Guselkumab Treats Axial Disease in Psoriatic Arthritis Save
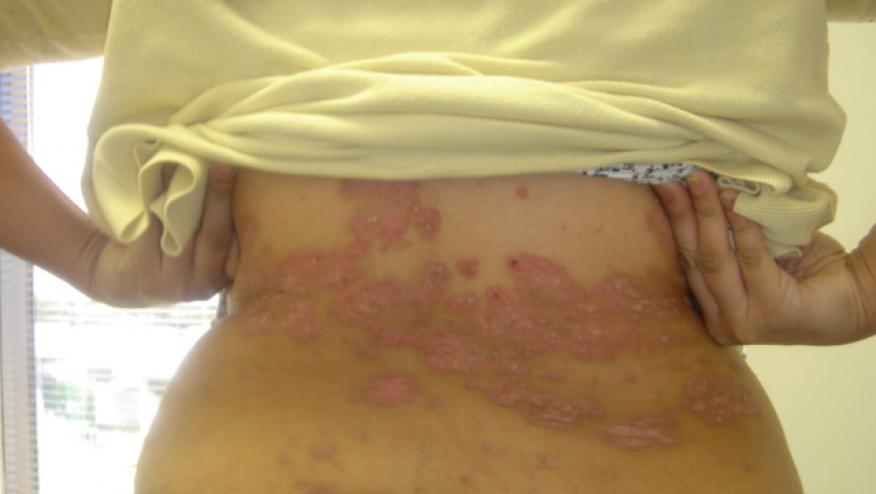
Pooled analysis of the DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 trials have shown that guselkumab, an IL-23 inhibitor, was effective and safe in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients with axial involvement and imaging-confirmed sacroiliitis.
The results of the DISCOVER-1 (381 PsA patients) and DISCOVER-2 (739 PsA patients) trials have been previously presented. In the current post-hoc analyses of pooled data, investigators identified those PsA patients with axial disease and sacroiliitis (documented by imaging) and assessed efficacy using the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) score, modified BASDAI (mBASDAI; excluding peripheral joint pain), spinal pain, and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS), and 50% improvement in BASDAI score (BASDAI50) and achieving ASDAS responses of inactive disease.
Overall, 312 (28%) were included and randomized to either placebo or guselkumab and were treated either every 4 weeks or every 8 weeks. HLA-B27 was found in 30% of the 190 patients tested.
Week 24 results coompared GUS to PBO:
- BASDAI change: −2·7 GUS vs −1·3 PBO
- ASDAS change: −1·4 GUS vs −0·7 PBO
- BASDAI 50: 38%-40% GUS vs 19% PBO
These improvements were maintained at week 52 in the guselkumab groups.
Clinical improvements (separation from placebo) were observed after week 8 and GUS improvements were independent of HLA-B27 status.
Guselkumab has proven efficacy in psoriasis and PsA; these results suggest that axial symptoms and sacroilitis in PsA patients may also benefit from IL-23 targeting with GUS.









If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.