Psoriasis and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Save
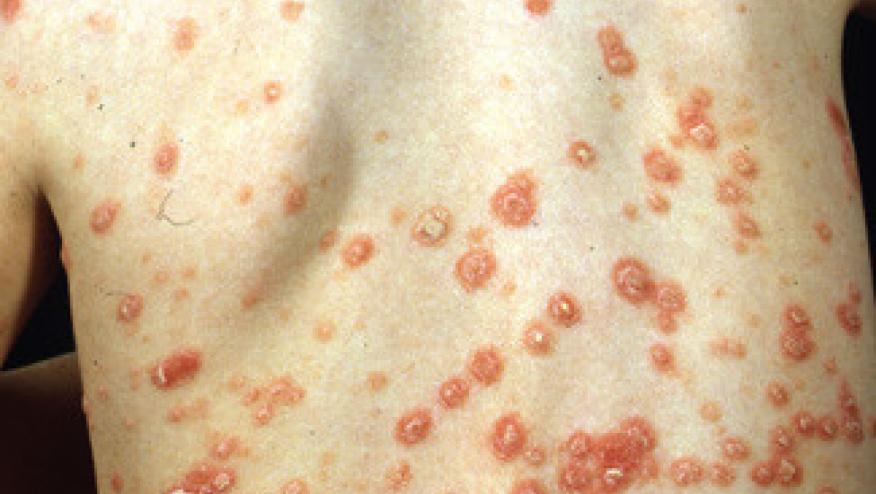
A large US population based study shows that psoriasis is associated with a higher risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
The study included 5672 US patients, aged 20 to 59 years from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The main outcome was NAFLD, defined as a US fatty liver index score greater than 30.
From the 5672 adults studied, 3% had psoriasis and 97% did not. A larger percentage had (26.8%) had NAFLD.
Patients with psoriasis had a higher prevalence of NAFLD (32.7% vs 26.6% without PSO).
NAFLD risk was higher in psoriasis (OR 1.67; 95% CI, 1.03-2.70). In subgroup analyses, psoriasis was associated with NAFLD in men (OR, 2.16; 95% CI, 1.10-4.24), in those 20 to 39 years (OR, 2.48; 95% CI, 1.09-5.67), and among diabetics (1.70; 95% CI, 1.05-2.76).
This is of potential interest and safety importace as several psoriatic therapies are potentially hepatotoxic








If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.