Recurrent Uveitis Increases the Risk of Ankylosing Spondylitis Save
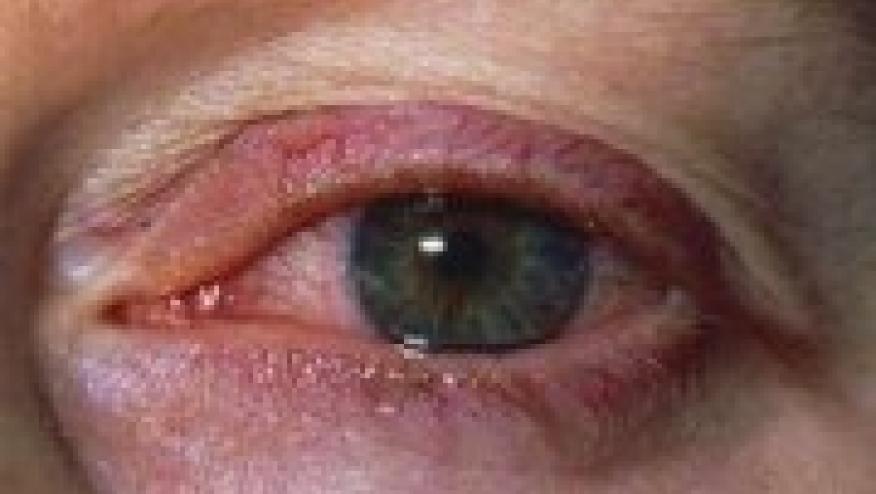
Arthritis Research and Therapy reports on the epidemiologic association between recurrent anterior uveitis and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) noting that as the number of uveitis episodes increases, so does the incidence of AS.
Uveitis is the most common extra-articular manifestation of AS, occurring in up to 40% of AS patients. As such AS-related anterior uveitis may first present to the ophthalmologist, not by a rheumatologist. These investigators asked the question - how oftent does recurrent anterior uveitis result in subsequent AS.
A national cohort of10,483 patients with new-onset uveitis (seen between 2004 -2013) was compared to 52415 matched control subjects (never had uveitis).
After the first uveitis episode, the AS risk was 7 fold higher (incidence rate ratio = 7.4 compared to normal controls).
After the the second uveitis episode, the IRR further increased to 17.71. High rates of AS were seen in both male and female patients with recurrent uveitis (IRR 284.1 and 268.7 per 100,000 person-years, respectively.
As disease controls, patients with RA or herniatiated vertebral discs did not show a correlation with the occurrence or recurrence of uveitis.
The risk of subsequent AS increased with the number of episodes of anterior uveitis.










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.