T2T Improves Primary Care Gout Management Save
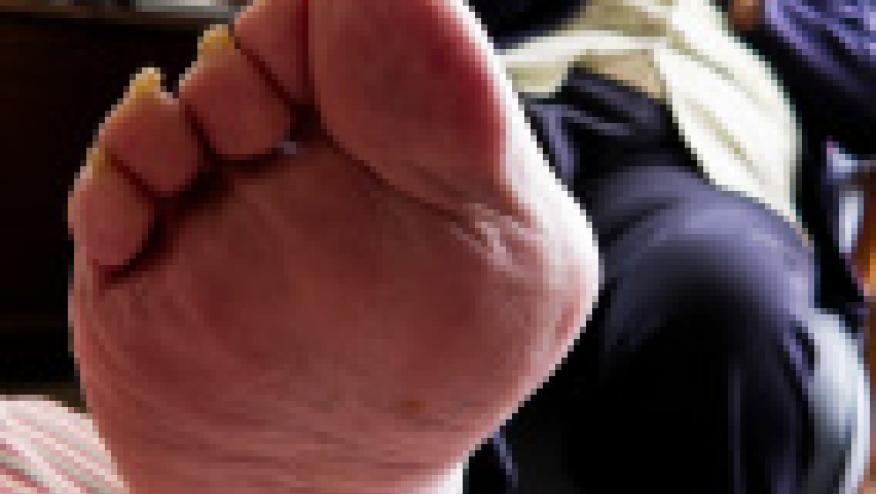

Researchers from Geisinger Medical center tested a pilot primary care gout management improvement intervention, and demonstrated significantly improved primary care gout management metrics when a treat to target approach was implemented.
They studied 2 large primary care sites - one underwent the intervention, the other/control, did not. The gout management plan ("intervention") included education of the intervention staff and EMR to assess outcomes; 1) percent of gout patients treated with urate lowering therapy; 2) percent of treated patients monitored with serum urate; and 3) percent of treated patients at target serum urate ≤ 6.0 mg/dl. The intervention site providers received monthly performance reports compared to their peers.
At 6 months, the intervention site significantly improved all 3 gout performance measures.
- ULT use increased from 54.4 to 61.1%, OR 1.19 (95% CI 1.08, 1.31 and p-value <0.001);
- Monitoring increased from 56.1 to 79.2% OR 1.52 (95% CI 1.24, 1.87 and P-value <0.001);
- Achieving a T2T goal (< 6.0) increased from 26.8 to 43.3% OR 1.43 (95% CI 1.16, 1.77 and p-value <0.001.
At 6 months gout patients at the intervention site were 3.5 times more likely to be monitored and 2 times more likely to achieve their urate goal (p-value <0.001) than control site patients.








If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.