APEX Study: Inhibition of structural damage progression with Guselkumab in Psoriatic Arthritis Save
Guselkumab, a human IL-23 inhibitor, was evaluated in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and shown to have both clinical and radiographic benefits at weeks 24 and 48.
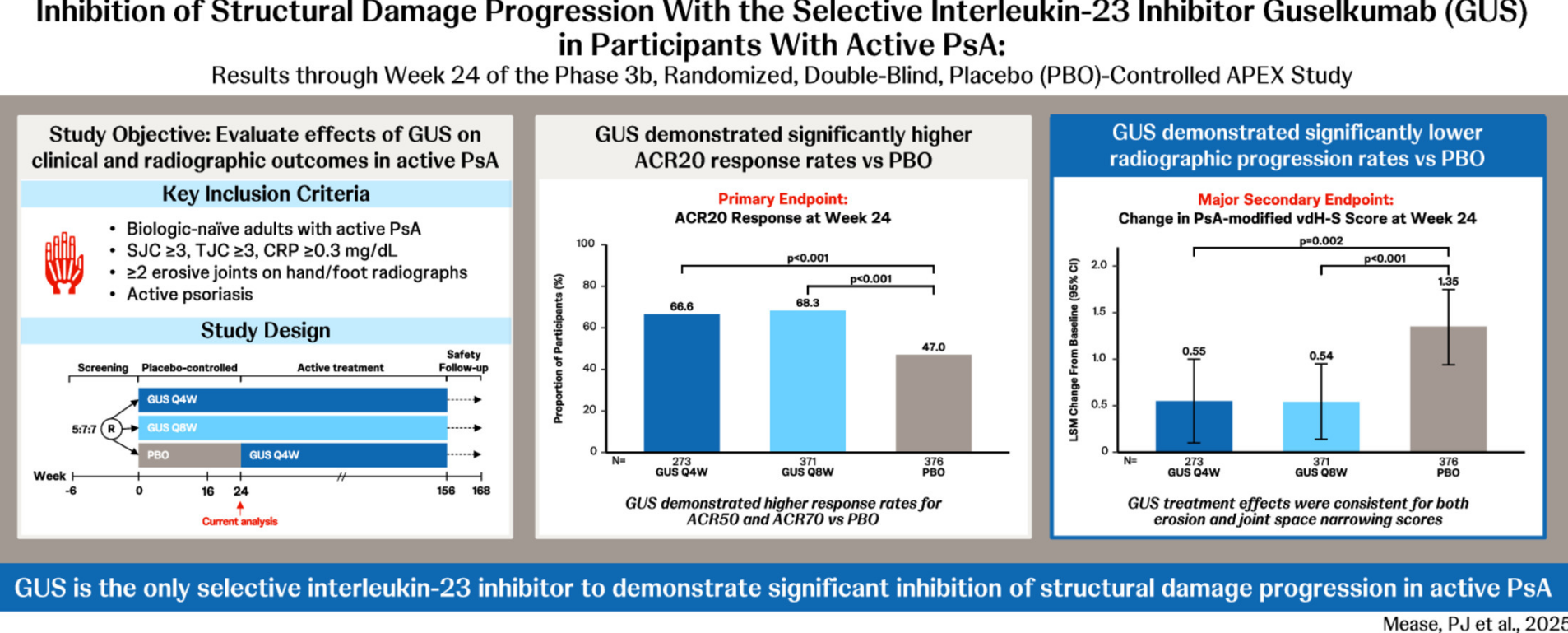
The APEX study was a phase 3b, double-blind, placebo-controlled, trial in biologic-naïve active PsA patients (≥3 tender, ≥3 swollen joints; C-reactive protein ≥0.3 mg/dL; ≥2 erosive joints). Patients were randomised to subcutaneous guselkumab (GUS) 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); guselkumab 100 mg at week 0, week 4, then every 8 weeks (Q8W); or placebo every 4 weeks. Primary outcome was the ACR20 response at week 24.
From a total of 1020 PsA patients, ACR20 responses were superior for GUS Q4W (66.6%) and GUS Q8W (68.3%) compared to placebo (47.0%) achieved ACR20 at week 24 (P < 0.001). Likewise, GUS Q4W- and Q8W-treated participants had significantly lower rates of radiographic progression versus placebo at week 24 (total vdH-S score LSM change: 0.55 and 0.54 vs 1.35; P = 0.002 and P < 0.001, respectively).
In a recent press release, data continued to show the clinical and radiographic benefits our to week 48. These data were presented at the Inflammatory Skin Disease Summit (ISDS) 2025.
ADD THE FIRST COMMENT
Disclosures
The author has no conflicts of interest to disclose related to this subject










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.