Oral IL-23 Inhibitor Effective in Psoriasis Save
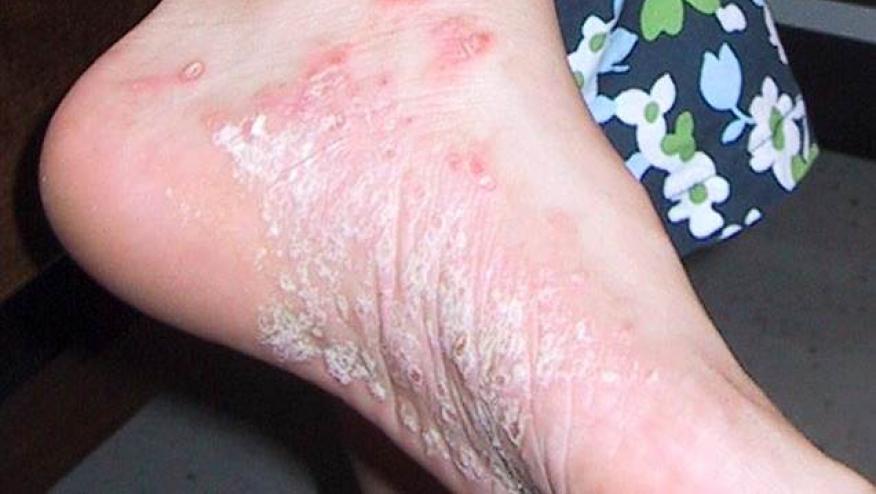
The NEJM has published the results of the FRONTIER 1 trial demonstrating the efficacy of JNJ-77242113, an oral interleukin-23 (IL-23) receptor antagonist peptide, in patients with psoriasis (PSO).
This phase 2 dose-finding trial randomized 255 PSO patients, with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, to receive either placebo or study drug (25 mg qd; 25 mg bid; 50 mg qd; 100 mg qd, or 100 mg bid for 16 weeks. The primary end point was achieving at least 75% in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score (PASI 75 response) at week 16.RESULTS
Patients had active PSO with a mean PASI score at baseline was 19.1. The disease duration was 18.2 years, and 78% of patients previously received systemic treatments. At week 16 PASI 75 response for placebo was 9%, but was significantly higher with JNJ-77242113:
- 25 mg qd: 37%
- 25 mg bid: 51%
- 50 mg qd: 58%
- 100 mg qd: 65%
- 100 mg bid: 79%
The most common adverse events included COVID19 (12% PBO; 11% JNJ-77242113 dose groups) and nasopharyngitis (PBO 5% and JNJ 7%,). There was no dose-related increase in adverse events across the JNJ-77242113 dose groups.
An orally administered, peptide against IL-23 was shown to be effect in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, in this phase II trial.










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.