Methotrexate's Low Efficacy in Cutaneous Psoriasis Save
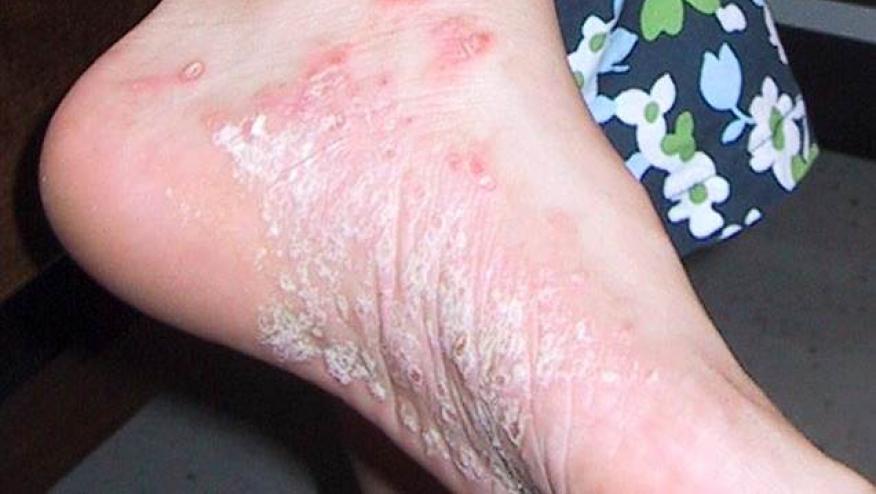
In a prospective, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled study, Warren et al. studied the effect of an intensified methotrexate (MTX) in chronic plaque psoriasis and showed MTX to be effective and superior to placebo.
A total of 120 patients who were MTX-naive adults with active plaque psoriasis patients were randomized to receive 16 weeks of subcutaneous injections of either methotrexate (17.5 mg/wk) or placebo. MTX doses could be escalated to 22.5 mg per week after 8 weeks if patients did not achieve ≥ PASI50% improvement. All patients received folic acid 5 mg per week.
A PASI 75 response was achieved in 41% of MTX treated but only in 10% of placebo treated patients (P = 0·0026) by week 16. Subcutaneous methotrexate was generally well tolerated, with no serious adverse events related to this treatment over the 52-week study.
Other analyses and skin biopsies at baseline and week 16 showed MTX clinical effect were mediated by decreases in CD3+ lymphocytes and T helper 17 cell-mediated cytokine transcription.
The authors note that these results are in line with other MTX trials in psoriasis, showing PASI 75 responses of 36–42% i 3 previous studies using oral methotrexate. Nevertheless, these results are far less than that achieved using biologic therapies, especially the IL-17, IL-23 adn IL-12.23 inhibitors.








If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.