All News
New Treatments for Systemic Sclerosis
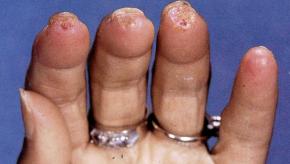
Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (aHSCT) for SSc has been proven the most effective treatment strategy with regard to overall and event free survival in selected patients.2 But a key limitation is its toxicity, and new treatment options are needed.
Read ArticleIs Cannabis Safe? (6.7.2024)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews FDA approval, news and journal articles -- and it’s the week before EULAR 2024 in Vienna!!
Read ArticleThe Window of Opportunity (5.24.2024)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the journal reports and news from the past week on RheumNow.com. This week: blockbuster drugs, opioids in rheumatology and nontreatment of inflammatory arthritis?
Read Article"Don't You Know Who I am?" (5.17.2024)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports from the past 2 weeks. This week's question: can we prevent gout, ILD or psoriasis?
Read ArticlePharmacologic Efficacy in Still's Disease
A systematic review of the effectiveness and safety of pharmacological treatments for adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) supports the use of either IL-1 or IL-6 inhibitors.
Cutoffs for Systemic Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score
An international cohort of children with systemic Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (Still's disease) validated the systemic Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score 10 (sJADAS10), a disease activity measure distinguish patients with inactive disease, minimal disease activity, moderate disease activity, and high disease activity.
Read ArticleImaging-Only Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis Is Feasible
Positive findings with color Doppler ultrasound were enough to diagnose giant cell arteritis (GCA) accurately without need for confirmation with temporal artery biopsy (TAB), a prospective study indicated.
Read ArticleFeatured BSR Abstracts (5.2.2024)
Dr. Jack Cush muses on the news, journal reports, FDA announcements and the 2024 BSR abstracts just released.
Read ArticleMethotrexate Does Not Increase ILD Risk in Dermatomyositis
A cohort analysis of dermatomyositis (DM) patients starting immunomodulators finds that methotrexate use was not associated with an increased risk of interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Read ArticleRheum Chapter Notes (4.26.2024)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews this past week’s news and journal articles from RheumNow.com.
Read ArticleCanary in a Coal Mine (4.19.2024)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews regulatory reports, news and novel journal articles - this week focusing on Sjogren's, ILD, Gout and Uveitis.
Read ArticleBurnout or Retire (4.12.2024)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports from this past week on RheumNow.com. Is it time to worry about burnout and those who are leaving healthcare?
Read ArticleILD Onset in MDA-5 Dermatomyositis
Anti–melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) antibody-positive dermatomyositis (DM) is a rare, aggressive and progressive subtype of DM.
Read ArticleNeuropsychiatric SLE - 2/3 Improved at 12 Months
The management and outcomes of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE) can be challenging as there is limited data.
Best Imaging in Giant Cell Arteritis - US, PET, MRI?
Imaging is often instrumental in diagnosing and staging patients diagnosed with giant cell arteritis (GCA).
Read ArticleSeasonal Pathogens and Henoch-Schönlein Purpura
Epidemiologic studies of Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP) have suggested seasonal variation in occurrence rates (higher from September-April, lower in June-August), suggesting a role for infectious triggers.
Read Article1/600 Falls May Die (4.5.2024)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and Journal reports from this past week on RheumNow.com - including problems w/ falls, pain and treatment of Dupuytren’s contractures.
Read ArticleSerious Infections in Takayasu arteritis
The large vessel vasculitis, Takayasu arteritis (TAK), carries a significant morbid risk and a cohort analysis shows these patients are also at high risk of serious infection with resultant higher risk of death.
Systemic Score Predicts Still's Disease Severe Complications
A multinational study of adults with Still's disease found that calculating their systemic score at baseline significantly predicted the patients risk for life-threatening outcomes (MAS or death).
Predicting Vasculitis Relapse
Scores on a patient-reported sino-nasal symptom questionnaire were associated with subsequent flares of one type of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), researchers said.
Read Article