Eczema May Respond to Tofacitinib Save
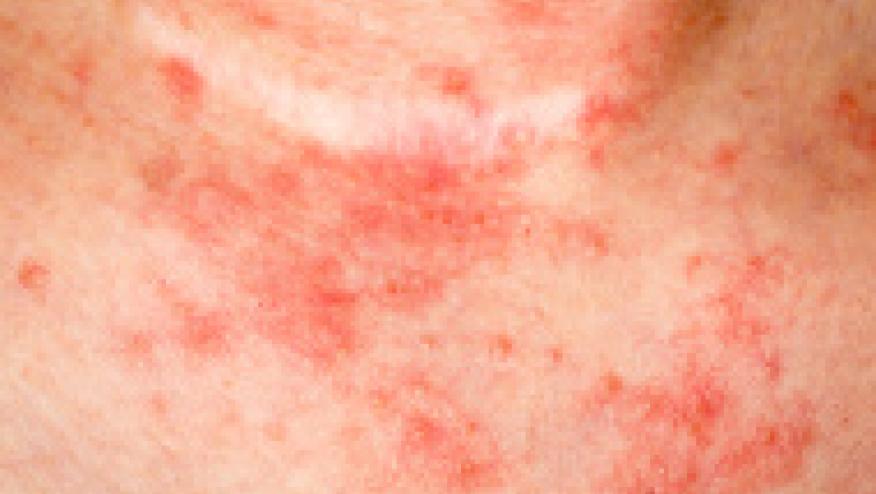
A recent report from the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that the oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib to be effective in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.
Six patients with eczema had all failed standard atopic dermatitis treatment. The patients were treated with tofacitinib and their response to the treatment was assessed using the Scoring of Atopic Dermatitis index. All patients improved sleep and reduced itch significantly. The patients also showed reduced redness and thickening of the skin. The scoring index decreased 66.6% (from 36.5 to 12.2) between weeks 8 and 29.
These uncontrolled reports of tofacitinib success are similar to promising results in other skin disorders, such as alopecia universalis and atopic eczema. Future larger trials are being planned.










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.