All News
Might IL-17 Inhibition Be Effective in RA?
Interleukin 17 (IL-17) inhibitors are highly effective and FDA approved for use in psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. However, many of the initial trials were done in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) where it was projected to be effective, but was not. A recent metanalysis examines how effective IL-17 inhibition was in two RA populations: biologic-naïve or tumor necrosis factor inhibitor inadequate responders (TNF-IR).
Read ArticleKnee Injuries Increases Osteoarthritis Risk
A systematic review of the medical literature shows anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), meniscus or combined ACL and meniscus injury significantly increases the risk of future knee osteoarthritis (OA).
Read ArticleRheumNow Podcast – Rituximab Monitoring (5.31.19)
Dr. Jack Cush presents the news and best of rheumatology and medicine from the past week on RheumNow.com
Read ArticleUpadacitinib Monotherapy in MTX-IR Rheumatoid Arthritis
Upadacitinib (UPA) is an oral, selective JAK1-selective inhibitor being developed for use in rheumatoid arthritis patients; Lancet has reported the SELECT-MONOTHERAPY trial showing that UPA is safe and effective in RA patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX).
Read ArticlePredictors of Serious Infections with Rituximab
The risk of serious infectious events (SIE) with rituximab (RTX) is similar to that seen in other biologics (e.g., RA: 2% or 4.3/100PY), but with prolonged use the risk may change. Recent research says that low IgG levels, RTX induced neutropenia, prior SIE and comorbidities can significantly augment this risk.
A retrospective longitudinal single center study of 700 rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) treated monitored serum immunoglobulins (at baseline and 4–6 months after each cycle), clinical outcomes and SIE over time.
ACR Statement on CMS Medicare Advantage Final Rule
In August 2018, the CMS announced that Medicare Advantage (MA) plans would be allowed to utilize step therapy for Part B drugs. The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) expressed strong concerns about this proposal.
Read ArticleLung Disease in RA: Which Factors are Linked With Mortality?
Among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who had interstitial lung disease (ILD), the pattern of ILD did influence mortality, but other pulmonary factors also contributed, a meta-analysis suggested.
Read ArticleSteroids, Not Biologics, Drive Arthroplasty Infections in RA
Medicare and Truven MarketScan administrative data study (2006 through 2015) of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) undergoing arthroplasty found that while that the risks of perioperative infection was similar across biologics, the infection risk with glucocorticoid use, especially at
Read ArticleEMA Restricts Tofacitinib Dosing
The Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee of the European Medicines Agency issued recommendations limiting the use of Xeljanz (tofacitinib) 10 mg twice daily in patients with ulcerative colitis in the EU.
The new recommendations are temporary while PRAC undertakes a review of all available evidence on the safety and efficacy of tofacitinib. The review follows warnings of an increased risk of pulmonary embolism (PE) and death from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration based on Pfizer's large post-marketing safety study (in high risk rheumatoid arthritis patients with one or more underlying cardiovascular risk factors) wherein those receiving in tofacitinib 10 mg twice daily in study A3921133 had more PE and mortalities than comparator groups (tofacitinib 5 mg bid or adalimumab).
Opioids, SSRIs and Steroids Increase Fracture Risk in RA
Analysis of a large US observational rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients finds that opioids, SSRIs and glucocorticoids were associated with increased risk of fracture in RA, whereas statins and TNFi had a decreased vertebral fracture risk.
Read ArticleRheumNow Podcast – Richer or Poorer (5.17.19)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow.com
Read ArticleCoexistent Gout Increases Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis
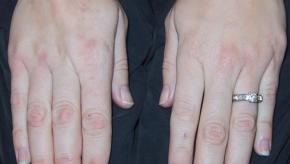
It his often said that gout and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cannot coexist and where confusion exists, a good history and testing for serum urate (SUA) and rheumatoid factor (RF) can usually clarify the dominant disorders. A recent study shows that hyperuricemia and gout are uncommon in RA, but when present shows an increased risk of comorbidities and cardiovascular (CV) mortality.
FDA Final Guidance on Interchangeability with Biosimilars
The FDA has published an industry guidance document to define interchangeability as regards to biosimilar use in the United States under section 351(k) of the Public Health Service Act (PHS Act) (42 U.S.C. 262(k)).
Read ArticleMethotrexate Use Not Linked to Interstitial Lung Disease in RA
People with rheumatoid arthritis have a significant risk of developing interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD), yet there is often a question as to whether methotrexate (MTX) exposure can cause or worsen ILD. A controlled cohort study suggests that MTX use is not associated with an increased ris
Read ArticleRheumNow Podcast – Periodontitis in RA Relatives (5.10.19)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow.com
Read ArticleDenosumab Protects Against RA Erosions
Combining denosumab (Prolia) with a conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) such as methotrexate showed promise for slowing radiographic damage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a manufacturer-sponsored phase III trial called DESIRABLE found.
Read ArticleCDC: One in Four US Adults have Arthritis
MMWR reports that in 2017, one in four US adults have arthritis (range from 22.8% to 34.6%), with higher rates in Appalachia and Lower Mississippi Valley regions. Of those with arthritis, 31% reported to have "severe arthritis".
Read ArticleNew ACR/AF Guidelines on JIA Polyarthritis and Uveitis
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and the Arthritis Foundation (AF) have released two guidelines on management of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Read ArticleShorter Treatment Succeeds in Septic Arthritis
Two weeks of antibiotic therapy was as effective as 4 weeks for septic arthritis, a prospective single-center study found.
Read ArticleTargeting GM-CSF Works in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Namilumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) ligand, showed promise as a treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a phase II study.
Read Article