RA Extra-articular Manifestations Declining Save
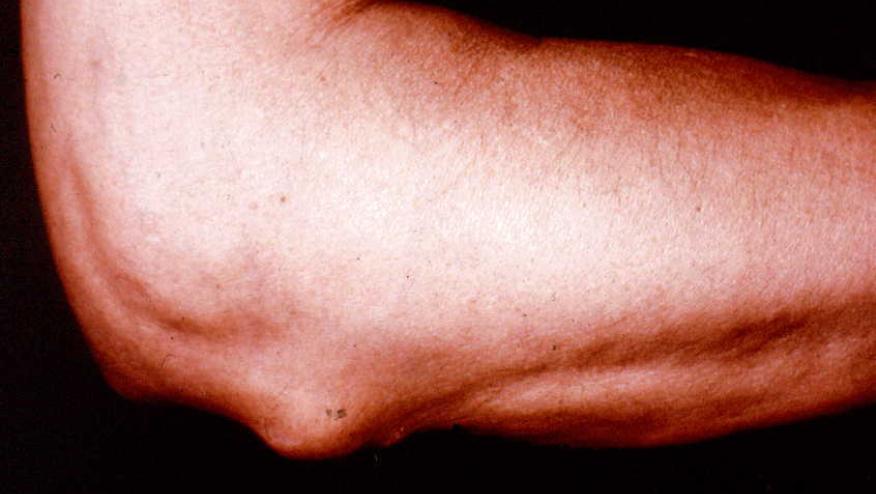
A Mayo Clinic population based cohort study shows the extraarticular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis (ExRA) have declined with time; but the increased mortality risk of RA remains unchanged.
They defined their cohort as adult patients with incident RA (ACR Criteria positive) from 1985 through 2014 seen in 2 eras, 1985-1999 and 2000-2014. The occurrence of ExRA was determined by manual chart review.
A total of 907 RA patients were included; 296 in the 1985-1999 cohort and 611 in the 2000-2014 cohort.
The 10-year cumulative incidence of any ExRA decreased significantly from 45.1% (1985-1999) to 31.6% (2000-2014) (p<0.001).
The greatest change was a significant decline in subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules (30.9% vs 15.8%, p<0.001) and non-severe ExRA (41.4% vs 28.8%, p=0.001).
Risk factors for ExRA manifestations included:
- RF positivity (HR 2.02)
- Current smoking (HR 1.61)
Mortality remained significantly increased in patients with either non-severe (HR 1.83, 95% CI 1.18-2.85) or severe ExRA (HR 3.05, 95% CI 1.44-6.49).
The incidence of ExRA has decreased over time.









If you are a health practitioner, you may Login/Register to comment.
Due to the nature of these comment forums, only health practitioners are allowed to comment at this time.