Antibiotics Increase Rheumatoid Risk - Again Save
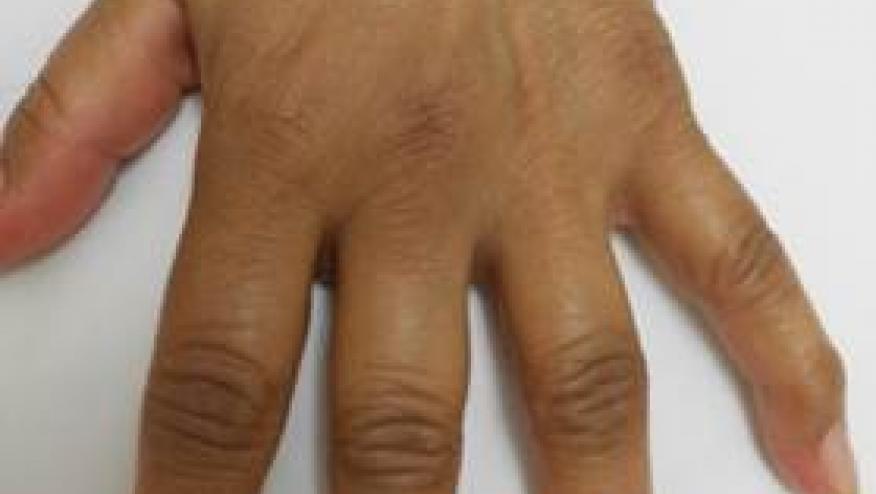
Another UK study has suggested that prior use of antibiotics increases the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Rheumatology has published a 15 year case–control study that compared 8482 newly diagnosed RA patients and 22,661 controls from the UK’s Royal College of General Practitioners Research and Surveillance Centre database (between 2006 and 2018).
Antibiotics were associated with a dose related risk of an RA diagnosis. Patients receiving >10 antibiotics in a 5 year period were more than twice as likely to receive an RA diagnosis as controls [adjusted odds ratio 2.65 (CI 2.40, 2.93)].
Exposure to antibiotics prior to the diagnosis was a significant risk factor for RA. This was previously reported by the UK Clinical Practice Research database examined 22677 RA pts. (1995–2017) showing antibiotic exposure increased the risk of RA by 60% (OR 1.60; 95% CI 1.51–1.68). Both studies postulate the potential of antibiotics to unfavorable lead to microbiome changes conducive to developing RA or autoimmunity.










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.