Barriers to Treat-to-Target in Rheumatoid Arthritis Save

A systematic and scoping literature examined the Treat-to-target (T2T) approach to rheumatoid arthritis (RA), noting its implementation is suboptimal and finding many barriers to implementation.
The review by Gossec et al, identified 146 relevant articles, 329 relevant statements, 56 interventions and 18 target issues, including: healthcare professional and patient knowledge or perceptions; communication or alignment; time and resources. Of these 54% addressed disease activity or patient outcomes. Of the 56 interventions, 36 improved T2T implementation or patient outcomes in RA.
Key points of the review:
- T2T approach is still suboptimally implemented in clinical practice
- Despite interventions to improve T2T, there is limited evidence for their direct impact on implementation and patient outcomes
- Many interventions were designed to ease activity reporting, PRO outcomes, shared decision-making, or the burden of time aquistion
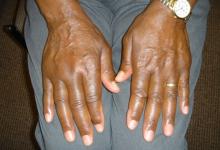
Barriers are related to patients, providers or both. There were numerous challenges to T2T, including physician adherence, patient willingness, comorbidities, communication, healthcare system, patient and physician perceptions disease assessment and tools/time/resources. Communication, education, perceptions, interpersonal relationships and social determinants of health remain problematic.
Significantly more research and effort is needed to improve T2T implementation in RA. T2T efforts may need to be tailored to individual different geographies, populations and healthcare settings.










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.