All News
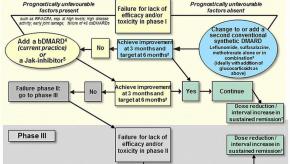
2016 EULAR Guidelines on RA Management
The management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has evolved significantly with time. Nevertheless, there are still some uncertainties - such as when, what and which biologic or novel therapy should be used.
Read ArticleThe RheumNow Week in Review - 6 October 2017
The RheumNow Week in Review discusses the past week's news, journal articles and highlights from RheumNow.com. In this week's report, Dr. Jack Cush discusses when to hold the biologic, lymphoma risk with tofacitinib, early clues to the diagnosis of RA, biologic use in pregnancy, what's killing psoriasis patients and the 2016 top 5, best selling drugs in rheumatology.
Read ArticleIBD Associated with Increased risk of Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases
A registry based study has shown higher rates of immune mediated diseases (IMD) in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Read Article29 September 2017 The RheumNow Week in Review
The RheumNow Week in Review discusses the past week's news, journal articles and highlights from RheumNow.com. This week's report discusses regulatory actions by NICE and FDA, higher death rates in RA and psoriasis, increased risk of RA with Asthma, rising numbers for OA, RA, and STDs.
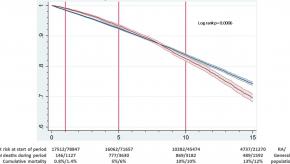
Read ArticleIncreased Deaths in RA, Despite Decreasing Mortality Rates
Data from the Swedish Rheumatology Quality (SRQ) Register studied death rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) between 1997 and 2014. Holmqvist and colleagues studied 17,512 RA and 78,847 matched controls from the general population, until their death.
Read ArticleNo Cancer Risk With Biologic Use
A polulation-based study from Sweden has shown that treatment with tocilizumab, abatacept, rituximab, or tumor necrosis factor (TNFi) inhibitors does not affect the risk of malignant neoplasms among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Specifically, use of a first or second TNFi or biologic DMARDs (bDMARD) does confer a different cancer risk when compared to conventional DMARDS in biologic–naive RA patients.
Read ArticleOsteoporotic Fractures as Back Pain in Older Men
The Journal of Bone and Mineral Research reports that older men with undiagnosed vertebral fractures are likely to report new or worsening back pain. (Citation source bit.ly/2y9rMiZ)
Read ArticleCDC: 40% of U.S Adults Claim to Have Arthritis
The CDC has reported its 2013 and 2014 prevalence statistics for arthritis and other chronic medical conditions affecting U.S. adults aged ≥18 years. Data is drawn from the ongoing Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS), a state-based, telephone survey of noninstitutionalized adults. Data herein is self-reported arthritis (OA, RA, Gout, FM) and is quantified by state and metropolitan areas.
Read ArticleMortality with Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Annals of Rheumatic Disease has published a Danish population based study demonstrating the high mortality rates seen with interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Read Article15 September 2017 The RheumNow Week in Review
The RheumNow Week in Review discusses the past week's news, journal articles and highlights from RheumNow.com. This week's report discusses metabolic syndrome in lupus, bisphosphonate holidays, vasculitis and vascular inflammation, vaccination, and the repeated wonders of Vitamin D.
Read ArticleSarcoid and Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Increased by Silica Exposure
A Swedish study has shown that occupational silica exposure increases the incidence rates of sarcoidosis and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in those exposed workers in Swedish iron foundries.
Read ArticleBiologic Use in Adult-Onset Still's Disease
Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is the adult continum of systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SoJIA). Treatment of this febrile polyarticular systemic disorder can be complex, but has been relieved by several specific biologic therapies.
Read ArticleNew Recommendations on Biosimilar Use
The introduction of a growing number of biosimilars into the market poses a substantial change in cost of care for patients with inflammatory rheumatologic disorders.
Read ArticleRheumatoid Arthritis Augments Cardiovascular Risk
A large multi-center study of cardiovascular (CV) risk factors in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has shown, after nearly 6 years follow-up, more CV events in males than females (21% vs. 11%, respectively) and that RA itself accounts for 30% of the attributable CV risk.
Read ArticleDo Rheumatologists Use ACR/EULAR Guidance on Rheumatoid Arthritis? “Live Vote” Results
The June 2017 RheumNow “Live Vote” surveyed US and non-US rheumatologists and patients about how they diagnose and treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and whether they rely on newer diagnostic criteria and management guidelines propagated by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
Read ArticleIncreasing Deaths and Breaking Bad with Fentanyl
Opioid overdose deaths quadrupled from 1999 to 2015 and accounted for 63% of drug overdose deaths in the United States in 2015. During 2010–2015, heroin overdose deaths quadrupled from 3,036 to 12,989, with heroin and illicitly manufactured fentanyl (IMF) as likely contributors to this trend.
Read ArticleWhat Can 30 Years of Rheumatic Disease Research Tell Us About the Future?
As a practicing rheumatologist for more than 30 years, I can recall a time – just a couple of decades ago – when waiting rooms were full of patients in wheelchairs, debilitated and in pain from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other related conditions.
Read ArticleTurnabout for Baricitinib
Eli Lilly and Company and Incyte Corporation announced today that, after discussions with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in late August 2017, Lilly will resubmit a revised New Drug Application for baricitinib before the end of January 2018. The resubmission package will include new safety and efficacy data.
Read ArticleShingles Vaccine Studies in A&R
The current issue of Arthritis & Rheumatology features an editorial and two novel articles on the herpes zoster vaccine.
Read ArticleCanakinumab Reduces CV Outcomes in High Risk Patients
The results of a randomized, double-blind trial have shown that canakinumab (CAN), an interleukin-1β inhibitor, given as 150 mg every 3 months, resulted in a significantly lower rate of recurrent cardiovascular events (in high-risk CV patients), independent of lipid-level lowering. The results of the CANTOS studywere simultaneously published in NEJM, Lancet and were presented at the European Society of Cardiology meeting in Barcelona.
Read Article