All News
RheumNow Podcast – COVID-19 Responds to Steroids (7.24.20)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the News and Journal Reports from the past week on RheumNow.com.
Read ArticleLow Risk of COVID in Biologic Treated Rheum Patients
In an Annals of Rheumatic Disease report, Italian investigators performed consecutive testing for SARS-CoV-2 (IgM and IgG) between 25 March to 25 May 2020 and compared test results between rheumatic disease (RMD) patients and the general population.
Read ArticleRapid Loss of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Mild Disease
According to a small, observational study out of UCLA published as correspondence in the NEJM on July 21, 2020, those with mild COVID-19 symptoms showed an approximate antibody half-life of 73 days.
COVID-19 infection was confirmed by PCR in 30 out of 34 study participants. The remaining four patients developed consistent symptoms and cohabitated with a person who had a known positive test but could not get testing due to availability or mild symptoms.
Higher Rates of SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity in the USA
The number of reporting cases of COVID-19 infection tends to underestimate the true prevalence of infection as only the more severe cases (e.g.,acute respiratory syndrome) get tested or go to the hospital. JAMA Internal Medicine reports that a cross-sectional seroprevalence study from the U.S. shows that COVID-19 is underreported and that actual infection rates can be 6 to 24 times more prevalent than currently reported infections due to SARS-CoV-2.
Read ArticleSteroids and Tocilizumab in Cytokine Storm Syndrome
A recent study from the Netherlands has shown that patients with severe COVID-19-associated cytokine storm syndrome (CSS) with high dose steroids and tocilizumab had a faster recovery, less need for invasive mechanical ventilation and fewer deaths when compared to CSS patients receiving supportive care only.
They studed COVID-19 patients with CSS, defined as rapid respiratory deterioration plus at least two of the following biomarkers: a) C-reactive protein >100mg/L; b) ferritin >900 µg/L; or c) D-dimer >1500 µg/L.
RECOVERY Trial: Dexamethasone in COVID-19
Inflammatory events following infection with SARS-CoV-2 can often worsen the morbid or mortal outcomes with COVID, yet it has been unclear if glucocorticoids may modulate inflammation-mediated damage and lung injury. The RECOVERY trial reports that dexamethasone (DEX) use lowered 28-day mortality among COVID-19 patients requiring respiratory support.
The RECOVERY trial was performed in the UK and enrolled hospitalized COVID-19 patients who were randomly assigned patients to usual care alone or the addition of oral or intravenous dexamethasone (at a dose of 6 mg once daily) for up to 10 days. The primary outcome was 28-day mortality.
Characteristics Underlying Mortal COVID-19 Outcomes
From January 1, 2020–May 18, 2020, approximately 1.3 million cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and 83,000 COVID-19–associated deaths were reported in the United States.
Read ArticleRheumNow Podcast – LTF – Listen to Fauci (7.17.20)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news, tweets and journal articles from the past week on RheumNow. Let's dig into this week's 14 highlights.
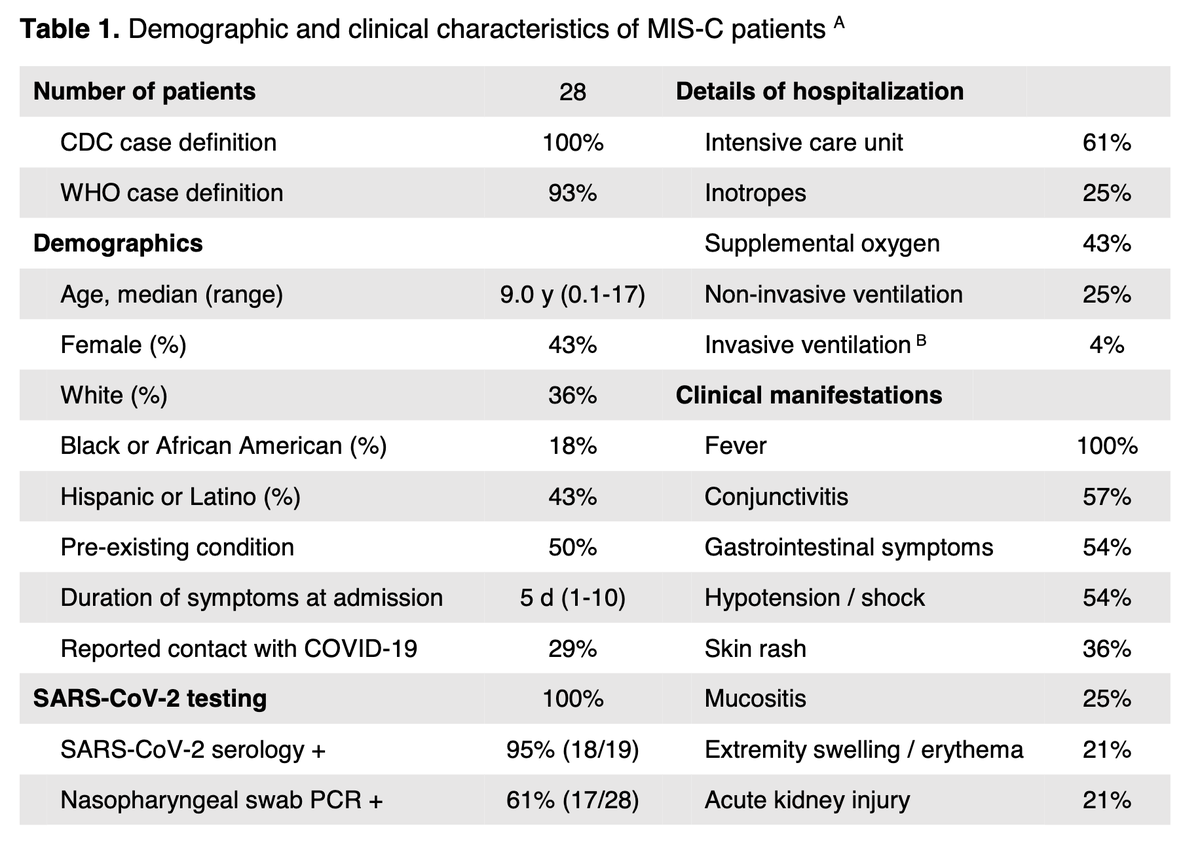

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

NEJM NEJM ( View Tweet)

Mohammad A. Ursani MD, RhMSUS DrMAUrsani ( View Tweet)

Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Jeff Sparks jeffsparks ( View Tweet)

Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Victoria Shanmugam VickiShanmugam ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)

Links:
Dr. John Cush RheumNow ( View Tweet)