All News
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis - NEJM Review
Sandborg et al. has published an overview of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) - its classification, biology, genetics, , clinical presentations and treatment advances in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM).
Read ArticleAging Quiets Lupus
UCSF researchers have found that epigentic changes in interferon genes over time may lead to lupus being less active as they age. Lupus is a “classic” autoimmune disease. It causes the immune system’s first-line viral defenses — known as interferons — to attack the body. Nearly every organ is at risk, leading to conditions like kidney and heart disease. But unlike many other autoimmune or chronic illnesses, lupus can improve as patients reach their 60s and 70s.
Read ArticlePractical management of rheumatic immune-related adverse events with immune checkpoint inhibitors
Clinical Associations with Anti-RNA Polymerase III Antibodies
A systematic review of anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies (ARA) in systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients finds ARA positivity in only 9% of SSc patients, but come with a higher risk of many potentially worrisome outcomes.
Read ArticlePesticides and Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Women exposed to pesticides through farm work or as farmers' wives face increased risk for developing rheumatoid arthritis, a new analysis of Agricultural Health Study data indicated.
Read ArticleNHANES, Numbers, & Risk (7.18.2025)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports from this past week on RheumNow.com along with interesting case questions from "Ask Cush Anything".
Read ArticleZasocitinib (Tyk2 Inhibitor) Efficacy in Psoriatic Arthritis
A highly selective, tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor zasocitinib (TAK-279), was studied in a phase 2b trial and found to be effective and safe patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Read ArticleMolecular profiling of RA synovium predicts biologic responses
Machine learning analysis of pre-treatment synovial tissue biopsy from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients starting either etanercept (ETN), tocilizumab (TCZ) and rituximab (RTX) revealed
Immunomodulators in the Treatment of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic, progressive inflammatory liver disease driven by autoimmune mechanisms, characterized by elevated serum aminotransferases, hypergammaglobulinemia, and interface hepatitis on histology.
Read ArticleICYMI: Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Becoming Milder?
A 24 year, prospective study analyzing very early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in three consecutive eras suggests that RA has evolved since 2005, demonstrating less seropositivity, inflammation, and erosions but is characterized by more comorbidity, smoking and corticosteroid use.
Read Article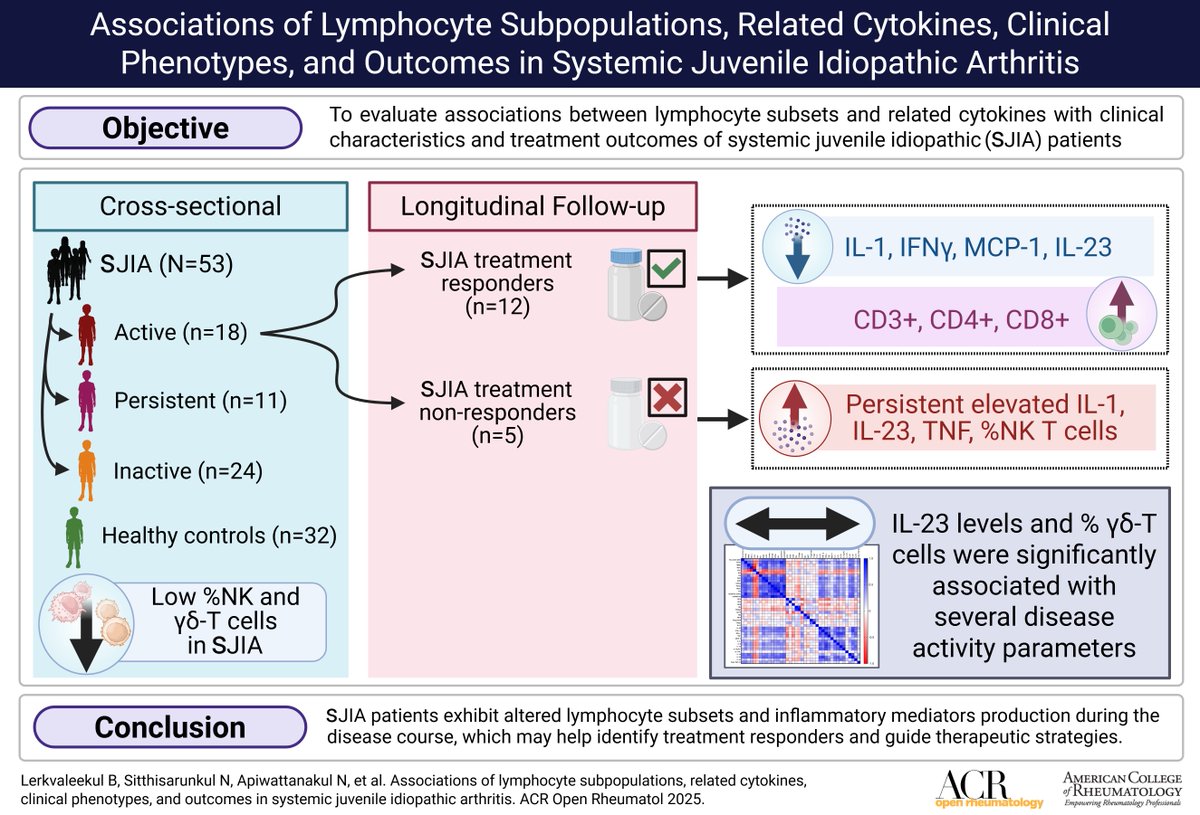
Links:



Links:





Mrinalini Dey DrMiniDey ( View Tweet)