All News
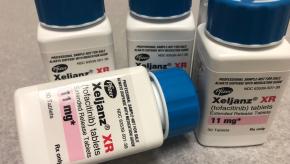
Thromboembolic Risk with Tofacitinib in RA, PsA and UC
An analysis of the tofacitinib (Xeljanz) drug development program in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and ulcerative colitis suggests a low level risk for venous (VTE) and arterial thromboembolism (ATE).
Read ArticleMethotrexate Not Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease
A case-controlled study shows that methotrexate (MTX) use in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is not associated with interstitial lung disease (ILD) according to a report in the European Respiratory Journal.
Read ArticleIL-1 Blockade: A Treatment at Last for Osteoarthritis?
The interleukin (IL)-1β inhibitor canakinumab (Ilaris) showed promise for preventing the need for hip or knee replacement among patients with osteoarthritis in an exploratory analysis of data from a randomized clinical trial, investigators reported.
Among patients enrolled in CANTOS, the pooled incidence rate for total hip replacement/total knee replacement was 0.31 events per 100 person-years for those receiving the monoclonal antibody every 3 months for up to 5 years compared with 0.54 per 100 for those given placebo, according to Paul M. Ridker, MD, of Harvard Medical School in Boston, and colleagues.
Lovastatin Fails to Lower CRP and Activity in RA
Ridker and colleagues have shown that statins (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A (HMG Co-A) reductase inhibitors) are effective at treating hyperlipidaemia and lowering C-reactive protein levels; Aranaow and colleagues have shown that lovastatin, when given to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with elevated CRP levels failed to significantly lower disease activity.
Read ArticleColchicine Benefits COVID-19 Patients
A proof-of-concept study published in Annals of Rheumatic Disease suggests that colchicine significantly improves COVID-19 outcomes.
Efficacy and safety must be determined in controlled clinical trials.he outbreak of COVID-19 posed the issue of urgently identifying treatment strategies. Colchicine was considered for this purpose based on well-recognised anti-inflammatory effects and potential antiviral properties.
Characteristics Underlying Mortal COVID-19 Outcomes
From January 1, 2020–May 18, 2020, approximately 1.3 million cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and 83,000 COVID-19–associated deaths were reported in the United States.
Read ArticleRheumNow Podcast – LTF – Listen to Fauci (7.17.20)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news, tweets and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow. Let's dig into this week's 14 highlights.
HCQ May Help Prevent Fetal Heart Block
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) helped reduce recurrent maternal autoantibody-mediated congenital heart block (CHB) in fetuses, an open-label study suggested.
Read ArticleAnti-Rheumatic Therapies for COVID-19 Infection
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic numerous anti-rheumatic therapies have been proposed as being potentially beneficial. The mechanistic effects of these agents, either presumed antiviral, anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic effects, may benefit mitigate the damage seen with COVID-19 infection.
This review will examine the potential benefits and existing evidence for treating suspected or proven COVID-19 infection with antimalarials, inhibitors of interleukin-6 (IL-6) or interleukin-1 (IL-1) Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, TNF inhibitors or colchicine. There are many other antirheumatic and immunosuppressive therapies that are in clinical trials that will not be reviewed here including IVIG, rituximab, calcineurin inhibitors (sirolimus, etc.), apremilast, emapalumab (anti-IFN gamma), etc.
ICYMI: Protective Benefit of Colchicine in COVID-19 Infection
Colchicine has been advocated as a potential anti-inflammatory intervention in patients with the coronavirus 2 infection and clinical trials have been developed to assess its effect in early COVID-2 infection. JAMA has published a randomized clinical trial showing that low dose colchicine had less clinical deterioration without significant changes in biomarkers, such as high-sensitivity cardiac troponin and C-reactive protein.
Read ArticleICYMI: COVID-19 and Thrombotic Complications
Severe and fatal outcomes with coronavirus infection are often the result of the downstream damage that follows the viral infection. Rising high on the list of complications are the hematologic and vascular complications seen in severely affected patients, so much so that many centers are routinely anticoagulating hospitalized (but not ambulatory) COVID patients.
Read Article
Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)
Links:

Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Retrospective cohort of 147 Adult-Onset Stills Dz pts finds 18 (12.3%) with lung dz (LD) at the diagnosis of AOSD. AOSD-LD were older, w/ more myalgia, LN, pleuritis, ab,dominal pain, more systemic Dz, higher ferritin and more mortality (%39 vs 10%). https://t.co/2phEFwi6n2
Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)