News
Proposed Changes for 2019 Medicare Fee Schedule
On July 12th the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released its proposed rule changes for the 2019 Medicare physician fee schedule. This year, CMS has combined the Medicare physician fee schedule proposed rule with recommendations for the Quality Payment Program (QPP), whic
Predictors of Methotrexate Non-Response
New research from a UK study suggests that nonresponse to oral or subcutaneous MTX was seen in 43% and is predicted by seronegativity, higher disease activity measures and higher anxiety scores.The RheumNow Week in Review –Fateful Outcomes in Rheumatology (7.13.18)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow.com. Fateful outcomes in Rheumatology, what happens to Seronegatives, IL-23 fails, MRI progression, Not all inflammatory back pain becomes SpA:
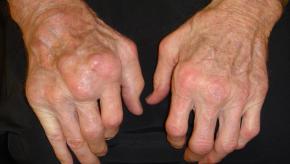
The Diverse Fate of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
A Finnish Rheumatology Center followed 435 early, seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients for 10-years and found that only 3% became erosive or seropositive RA.
Defining Refractory RA by Biologic Use
A study from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register (BSRBR) has shown that biologic refractory disease is seen in at least 6% of patients who have ever received a biologic DMARD (bDMARDs).
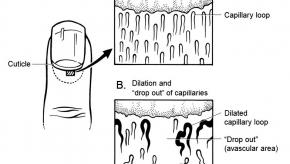
Nailfold Capillary Density Predicts Dermatomyositis Lung Involvement
In patients with juvenile dermatomyositis (DM), an association was seen between low nailfold capillary density and pulmonary involvement, European researchers reported.
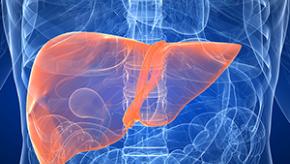
Liver Disease Increased in Psoriasis
An observational case-control study has shown that psoriasis is associated with an increased prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
IL-23 Inhibitor Fails in Ankylosing Spondylitis
A study of the IL-23 risankizumab in active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients failed to show efficacy and did not meet primary efficacy endpoints in a 6-month trial.
Systemic Sclerosis: More Common than Expected
Systemic sclerosis is more common in the United Kingdom than previously reported, a nationwide population-based study determined.
Obesity, Hypertension and Diuretics Drive Gout Risk
A recent metanalysis suggests that obesity, hypertension and diuretic use are associated with a two-fold increased risk of incident gout.
From a potential of 9923 articles, researchers analyzed 11 studies with data suitable for the meta-analysis.