younger SLE Patients
A Medicare study shows that young adults with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) exhibit very high 30-day rehospitalization rates (36%) that are significantly higher than older SLE patients and age matched non-SLE patients.
Read ArticleDoes Biologic Treatment in Psoriasis Reduce the Risk of Psoriatic Arthritis?
Retrospective claims analysis shows that psoriasis patients treated with either an IL-12/23 inhibitor or an IL-23 inhibitor had a lower risk of developing incident psoriatic arthritis, compared to TNF inhibitors or IL-17 inhibitors.
Read ArticleLong-Term Benefit of Rituximab in Systemic Sclerosis
A small cohort trial of rituximab (RTX) in 29 systemic sclerosis patients showed significantly improved skin sclerosis and lung function after a follow-up of 96 weeks.
Read Article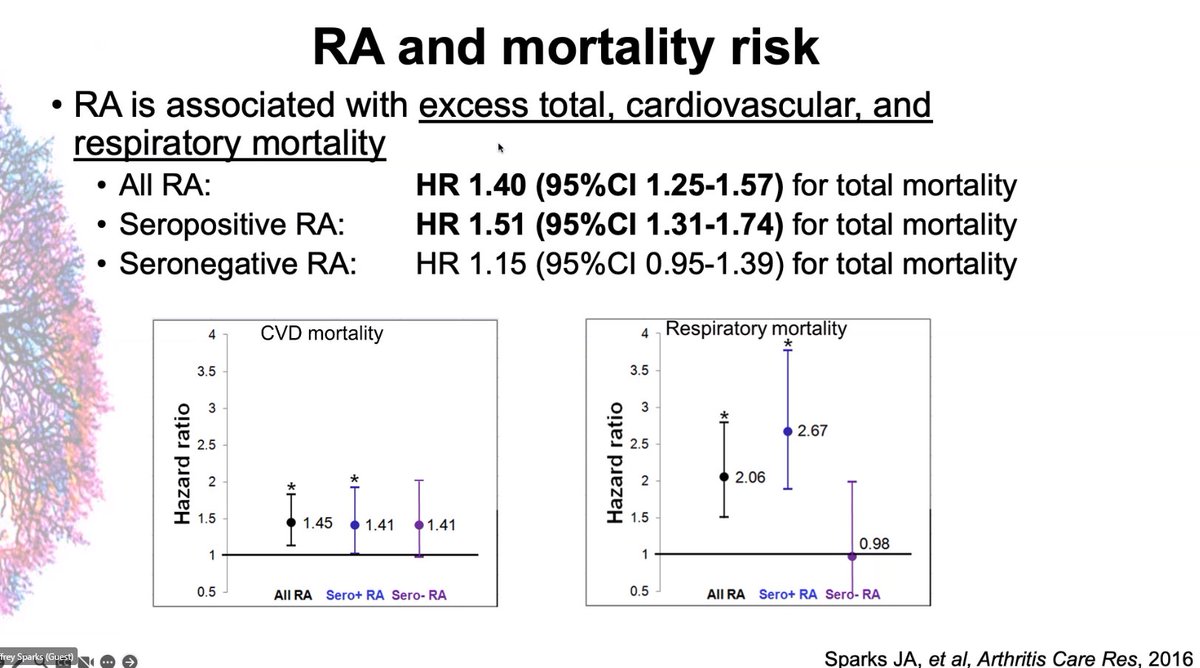
Links:

Links:
Links:
Links:
Links:
Links:
Links:

Links: