All News
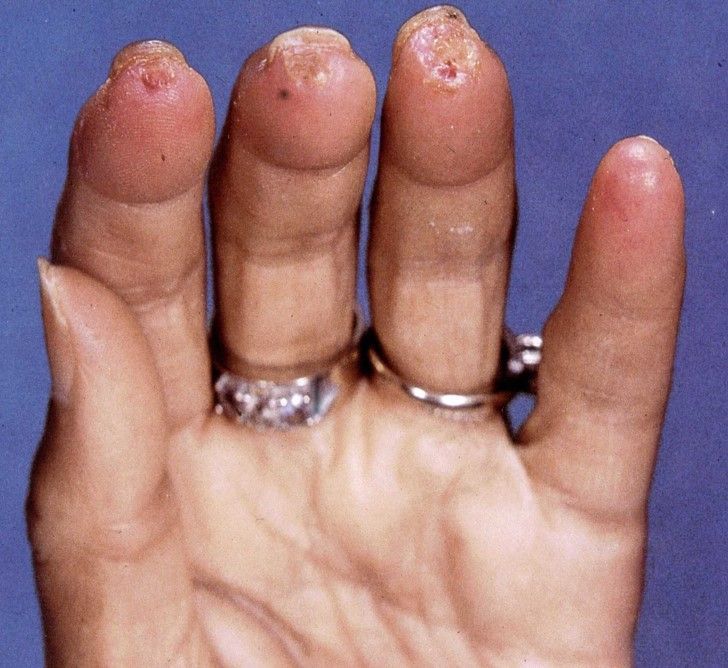
Is High Dose Aspirin Needed in Kawasaki Disease?
Does aspirin add any advantage to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) alone in children with Kawasaki disease (KD)?
Read ArticleEMR Messaging Woes (4.11.2025)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news, journal reports and regulatory approvals from this past week on RheumNow.com
Read Article1st Line Biologics vs csDMARDs in Adult Still's Disease
A German multicentre, retrospective study assessed the first-line efficacy of biologics and conventional synthetic DMARD therapy in patients with adult-onset Still's disease and found biologic agents were significantly better with sustained, event-free remissions and fewer complications.
Read ArticleCancer Survival with TNF Inhibitors (3.28.2025)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports from this past week on RheumNow.com
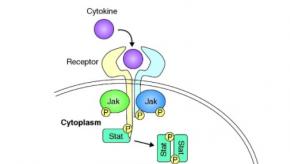
Read ArticleTreating chronic inflammatory diseases with JAK inhibitors
Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKis) are an important treatment option for people with chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
ERA, APPs, & Alpha GAL (3.21.2025)
Dr. Jack Cush reviews the news and journal reports from this past week on RheumNow.com. Listen in for 2 new case questions - Ask Cush Anything.
Read ArticleAdrenal Dysfunction after Steroids in PMR and GCA Patients
JAMA has published a study of PMR and GCA patients who stopped glucocorticoid (GC) therapy and noted a low (1.2%) risk of GC-induced adrenal insufficiency after planned cessation.
Read ArticleWorld Changers (3.14.2025)
Dr Jack Cush and his podcast friends are out to change the world. Here is his weekly review of the news and journal reports from the past week on RheumNow.
Read Article2024 Rheumatology Year in Review
2024 was a year of surprising new growth in technology, with the expansion of new therapeutic options for many patients and clinicians. While these many advances offer new hope, they are countered by disappointments and gapping unmet needs in rheumatology. Below is my top 10 list (in no particular order) of 2024 developments and desires that may change rheumatologic practices.
Read ArticleA Review of Relapsing Polychondritis
A current review in the Journal of Thoracic Disease on relapsing polychondritis (RP), suggests that while this rare disorder may have an uncertain pathogenesis, its diagnosis and therapeutical management has improved.
Read Article
Links:

Links: