Dual IL-17 Targeting is Effective but has More Candidiasis Save
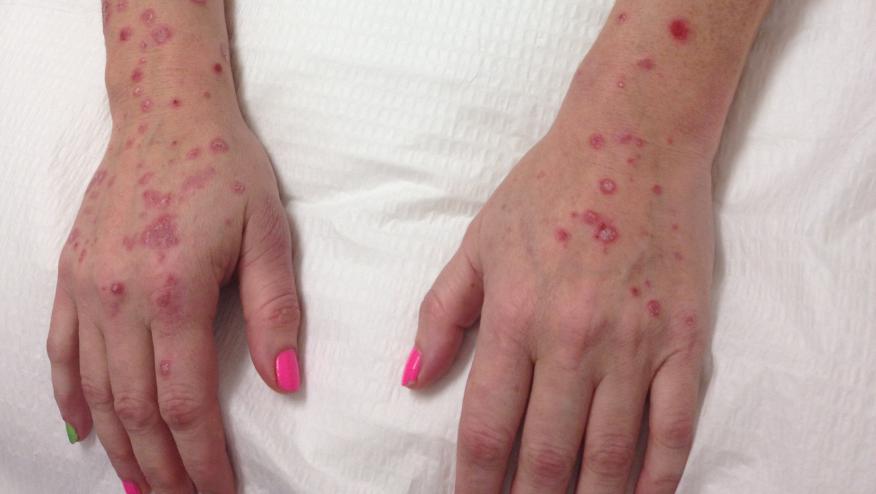
Bimekizumab (BIM) is a monoclonal antibody that targets both interleukin-17A and interleukin-17F, which as a biologic target has worked well in the management of psoriatic disease. The current issue of the NEJM has two reports wherein BIM was shown to be more effective than secukinumab and adalimumab in treating patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis; however, safety concerns arise.
Bimekizumab vs. Secukinumab
In this phase 3 trial, 1005 patients with plaque psoriasis received wither BIM (320 mg every 4 weeks) or SEC (300 mg weekly to week 4, followed by every 4 weeks to week 48) .The primary end point was 100% reduction from baseline in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score at week 16.
At week 16, the PASI100 results were achieved in 61.7% of BIM patients compared with 48.9% in the SEC group. (superiority to secukinumab, P<0.001). At week 48, similar results were seen (PASI100: 67% vs 46.2%; P<0.001).
Safety signals were similar, but oral candidiasis was seen moreso with BIM (19.3% vs 3%).
Despite the superior clinical efficacy, the risk of oral candidiasis could hamper the long term potential of BIM in psoriasis.
In the same issue, the results of the BIM vs ADA in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis was presented.
A total of 478 patients were enrolled and randomized to either BIM or ADA; in a 1:1:1 ratio of BIM (320 mg every 4 weeks for 56 weeks) or BIM (320 mg every 4 weeks for 16 weeks, then every 8 weeks for weeks 16 to 56) or ADA (40 mg every 2 weeks for 24 weeks, followed by bimekizumab at a dose of 320 mg every 4 weeks to week 56). The primary end points were a 90% or greater reduction from baseline in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 90) and an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1.
The mean PASI score at baseline was 19.8. By week 16, the PASI(90 responses were:
- BIM = 86.2% (both dose groups combined)
- ADA = 47.2% (P<0.001)
The most common adverse events with bimekizumab were upper respiratory tract infections, and oral candidiasis (mild to moderate) hypertension, and diarrhea.
In this 1 year trial, BIM was superior to ADA in plaque psoriasis but was associated with a higher frequency of oral candidiasis and diarrhea.
Another new agent, sonelokimab is a novel trivalent nanobody aimed at both IL-17A & IL-17F, was also shows to be effective vs SEC in 383 plaque psoriasis patients but also had a higher rate of Candida infections (SON 17·4% vs 1.9% SEC).
While preclinical and early studies suggested that inhibition of IL-17 might lead to more candida infections, the rate of such infections with currently approved agents (SEC, ixekizumab) is quite low, whereas dual targeting of both IL-17A and IL-17H appears to significantly augment the risk of Candidiasis in psoriasis patients.










If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.