Sons of Gout Study Save
The genetics and heritability of gout has suggested a higher risk in certain families. A UK cohort study examined the prevalence of gout and monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition among those at risk (sons of gout patients) for gout and found a high incidence of hyperuricemia and MSU crystal deposition.
The sons of patients with gout (n=131) were contacted, screened by telephone and subsequently had a study-visit evaluation for blood and urine collection, and musculoskeletal ultrasonography (MSK US).
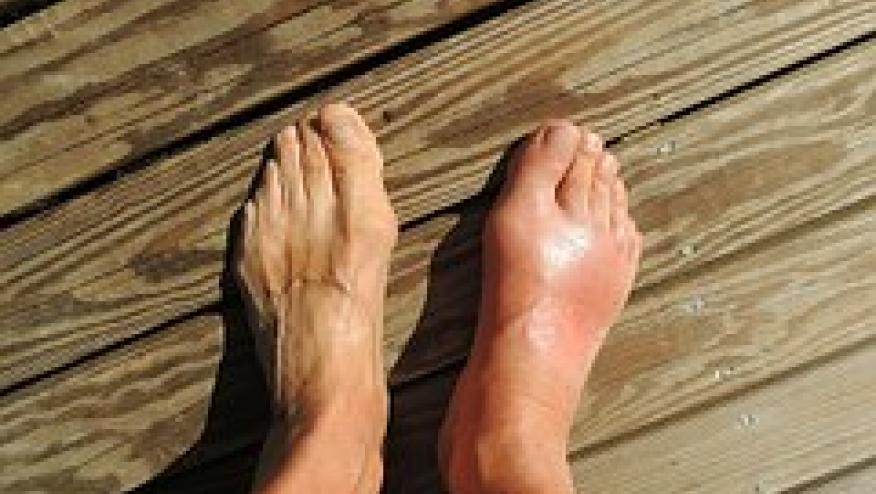
Amongst 131 sons of gout, 64.1% had serum urate (SU) ≥6 mg/dl, and 30% had MSK US evidence of either a double contour sign (DCS) or intra-articular aggregates/tophi in ≥1 joint.
All subjects with MSU deposition had involvement of 1st metatarsophalangeal joint and a subset (21%) had intra-tendinous aggregates.
For those with SU ≤5 mg/dl no MSU depositoin was found; but those 24% of those with SU between 5-6 mg/dl had ultrasonographic MSU deposition.
For every SU increased of 1 mg/dl, there was a 61% increase in the odds of finding MSU crystal deposition.










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.