Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Rheumatic Disease Save
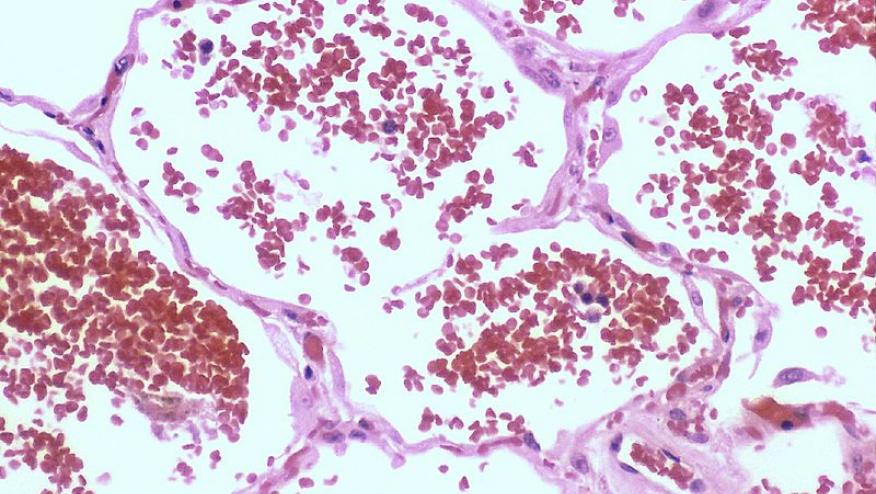
A retrospective, cross-sectional, single-center study of adult rheumatic disease patients with diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH), demonstrates a high proportion have coexistent pulmonary infection and significant mortality risk.
DAH is an uncommon but potentially life-threatening pulmonary complication in patients with rheumatic diseases. This analysis assessed the prevalence and factors associated with DAH with and without pulmonary infections in RD patients.
A total of 73 DAH patients with DAH were included; 31.5% had concurrent pulmonary infection.
The most common rheumatic disorders were systemic lupus erythematosus (68.5%) and ANCA-associated vasculitis (29%). Evidence of hemorrhage in bronchoalveolar lavage was more frequently observed in those with lung infections(76% vs. 48%; p = 0.02).
Among the pulmonary infections, bacterial infection was the most common (62%), fungal infection (21%).
Although the 30-day mortality rate was 10%, and infection was not an independent predictor of death.
Pulmonary infection in DAH patients was more likely to be seen in males (OR 9.8) requiring mechanical ventilation (OR 8.8).
This study underscores the need to assess for infection in RMD patients presenting with DAH.










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.