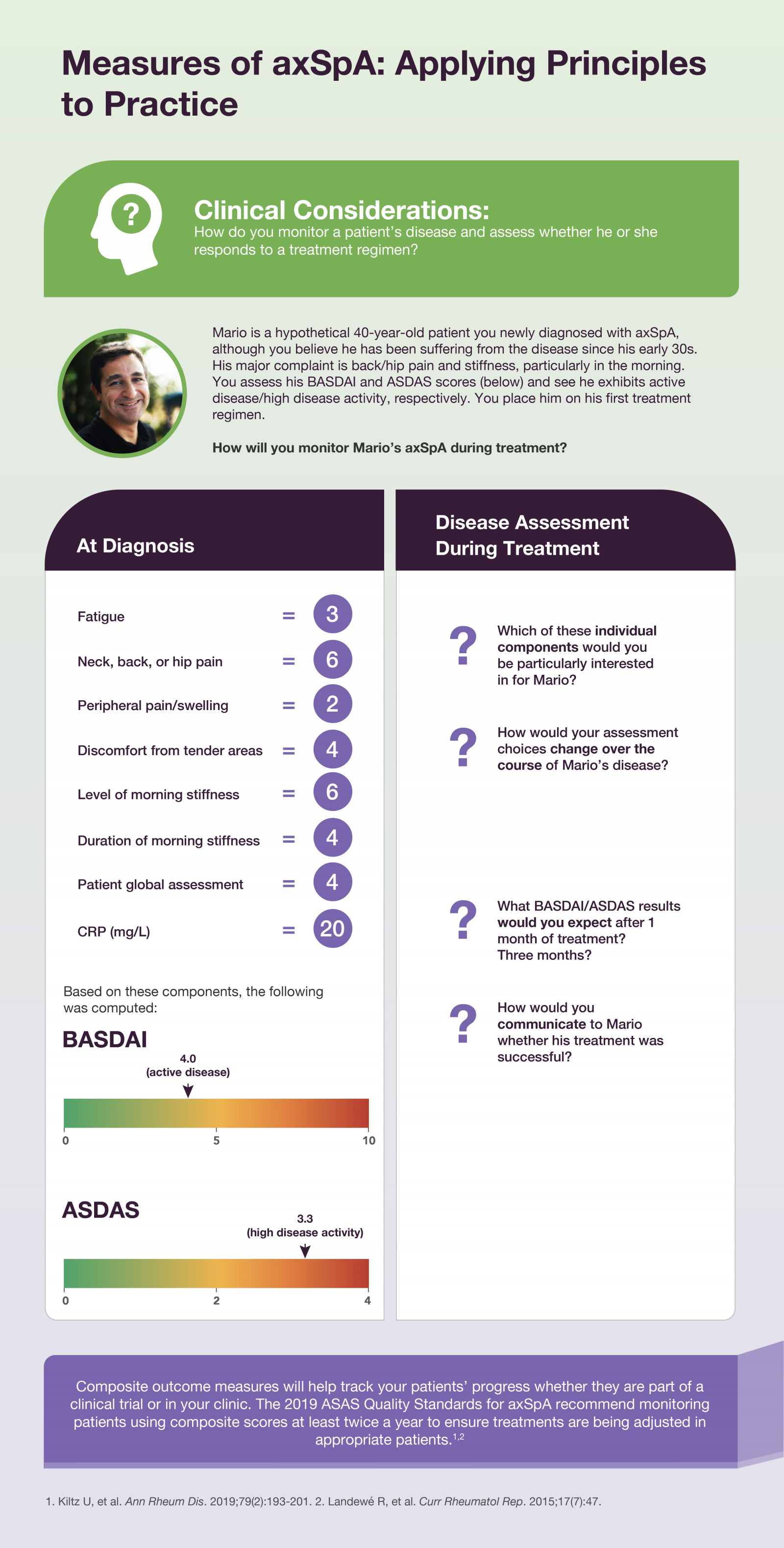
BASDAI, ASDAS, ASAS, Oh My! Outcome Measures for Axial Spondyloarthritis Save
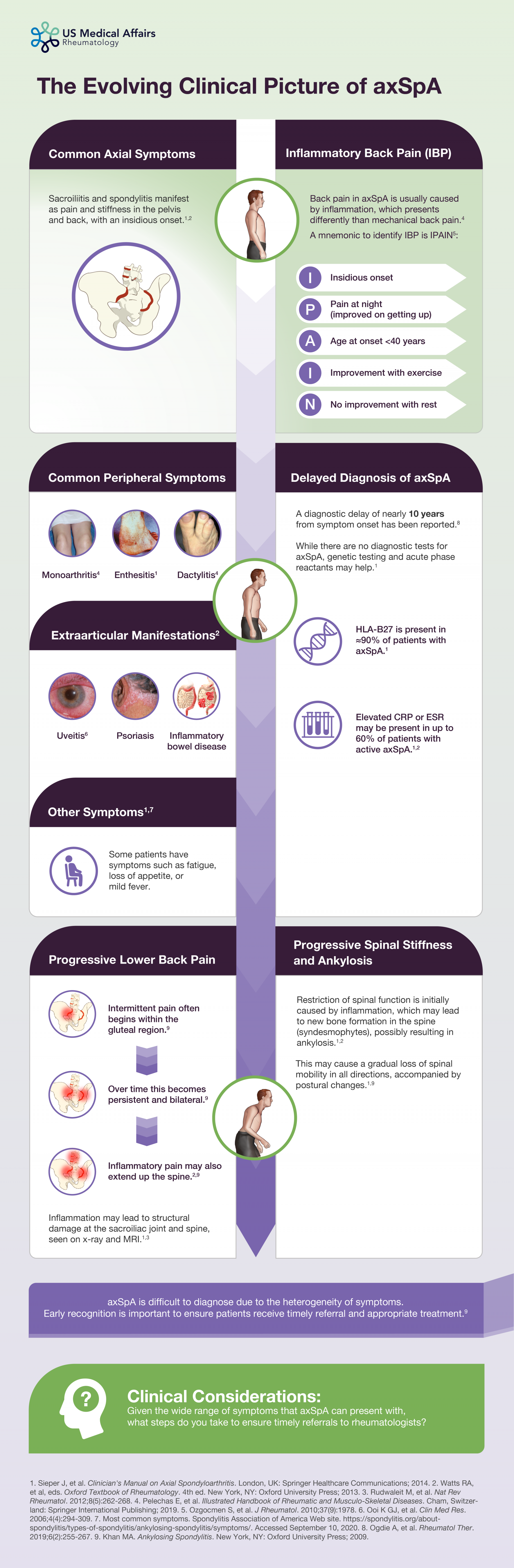
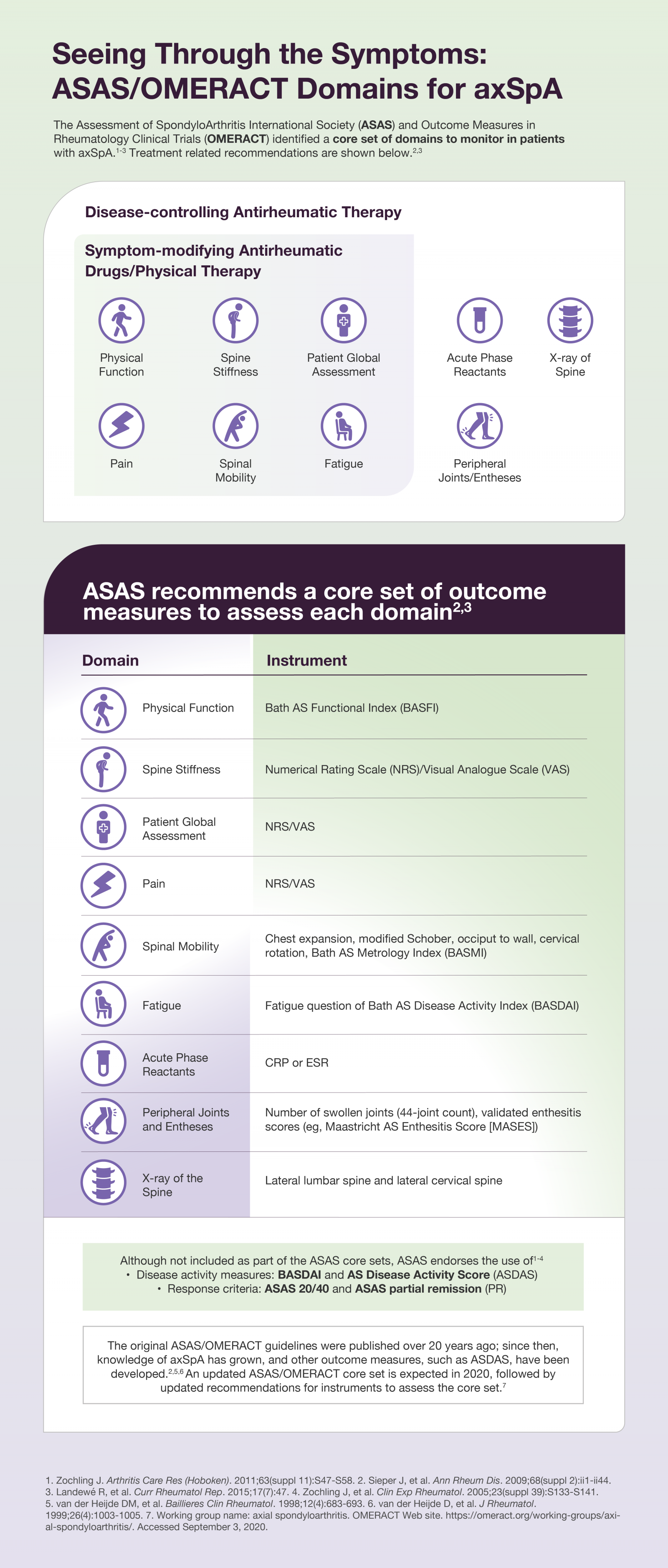
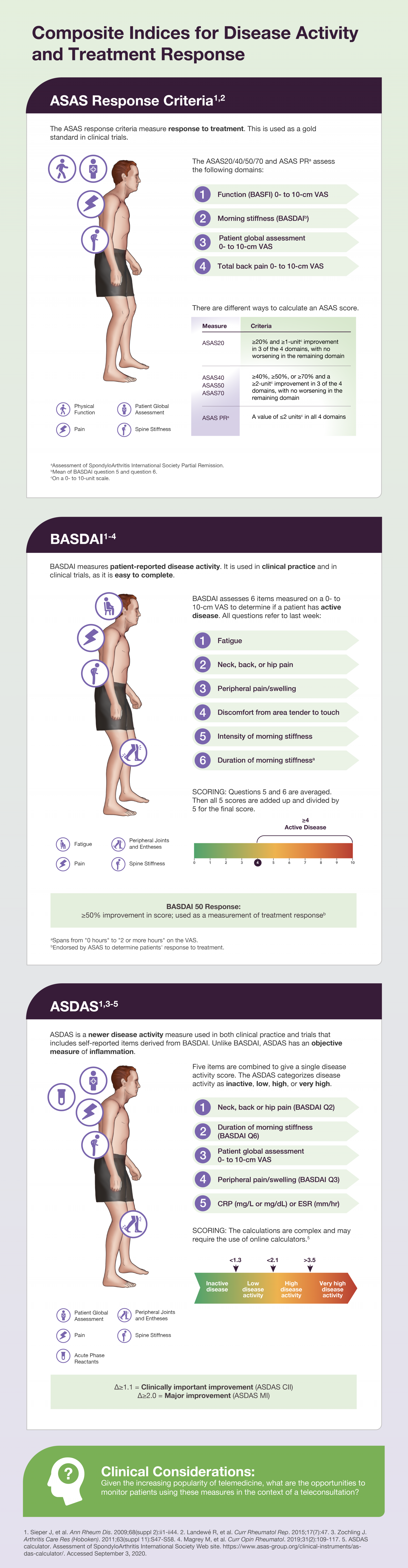
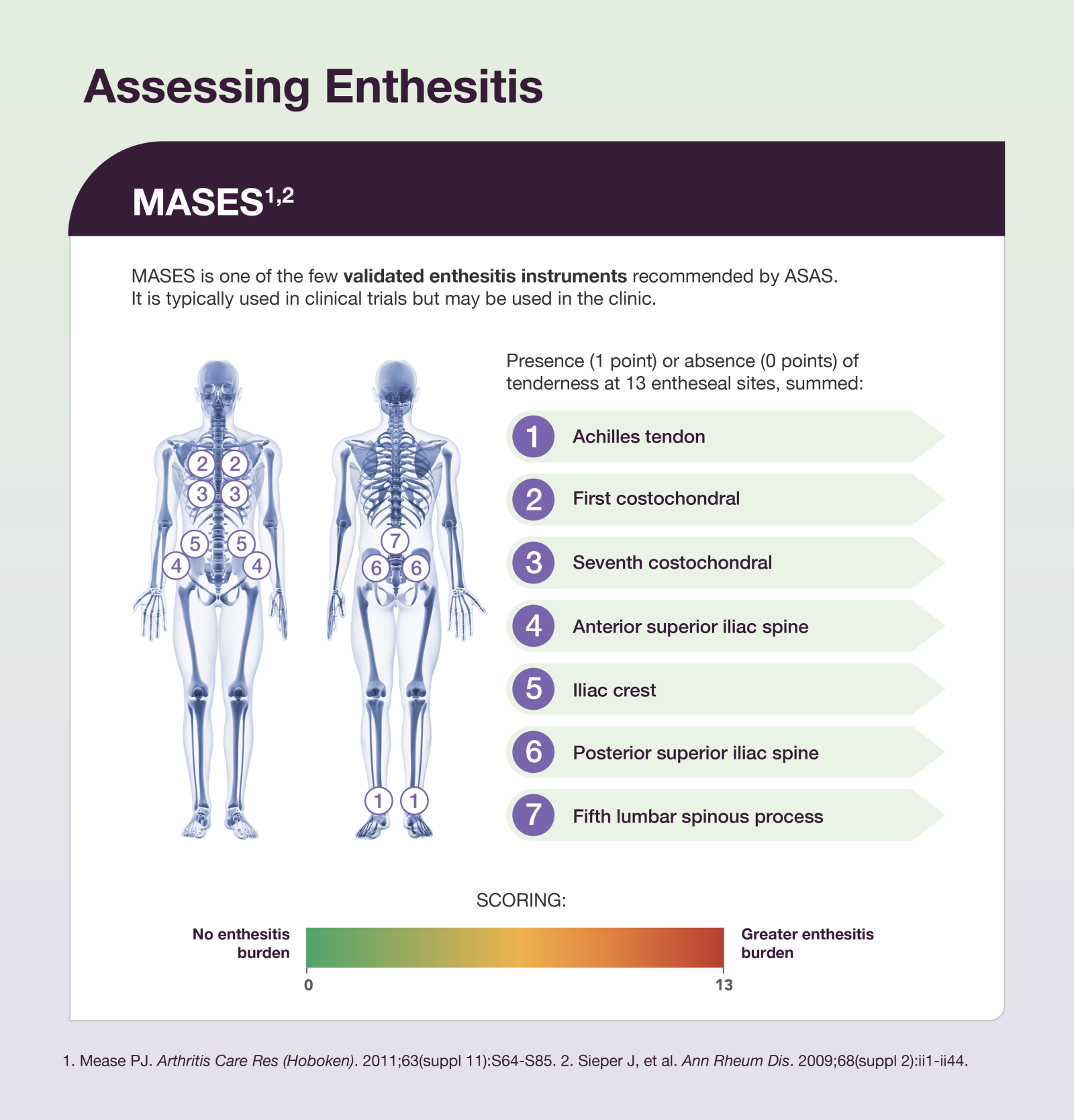
Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) diseases, consisting of radiographic axSpA (ankylosing spondylitis) and non-radiographic axSpA, are inflammatory arthritides that mainly affect the axial skeleton, particularly the sacroiliac joints and spine. Chronic inflammatory back pain and stiffness are often the most salient symptoms, although nonaxial symptoms accompany or may antedate axial symptoms. Enthesitis may also occur.1,2
Due to the heterogeneity of symptoms and lack of a single definitive diagnostic test, patients suffering from axSpA may cycle through different physicians, contributing to diagnostic delay. This delay can have profound effects on the patients, as untreated axSpA can lead to progressive functional impairment over time.1,3
1. Sieper J, et al. Clinician's Manual on Axial Spondyloarthritis. London, UK: Springer Healthcare Communications; 2014. 2. Watts RA, et al, eds. Oxford Textbook of Rheumatology. 4th ed. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2013. 3. Rudwaleit M, et al. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(5):262-268.
Click on the infographic below to view it in a separate tab.
Content developed by AbbVie Inc. This content is intended for US/PR Health Care Professionals. The US Medical Affairs department of AbbVie Inc. is the copyright owner of this presentation and has paid RheumNow to host this content.
AbbVie is solely responsible for all written and oral content within this presentation.
© 2020 AbbVie Inc. All rights reserved.
AbbVie Inc. ABBV-US-00217-MC
Approval Date: 09/2020 v1.0