News
CAR-T Product Shows Early Promise in Lupus
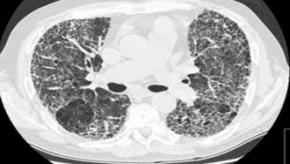
High-Resolution CT in CTD-Interstitial Lung Disease
A systematic review and meta-analysis examined the role of high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) in diagnosing and characterizing interstitial lung disease (ILD) associated with connective tissue diseases (CTDs).
Methylprednisolone plus Methotrexate in Giant Cell Arteritis
What is the optimal glucocorticoids (GC) regimen in giant cell arteritis (GCA)? Does methotrexate (MTX) work in GCA?
Scleroderma-associated Interstitial Lung Disease
While we know there are certain clinical features serving as predictors that patients with SSc may develop ILD, including diffuse skin disease and serologies such as anti-Scl-70 and Th/To antibodies, it is imperative that clinicians consider that any patient, particularly early in their disease course (5 years of disease since the first non-Raynaud phenomenon symptom) could develop ILD.Big Fat FDA Pink Slip (9.19.2025)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports from this week on RheumNow.com. Today we cover GLP-1 agonists, acupuncture, what JAKs won’t do & an FDA Pink Slip.
Did Hydroxychloroquine Reduce COVID-19 Mortality?
A multicenter study investigated the association between hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) dosage and COVID-19 mortality among hospitalized patients from multiple medical centers in China. The analysis focused on dose effects of HCQ on mortality.