Interleukin-37 Targeting in Gout Save
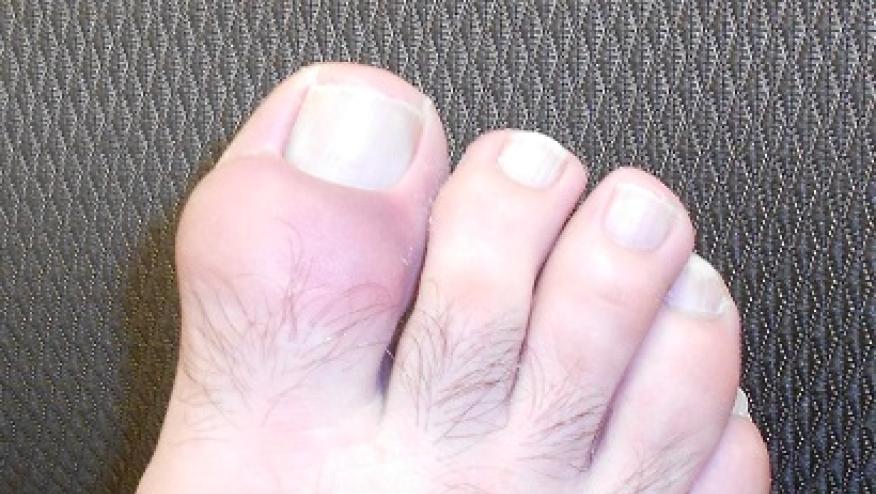
The Annals of Rheumatic Disease reports that interleukin- 27 (IL-37) may play an important role in the pathogenesis of gout, paving the way for future therapy with recombinant IL-37 in gouty arthritis.
Activation of the inflammasome by monosodium urate crystals is thought to be paramount to the innate immune response that drives IL-1-mediated joint inflammation in gout.
New research has focused on IL-37 - as it is a counterregulatory cytokine capable of suppressing IL-1 activity.
They studied 6 gout patients and found 4 rare variants in IL-37 [p.(A144P), p.(G174Dfs*16), p.(C181*) and p.(N182S)]. None of these were found in healthy controls (p=0.043). A
Treatment with recombinant IL-37 was evaluated in vitro and in vivo in a mouse model of gout and showed that recombinant IL-37 attenuated inflammation - substantiating the therapeutic potential of IL-37 in gout.
They also showed that the carrier status of p.(N182S)(rs752113534) was associated with increased risk (OR=1.81, p-value=0.031) of developing gout in hyperuricaemic individuals of Polynesian ancestry.
There may be a future role for therapeutic rIL-37 use in the treatment of gout.








If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.