All News

Age of onset is really important when thinking about #MAS
Primary HLH more frequent in pediatric population. But can continue to adulthood.
#EULAR2025 @RheumNow https://t.co/J7xmTiQiwr
Bella Mehta bella_mehta ( View Tweet)

MAS can be triggered by infections in VEXAS syndrome. The threshold is reached leading to a hyperinflammatory state
Georgin-Lavialle S @rheumnow #EULAR2025 https://t.co/NKLL75rOgP
Links:
Antoni Chan MD (Prof) synovialjoints ( View Tweet)

#infections in #JAKi
@drdavidliew
#JAKi sl ⬆️ infection risk vs #TNFi
⬆️HZ w JAKi
JAKi same risk w #latent #TB #LTBI and new TB ⬇️in JAKi v bDMARDs
He didn’t discuss TYK2i
Reassuring - risk⬇️ over time for infection
@RheumNow #EULAR2025 @eular_org
JAKi & infection https://t.co/KVsY2gXVkQ
Links:
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)
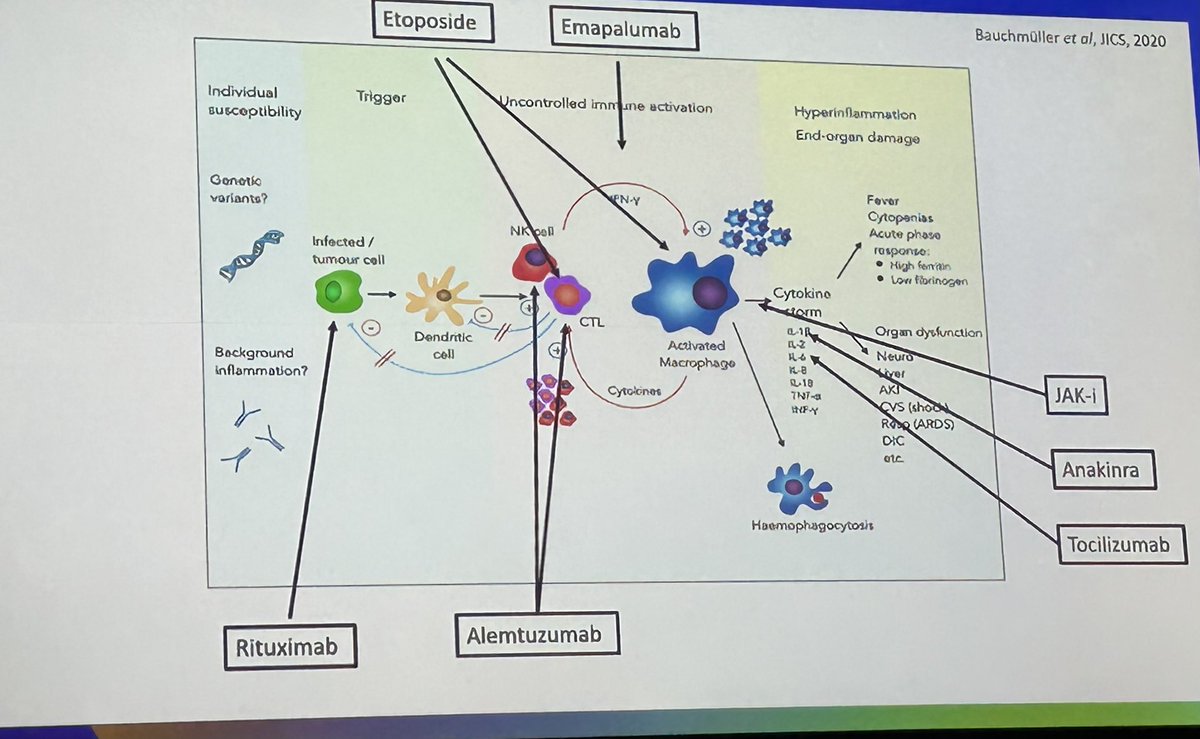
Management of HLH/MAS and modes of action of advanced therapies
Jessica Manson @RheumNow #EULAR2025 https://t.co/Op3u53ZXeK
Links:
Antoni Chan MD (Prof) synovialjoints ( View Tweet)

JAKi: expanding RMD indications—but important safety concerns to consider
⚠️ Cancer: Neutral vs MTX/placebo, ↑ risk vs TNF
⚠️ Infection: ↑ with age, disease activity & GC use—not uniformly higher with JAKi
🗣️ Patients rank infection risk as top concern
@rheumnow #EULAR2025 https://t.co/RJRDWQjqNC
Links:
Jiha Lee JihaRheum ( View Tweet)

Age & dose ⬆️ infections in JAKi
Not all JAKi are created w equal risk
@RheumNow @eular_org #EULAR2015 @drdavidliew
#JAKi & #infection https://t.co/F7zLUBuzJR
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)

Stabilize the pts with HLH with steroids when still trying to figure out the diagnosis of #HLH/ #MAS
Many drugs can be used...but important to balance infection risk with immunosuppression
These are critical pts. Be vigilant..
#EULAR2025 @RheumNow https://t.co/id4ae3SWtj
Links:
Bella Mehta bella_mehta ( View Tweet)

3 Fs of diagnosis of #HLH
-Fever
-Ferritin
-Falling blood count
Raising awareness is the key! Especially in rare diseases like this where the morbidity and mortality is super high!
Collaboration between specialists help
HLH networks will be helpful like this
@RheumNow #EULAR2025 https://t.co/HWbvIma3yx
Bella Mehta bella_mehta ( View Tweet)

In #axSpA post #TNFi-IR
What to use next?
👇
#ATTRA registry
90% #SpA on #bDMARDs are captured
Comparison of
TNFi to ▶️
2nd TNFi vs
#IL17i
▶️No diff in #retention
✅better #BASDAI and other outcomes w TNFi!
❎less safety
🤔
#EULAR2025 @RheumNow @eular_org
Abst#POS0116 https://t.co/7mqFfD4Amf
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)

#Cancer is not ⬆️in JAKi vs #bDMARDs in
#rheumatoid #arthritis
When adjusted for #confounders
#JAKPOT data
Now you see it (unadjusted ⬆️risk)
Now you don’t (adjusted =#malignancy)
JAKi vs bDMARDs in RA
EULAR2025 @RheumNow @eular_org
#JAK it out! new perspective on JAKi https://t.co/wCQ3dHNAVa
Links:
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)

Rheumatology #AI to optimize rheumatology triage. Only 53 percent correlation between the AIs diagnosis with rheumatologists final diagnosis. Not sure if we want 47 percent pts to drop off...without a chance for diagnosis?
#POS0883 #EULAR2025 @RheumNow https://t.co/UWsCHG00t1
Bella Mehta bella_mehta ( View Tweet)

Are we all going to be replaced by robots?
Not just yet
ARTHUR trial: the robotic ultrasonographer
vs. human
While the concept is promising, and ICC with humans were low to moderate, the robot is overestimating grey scale scores in MCPs of both HC and RA pts
#EULAR2025 https://t.co/mTtbknu0lO
Links:
Aurelie Najm AurelieRheumo ( View Tweet)

Treatment strategies for steroid free management of #relapsingpolychondritis
56 patients from a single center
#POS0149 #EULAR2025 @RheumNow https://t.co/d4I56opS02
Bella Mehta bella_mehta ( View Tweet)

Multimodal data using clinical histological and serological predictors in renal function in #sle nephritis. Using the AMP SLE data.
Low baseline eGFR and histological damage predicted worsening renal function but not NIH activity index
#POS0173 #EULAR2025 @RheumNow @andreafa https://t.co/Eh8dZXHRVX
Links:
Bella Mehta bella_mehta ( View Tweet)

#D2T #RA ~20%
#Polyrefractory 3%
Many reasons for d/c ing #Rx - D2T
AEs
Intolerance
Chronic pain
Etc
My approach is different depending on reasons why drugs were d/c
Ie ?obj inflammation vs pain or intolerance
@RheumNow @eular_org #EULAR2025
#whatmakes D2T RA difficult https://t.co/AL6TMVJIk9
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)

Would you use #CAR-T in #polyrefractory #RA
#EULAR2025 @RheumNow @eular_org
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)

POS0150: From 12 RA registries, JAKi starts fell by ~13% after FDA safety alerts.
Tofa & bari took biggest hits; upa growth slowed but offset losses.
Real-world prescribing adapts—but doesn’t abandon.
@RheumNow #EULAR2025 https://t.co/QZ5haW2vhX
Jiha Lee JihaRheum ( View Tweet)

?fishing for + results #EULAR2025
⚠️opinion
be aware that results do not live or die on P values
Impt findings beyond primary endpoints may be Impt beyond P<0.05
Conversely
Unexpected P values in a database
❎interpret w caution
Consider as hypothesis only
@RheumNow
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)

Ultrasound for ILD detection in RA 🫁
Sens 88.6
Spe 92.8
NPV 91.4
PPV 90.7
While if abnormal or high suspicion, HRCT should be the reference, I see this as an interesting tool in clinics for quick screening
POS0180 #EULAR2025 @RheumNow https://t.co/pUy0ki7Y6S
Links:
Aurelie Najm AurelieRheumo ( View Tweet)

#HOT topic
Lung 🫁 #ultrasound for #RA #ILD
#LUS B lines vs HRCT
Single site 🇫🇷 study
V sensitive & specific
🤔needs standardization & comparison in other groups
Abst#POS-180
#EULAR2025 @RheumNow @eular_org https://t.co/PwGE4rgk40
Janet Pope Janetbirdope ( View Tweet)



