All News
Preview of EULAR 2019 Abstracts
EULAR 2019 begins today in Madrid and features over 2000 presentations. After an initial review of titles and abstracts, I’ve compiled a hit list of presentations of interest to me and hopefully other practicing rheumatologists.
Read ArticleMore Trouble for Mallinckrodt’s Acthar Gel
Reuters has reported that Mallinckrodt Plc has tentatively agreed to pay $15.4 million to resolve a US Justice Department investigation into company promotional practices for Acthar gel.
Read ArticleRheumNow Podcast – Rituximab Monitoring (5.31.19)
Dr. Jack Cush presents the news and best of rheumatology and medicine from the past week on RheumNow.com
Read ArticleLupus Disease Control with Rituximab
Rituximab (Rituxan) may be an option for maintenance therapy in patients with difficult-to-treat systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), European researchers reported.
Read Article2019 EULAR Guidelines on Antiphospholipid Syndrome Management
A EULAR task force has reviewed the medical literature and developed evidence-based recommendations for the management of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) in adults. They note that a high-risk antiphospholipid antibody (aPL) profile is associated with greater risk for thrombotic and obstetric APS.
Read ArticlePredictors of Serious Infections with Rituximab
The risk of serious infectious events (SIE) with rituximab (RTX) is similar to that seen in other biologics (e.g., RA: 2% or 4.3/100PY), but with prolonged use the risk may change. Recent research says that low IgG levels, RTX induced neutropenia, prior SIE and comorbidities can significantly augment this risk.
A retrospective longitudinal single center study of 700 rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) treated monitored serum immunoglobulins (at baseline and 4–6 months after each cycle), clinical outcomes and SIE over time.
RheumNow Podcast – Medical Selfies (5.24.19)
Dr. Jack Cush Reviews the news and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow.com
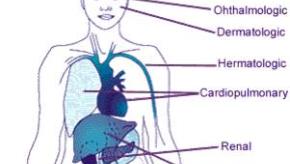
Read ArticleLupus Outcomes Influenced by Race/Ethnicity
A lupus registry from San Francisco County analyzed racial/ethnic differences in lupus manifestations and found significant differences in SLE manifestations among racial/ethnic groups. Researchers found that Blacks, Asians/Pacific Islanders (API), and Hispanics are more likely to develop severe manifestations following a diagnosis of SLE.
From their database, they identified 724 SLE patients, and identified specific features in different subgroups.
Nintedanib May Benefit Systemic Sclerosis Related Interstitial Lung Disease
The NEJM reports a randomized placebo controlled trial of nintedanib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in systemic sclerosis patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) resulted in less pulmonary decline, but had no effect on other features of systemic sclerosis.
Read ArticleRisk Score Predicts Thrombosis Recurrence in APS
A combination risk score helped predict recurrent thrombosis -- particularly arterial -- among patients with antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), an international study found.
Read ArticleRacial Disparities in Mortality Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
A Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report on a registry of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients from two Georgia counties (Fulton and Dekalb) shows SLE mortality was 2-3 times higher compared to the general population, especially amongst blacks; notably deaths occurred sooner after diagnosis
Read ArticleCalcineurin Inhibitors in Anti-Synthetase Dermatomyositis ILD
A pilot treatment study of patients with anti-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase antibody–positive polymyositis/dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease (anti-ARS-PM/DM-ILD) shows therapy with glucocorticoids and calcineurin inhibitors (CNI) to be highly effective.
Read ArticleBiomarkers Predict Thrombosis in Lupus
A composite risk score that included three biomarkers predicted thrombotic events among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a cross-sectional study found.
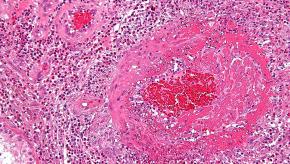
Read ArticleMonocyte Patrolling Contributes to Lupus Glomerulonephritis
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease with a propensity to develop glomerulonephritis (47-70%) or end-stage kidney disease despite therapy.
Read ArticleHigh GPA Hospital Readmission Rates
A national database reveals that patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) have 22.3% risk of hospital readmissions within 30 days of discharge.
From a total of 9749 hospital admissions with GPA, there were 2173 readmissions within 30 days of discharge.
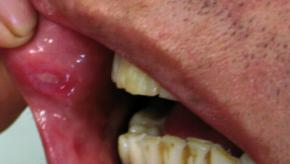
Read ArticleUstekinumab Effective in Behcet's Disease
A small prospective study has shown that ustekinumab is safe and effective in Behçet's disease (BD) with recurrent oral ulcers (OU).
Read ArticleImproved Survival in Lupus
A longitudinal study of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) from the Toronto Lupus Clinic has shown that mortality has decreased over time.
Read ArticleHigher Comorbidities in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
JAMA Dermatology reports that patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have significantly more comorbidities than do patients with psoriasis.
Read ArticleEULAR 2019 Update to Lupus Management
The goal of SLE treatment is remission or low disease activity and flare prevention. Hydroxychloroquine is recommended in all patients with lupus, at a dose not exceeding 5 mg/kg real body weight. Glucocorticoids (GC) should be minimised to less than 7.5 mg/day (prednisone equivalent). Appropriate initiation of immunomodulatory agents (methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate) can be tailored to the clinical scenarios and may allow for tapering or discontinuation of GC.
Read Article